Abstract
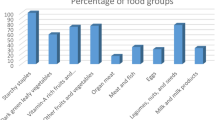
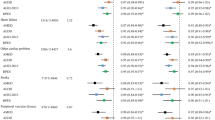
Maintaining a good nutritional status is important for immune health and for managing metabolic comorbidities in adults with HIV infection. Little is known about the dietary habits of adults living with HIV infection in the United Kingdom. The aims of this study were to characterise their dietary intakes, and to identify subgroups of patients who may require nutritional counselling and/or food support services. An observational study of adults attending a London HIV out-patient clinic who completed a demographics questionnaire and a structured 24 h diet recall interview was conducted. In all, 196 (162 men, 34 women) adults participated. Forty-three percent (n=66) of men and thirty-six percent (n=11) of women did not consume enough energy to meet their basal metabolic requirements and activity factor. The majority of both men (64%) and women (56%) consumed more than the recommended amount of saturated fat. Self-report of lipodystrophy (B coefficient −2.27 (95% CI −3.92 to −0.61), P=0.008) was associated with lower dietary fibre intake/1000 kcal per day, and a more recent diagnosis of HIV (B coefficient −0.11 (95% CI −0.20 to −0.02), P=0.013) was associated with a higher dietary fibre/1000 kcal intake per day. Recreational drug use was associated with a higher overall calorie (P=0.003) and protein (P=0.001) intake than non-usage after adjusting for basal metabolic requirements and weight, respectively. Our data describe the dietary intakes of a diverse group of adults with HIV infection in the United Kingdom. These dietary habits may have an impact on their overall health and development of other metabolic comorbidities common in people with HIV.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durand M, Sheehy O, Baril JG, Lelorier J, Tremblay CL . Association between HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy and risk of acute myocardial infarction: a cohort and nested case-control study using Québec’s public health insurance database (RAMQ). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2011; 57: 245–253.
Brown TT, Cole SR, Li X, Kingsley LA, Palella FJ, Riddler SA et al. Antiretroviral therapy and the prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus in the multicenter AIDS cohort study. Arch Intern Med 2005; 165: 1179–1184.
Hendricks KM, Willis K, Houser R, Jones CY . Obesity in HIV-infection: dietary correlates. J Am Coll Nutr 2006; 25: 321–331.
Wiig K, Smith C . An exploratory investigation of dietary intake and weight in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive individuals in Accra, Ghana. J Am Diet Assoc 2007; 107: 1008–1013.
Forrester JE, Woods MN, Knox TA, Spiegelman D, Skinner SC, Gorbach SL . Body composition and dietary intake in relation to drug abuse in a cohort of HIV-positive persons. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2000; 25 (Suppl 1), S43–S48.
Hendricks KM, Dong KR, Tang AM, Ding B, Spiegelman D, Woods MN et al. High-fiber diet in HIV-positive men is associated with lower risk of developing fat deposition. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 78: 790–795.
Sheehan LA, Macallan DC . Determinants of energy intake and energy expenditure in HIV and AIDS. Nutrition 2000; 16: 101–106.
Council UMR. Dietary assessment—Recalls 08 July 2011. Available from http://toolkit.s24.net/dietary-assessment/methods/recalls/index.html.
Schofield WN . Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Human Nutrition Clinical Nutrition 1985; 39 (Suppl 1), 5–41.
Poslusna K, Ruprich J, de Vries JH, Jakubikova M, van’t Veer P . Misreporting of energy and micronutrient intake estimated by food records and 24 hour recalls, control and adjustment methods in practice. Br J Nutr 2009; 101 (Suppl 2), S73–S85.
Macallan DC, Noble C, Baldwin C, Jebb SA, Prentice AM, Coward WA et al. Energy expenditure and wasting in human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 83–88.
Batterham MJ, Morgan-Jones J, Greenop P, Garsia R, Gold J, Caterson I . Calculating energy requirements for men with HIV/AIDS in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Eur J Clin Nutr 2003; 57: 209–217.
Wang EA, McGinnis KA, Fiellin DA, Goulet JL, Bryant K, Gibert CL et al. Food insecurity is associated with poor virologic response among HIV-infected patients receiving antiretroviral medications. J Gen Intern Med 2011; 26: 1012–1018.
Weiser SD, Hatcher A, Frongillo EA, Guzman D, Riley ED, Bangsberg DR et al. Food Insecurity Is Associated with Greater Acute Care Utilization among HIV-Infected Homeless and Marginally Housed Individuals in San Francisco. J Gen Intern Med 2012; 28: 91–98.
Acknowledgements
Karen Friend and Joanne Jeffs completed the participant interviews and data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Conference presentation: 32nd ESPEN Congress, Nice, France, 2010
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klassen, K., Goff, L. Dietary intakes of HIV-infected adults in urban UK. Eur J Clin Nutr 67, 890–893 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2013.109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2013.109