Abstract
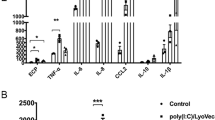
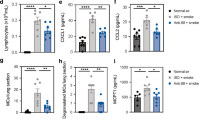
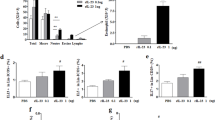
The novel interleukin (IL)-1 family cytokine IL-33 has been shown to activate T helper 2 (Th2) lymphocytes, mast cells and basophils to produce an array of proinflammatory cytokines, as well as to mediate blood eosinophilia, IgE secretion and hypertrophy of airway epithelium in mice. In the present study, we characterized the activation of human eosinophils by IL-33, and investigated the underlying intracellular signaling mechanisms. IL-33 markedly enhanced eosinophil survival and upregulated cell surface expression of the adhesion molecule intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 on eosinophils, but it suppressed that of ICAM-3 and L-selectin. In addition, IL-33 mediates significant release of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and the chemokines CXCL8 and CCL2. We found that IL-33-mediated enhancement of survival, induction of adhesion molecules, and release of cytokines and chemokines were differentially regulated by activation of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathways. Furthermore, we compared the above IL-33 activities with two structurally and functionally related cytokines, IL-1β and IL-18. IL-1β, but not IL-18, markedly upregulated cell surface expression of ICAM-1. IL-1β and IL-18 also significantly enhanced eosinophil survival, and induced the release of IL-6 and chemokines CXCL8 and CCL2 via the activation of the NF-κB, p38 MAPK and ERK pathways. Synergistic effects on the release of IL-6 were also observed in combined treatment with IL-1β, IL-18 and IL-33. Taken together, our findings provide insight into IL-33-mediated activation of eosinophils via differential intracellular signaling cascades in the immunopathogenesis of allergic inflammation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan T, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005; 23: 479–490.
Barksby HE, Lea SR, Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ . The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role in destructive inflammatory disorders. Clin Exp Immunol 2007; 149: 217–225.
Kondo Y, Yoshimoto T, Yasuda K, Futatsugi-Yumikura S, Kondo Y, Yoshimoto T, et al. Administration of IL-33 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia in the lungs in the absence of adaptive immune system. Int Immunol 2008; 20: 791–800.
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Kewin P, Murphy G, Russo RC, Stolarski B, Garcia C, et al. IL-33 induces antigen-specific IL-5+ T cells and promotes allergic-induced airway inflammation independent of IL-4. J Immunol 2008; 181: 4780–4790.
Sakashita M, Yoshimoto T, Hirota T, Harada M, Okubo K, Osawa Y, et al. Association of serum interleukin-33 level and the interleukin-33 genetic variant with Japanese cedar pollinosis. Clin Exp Allergy 2008; 38: 1875–1881.
Allakhverdi Z, Smith DE, Comeau MR, Delespesse G . Cutting edge: The ST2 ligand IL-33 potently activates and drives maturation of human mast cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 2051–2054.
Iikura M, Suto H, Kajiwara N, Oboki K, Ohno T, Okayama Y, et al. IL-33 can promote survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cells. Lab Invest 2007; 87: 971–978.
Pecaric-Petkovic T, Didichenko SA, Kaempfer S, Spiegl N, Dahinden CA . Human basophils and eosinophils are the direct target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member IL-33. Blood 2009; 113: 1526–1534.
Gagliardo R, Chanez P, Mathieu M, Bruno A, Costanzo G, Gougat C, et al. Persistent activation of nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in severe uncontrolled asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168: 1190–1198.
Wong CK, Ip WK, Lam CW . Interleukin-3, -5, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced adhesion molecule expression on eosinophils by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2003; 29: 133–147.
Cheung PF, Wong CK, Lam CW . Molecular mechanisms of cytokine and chemokine release from eosinophils activated by IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-23: implication for Th17 lymphocytes-mediated allergic inflammation. J. Immunol 2008; 180: 5625–5635.
