Abstract
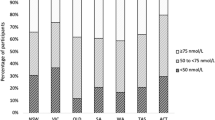
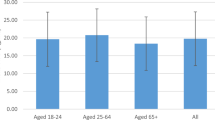
In this report, the Health Council of the Netherlands advises the government on the best policies to achieve an adequate vitamin D supply for the Dutch population. People with a dark skin, those who spend little time outdoors, pregnant and lactating women, veiled women, elderly and children who do not receive vitamin D supplements or infant formula are at risk of vitamin D deficiency. To improve this, more consistent information about vitamin D should be provided. Spending at least 15 min a day outdoors in combination with a healthy diet generates sufficient vitamin D in children and adults with a light skin. All other groups need additional vitamin D from supplements (10–20 μg/day). Fortified foods can only provide part of the additional vitamin D needed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cranney A, Horsley T, O'Donnell S, Weiler HA, Puil L, Ooi DS et al. (2007). Effectiveness and Safety of Vitamin D in Relation to Bone Health. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No.158 (Prepared by the Ottawa Evidence-based Practice Center (UO-EPC) under Contract No.290-02-0021: Rockville, MD AHRQ Publication No. 07-E013.
Hathcock JN, Shao A, Vieth R, Heaney R (2007). Risk assessment for vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr 85, 6–18.
Health Council of the Netherlands (2000). Dietary Reference Intakes: Calcium, Vitamin D, Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Pantothenic Acid and Biotin. Health Council of the Netherlands: The Hague. publication no. 2000/12E.
Health Council of the Netherlands (2008). Towards an Adequate Intake of Vitamin D. Health Council of the Netherlands: The Hague. publication no. 2008/15E.
Holick MF (2004). Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr 80, 1678S–1688S.
Huang HY, Caballero B, Chang S, Alberg AJ, Semba RD, Schneyer C et al. (2006). Multivitamin/mineral supplements and prevention of chronic disease. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 1–127.
Scientific Committee on Food, Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (2006). Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for Vitamins and Minerals. European Food Safety Authority: Parma.
Tang BM, Eslick GD, Nowson C, Smith C, Bensoussan A (2007). Use of calcium or calcium in combination with vitamin D supplementation to prevent fractures and bone loss in people aged 50 years and older: a meta-analysis. Lancet 370, 657–666.
Webb AR (2006). Who, what, where and when-influences on cutaneous vitamin D synthesis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 92, 17–25.
World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (2007). Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective. AICR: Washington DC.
Acknowledgements
All authors contributed substantially to the realization of the advisory report and the short communication arising from it. RMW wrote the article and GS and DK provided valuable input. The advisory report has been drafted by a committee of the Health Council of the Netherlands. GS was the chairman and RMW the scientific secretary. The other members were H van den Berg, EN Blok (advisor), HJ Blom, CPGM de Groot, M den Heijer, KFAM Hulshof, PTAM Lips, IMCM Rietjens, PJJ Sauer, P van ‘t Veer and T Vulsma. The Health Council of the Netherlands thanks them for their contribution. Commitee member PTAM Lips was a member of the Advisory Board of Merck, Sharp and Dohme until 1 December 2006 and has received research grants from Wyeth, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Procter and Gamble and Aventis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is an official release by the Health Council of the Netherlands. Issued in September 2008 in Dutch, a translation into English became available in February 2009 at www.healthcouncil.nl
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weggemans, R., Schaafsma, G. & Kromhout, D. Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D. An advisory report of the Health Council of the Netherlands. Eur J Clin Nutr 63, 1455–1457 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.67
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.67
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A decrease in vitamin D levels is associated with methotrexate-induced oral mucositis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Supportive Care in Cancer (2019)
-
Vitamin D deficiency in adult fracture patients: prevalence and risk factors
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery (2016)
-
New dietary reference values for vitamin D in the Netherlands
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013)
-
Response to: Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D. An advisory report of the Health Council of the Netherlands
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2010)
-
Towards an adequate intake of vitamin D. An advisory report of the Health Council of the Netherlands
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2010)