Komai-Koma M, Xu D, Li Y, McKenzie AN, McInnes IB, Liew FY . IL-33 is a chemoattractant for human Th2 cells. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 2779–2786.
Smithgall MD, Comeau MR, Yoon BR, Kaufman D, Armitage R, Smith DE . IL-33 amplifies both Th1- and Th2-type responses through its activity on human basophils, allergen-reactive Th2 cells, iNKT and NK cells. Int Immunol 2008; 20: 1019–1030.
Suzukawa M, Iikura M, Koketsu R, Nagase H, Tamura C, Komiya A, et al. An IL-1 cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its ST2 receptor. J Immunol 2008; 181: 5981–5989.
Cherry WB, Yoon J, Bartemes KR, Iijima K, Kita H . A novel IL-1 family cytokine, IL-33, potently activates human eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121: 1484–1490.
Suzukawa M, Koketsu R, Iikura M, Nakae S, Matsumoto K, Nagase H . Interleukin-33 enhances adhesion, CD11b expression and survival in human eosinophils. Lab Invest 2008; 88: 1245–1253.
Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Napolitani G, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F . Interleukins 1β and 6 but not transforming growth factor-β are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 942–949.
Dinarello CA . Interleukin-18. Methods 1999; 19: 121–132.
Whitcomb EA, Dinarello CA, Pincus SH . Differential effects of interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta on human peripheral blood eosinophils. Blood 1989; 73: 1904–1908.
Wang W, Tanaka T, Okamura H, Sugita M, Higa S, Kishimoto T, et al. Interleukin-18 enhances the production of interleukin-8 by eosinophils. Eur J Immunol 2001; 31: 1010–1016.
Arend WP, Palmer G, Gabay C . IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev 2008; 223: 20–38.
Hayakawa H, Hayakawa M, Kume A, Tominaga S . Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic airway inflammation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 26369–26380.
Oshikawa K, Yanagisawa K, Tominaga S, Sugiyama Y . ST2 protein induced by inflammatory stimuli can modulate acute lung inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 299: 18–24.
Becerra A, Warke RV, de Bosch N, Rothman AL, Bosch I . Elevated levels of soluble ST2 protein in dengue virus infected patients. Cytokine 2008; 41: 114–120.
Oshikawa K, Kuroiwa K, Tago K, Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Ohno S, et al. Elevated soluble ST2 protein levels in sera of patients with asthma with an acute exacerbation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164: 277–281.
Vignola AM, Chanez P, Chiappara G, Siena L, Merendino A, Reina C, et al. Evaluation of apoptosis of eosinophils, macrophages, and T lymphocytes in mucosal biopsy specimens of patients with asthma and chronic bronchitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999; 103: 563–573.
Kankaanranta H, Lindsay MA, Giembycz MA, Zhang X, Moilanen E, Barnes PJ . Delayed eosinophil apoptosis in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000; 106: 77–83.
Kobayashi T, Hashimoto S, Imai K, Amemiya E, Yamaguchi M, Yachi A, et al. Elevation of serum soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and sE-selectin levels in bronchial asthma. Clin Exp Immunol 1994; 96: 110–1115.
Moser R, Fehr J, Olgiati L, Bruijnzeel PL . Migration of primed human eosinophils across cytokine-activated endothelial cell monolayers. Blood 1992; 79: 2937–2945.
McCourt PA, Ek B, Forsberg N, Gustafson S . Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is a cell surface receptor for hyaluronan. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 30081–30084.
Burke-Gaffney A, Hellewell PG . A CD18/ICAM-1-dependent pathway mediates eosinophil adhesion to human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1998; 19: 408–418.
Kessel JM, Sedgwick JB, Busse WW . Ligation of intercellular adhesion molecule 3 induces apoptosis of human blood eosinophils and neutrophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 118: 831–836.
Kitayama J, Fuhlbrigge RC, Puri KD, Springer TA . P-selectin, L-selectin, and alpha 4 integrin have distinct roles in eosinophil tethering and arrest on vascular endothelial cells under physiological flow conditions. J Immunol 1997; 159: 3929–3939.
Mengelers HJ, Maikoe T, Brinkman L, Hooibrink B, Lammers JW, Koenderman L . Immunophenotyping of eosinophils recovered from blood and BAL of allergic asthmatics. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994; 149: 345–351.
Wong CK, Ho CY, Ko FW, Chan CH, Ho AS, Hui D, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-17, IL-6, IL-18 and IL-12) and Th cytokines (IFN-gamma, IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13) in patients with allergic asthma. Clin Exp Immunol 2001; 125: 177–183.
Tillie-Leblond I, Hammad H, Desurmont S, Pugin J, Wallaert B, Tonnel A, et al. CC chemokines and interleukin-5 in bronchial lavage fluid from patients with status asthmaticus. Potential implication in eosinophil recruitment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162: 586–592.
Alam R, York J, Boyars M, Stafford S, Grant JA, Lee J, et al. Increased MCP-1, RANTES, and MIP-1alpha in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of allergic asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996; 153: 1398–1404.
Conti P, Boucher W, Letourneau R, Feliciani C, Reale M, Barbacane R, et al. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 provokes mast cell aggregation and [3H]5HT release. Immunology 1995; 86: 434–440.
Dunzendorfer S, Kaneider NC, Kaser A, Woell E, Frade JM, Mellado M, et al. Functional expression of chemokine receptor 2 by normal human eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001; 108: 581–587.
Rose CE Jr, Sung SS, Fu SM . Significant involvement of CCL2 (MCP-1) in inflammatory disorders of the lung. Microcirculation 2003; 10: 273–288.
Ferreira MA . Cytokine expression in allergic inflammation: systematic review of in vivo challenge studies. Mediators Inflamm 2003; 12: 259–267.
Kobayashi Y . The role of chemokines in neutrophil biology. Front Biosci 2008; 13: 2400–2407.
Jones SA . Directing transition from innate to acquired immunity: defining a role for IL-6. J Immunol 2005; 175: 3463–3468.
Schmidt-Weber CB, Akdis M, Akdis CA . TH17 cells in the big picture of immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007; 120: 247–254.
Wong CK, Zhang J, Ip WK, Lam CW . Intracellular signal transduction in eosinophils and its clinical significance. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2002; 24: 165–186.
O’Neill LA . The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: 10 years of progress. Immunol Rev 2008; 226: 10–18.
O’Neill L . The Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain: a molecular switch for inflammation and host defence. Biochem Soc Trans 2000; 28: 557–563.
Makarov SS . NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: recent advances. Mol Med Today 2000; 6: 441–448.
Wong CK, Ip WK, Lam CW . Biochemical assessment of intracellular signal transduction pathways in eosinophils: implications for pharmacotherapy. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2004; 41: 79–113.
Duan W, Wong WS . Targeting mitogen-activated protein kinases for asthma. Curr Drug Targets 2006; 7: 691–698.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Research Grant Committee General Research Fund, Hong Kong (Project code: CU08757; principal investigator: CK Wong; co-investigator: CWK Lam).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chow, J., Wong, C., Cheung, P. et al. Intracellular signaling mechanisms regulating the activation of human eosinophils by the novel Th2 cytokine IL-33: implications for allergic inflammation. Cell Mol Immunol 7, 26–34 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2009.106
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2009.106
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of IL-33-ST2 pathway in regulating inflammation: current evidence and future perspectives
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
The interleukin-33-mediated inhibition of expression of two key genes implicated in atherosclerosis in human macrophages requires MAP kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Anti-IL-33 Antibody Has a Therapeutic Effect in an Atopic Dermatitis Murine Model Induced by 2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
Inflammation (2018)
-
Involvement of the Negative Feedback of IL-33 Signaling in the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Electro-acupuncture on Allergic Contact Dermatitis via Targeting MicroRNA-155 in Mast Cells
Inflammation (2018)
-
Interleukin-33 promotes Th2 immune responses in infected mice with Schistosoma japonicum
Parasitology Research (2015)