Abstract
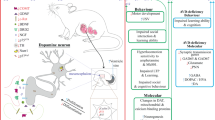
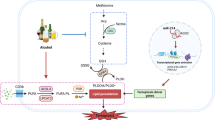
Ethanol is an important risk factor for the occurrence of several brain disorders that depend on the amount, period and frequency of its consumption. Chronic use of ethanol often leads to the development of neurodegenerative syndromes, which cause morphological and functional impairments such as foetal alcohol syndrome in newborns exposed to ethanol during pregnancy, Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome and, more rarely, Marchiafava–Bignami disease (MBD). MBD is characterized by primary degeneration of the corpus callosum, without inflammation and is associated with oxidative stress and hypovitaminosis, as well as altered mental status, to mention dementia, seizures, depression and so on. This review discusses MBD and poor nutrition as a risk factor for the development of such alcoholic syndrome, with focus on diagnosis, pathogenic aspects, signs and symptoms, as well as therapeutic perspectives. On the basis of the inclusion/exclusion criteria adopted, the performed search in scientific databases (Pubmed, Scielo and Google Scholar) resulted in 100 studies that are being presented and discussed in the present work. Review, case–control and cohort studies on alcoholism-associated hypovitaminosis, oxidative stress, MBD and ethanol metabolism pathways were admitted as relevant. We highlight that MBD is a poorly described, diagnosed, insidious and progressive condition, for which evidence suggests a synergism between ethanol-induced neurotoxic effects and hypovitaminosis B. Present treatment consists of vitamin B1(thiamine) supplementation. Nonetheless, other strategies such as the inclusion of antidepressants or steroidal anti-inflammatories as add-on therapies have been employed as an attempt to improve the damage. Indeed, both the diagnosis and treatment are difficult, and death occurs within few years.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harper C . The neuropathology of alcohol-related brain damage. Alcohol Alcohol 2009; 44: 136–140.
Crews FT, Nixon K . Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol 2009; 44: 115–127.
Harper CG, Kril JJ, Daly J . Are we drinking our neurons away? BMJ 1987; 294: 534–536.
Harding AJ, Halliday GM, Harper CG, Kril JJ . Loss of vasopressin-immunoreactive neurons in alcoholics is dose-related and time-dependent. Neuroscience 1996; 72: 699–708.
Baker K, Harding A, Halliday G, Kril JJ, Harper C . Neuronal loss in functional zones of the cerebellum of chronic alcoholics with and without Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Neuroscience 1999; 91: 429–438.
Fisher SJ, Lee IJ, Swaan PW, Eddington ND . Evaluation of the effect of ethanol’s toxic metabolite acetaldehyde on the gastrointestinal oligopeptide transporter, PEPT1: In vitro and in vivo studies. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2008; 32: 162–170.
Mercer DF . Animal models for studying hepatitis C and alcohol effects on liver. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: 2515–2519.
Oscar-Berman M . Function and dysfunction of prefrontal brain circuitry in alcoholic Korsakoff’s syndrome. Neuropsychol Rev 2012; 22: 154–169.
Jung YC, Chanraud S, Sullivan EV . Neuroimaging of Wernicke’s encephalopathy and Korsakoff’s syndrome. Neuropsychol Rev 2012; 22: 170–180.
Mulholland PJ, Self RL, Stepanyan TD, Little HJ, Littleton JM, Prendergast MA . Thiamine deficiency in the pathogenesis of chronic ethanol-associated cerebellar damage in vitro. Neurosciense 2005; 135: 1129–1139.
Keil VC, Greschus S, Schneider C, Hadizadeh DR, Schild HH . The whole spectrum of alcohol-related changes in the CNS: practical MR and CT imaging guidelines for daily clinical use. Rofo 2015; 187: 1073–1083.
Marchiafava E, Bignami A . Sopra un alterazione del corpo calloso osservata in soggetti alcoolisti. Riv Patol Nerv Ment 1903; 8: 544–549.
Kosaka K, Aoki M, Kawasaki N, Adachi Y, Konuma I, Iizuka R . A non-alcoholic Japanese patient with Wernicke's encephalopathy and Marchiafav-Bignami disease. Clin Neuropathol 1984; 3: 231–236.
Rusche-Skolarus LE, Lucey BP, Vo KD, Snider BJ . Transient encephalopathy in a postoperative non-alcoholic female with Marchiafava-Bignami disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2007; 109: 713–715.
Folescu R, Zamfir CL, Sişu AM, Motoc AG, Ilie AC, Moise M . Histopathological and imaging modifications in chronic ethanolic encephalopathy. Romanian J Morphol Embryol 2014; 55: 797–801.
Hoshino Y, Ueno Y, Shimura H, Miyamoto N, Watanabe M, Hattori N et al. Marchiafava-Bignami disease mimics motor neuron disease: case report. BMC Neurol 2013; 13: 208–212.
Mumenthaler MS, Taylor JL, O’Hara R, Yesavage JA . Gender difference in moderate drinking effects. Alcohol Res Health 1999; 23: 55–64.
Helenius J, Tatlisumak T, Soinne L, Valanne L, Kaste M . Marchiafava–Bignami disease: two cases with favourable outcome. Eur J Neurol 2001; 8: 269–272.
Carrilho PEM, Santos MBM, Piasecki L, Jorge AC . Marchiafava-Bignami disease: a rare entity with a poor outcome. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2013; 25: 68–72.
Boutboul D, Lidove O, Aguilar C, Klein I, Papo T . Marchiafava-Bignami disease complicating SC hemoglobin disease and Plasmodium falciparum infection. Presse Med 2010; 39: 990–993.
Cui Y, Zheng L, Wang X, Zhang W, Yuan D, Wei Y . Marchiafava-Bignami disease with rare etiology: a case report. Exp Ther Med 2015; 9: 1515–1517.
Suzuki Y, Oishi M, Ogawa K, Kamei S . A patient with Marchiafava–Bignami disease as a complication of diabetes mellitus treated effectively with corticosteroid. J Clin Neurosci 2012; 19: 761–762.
Yadala S, Luo JJ . Marchiafava-bignami disease in a nonalcoholic diabetic patient. Case Rep Neurol Med 2013; 2013: 1–4.
Pérez Álvarez AI, Carbajo CR, de la Tassa GM, Gómez JP . Diabetes mellitus mal controlada como desencadenante de un caso de enfermedad de Marchiafava-Bignami. Neurología 2015; 15: S0213–S4853.
Kilinc O, Ozbek D, Ozkan E, Midi I . Neurological and psychiatric findings of marchiafava-bignami disease in a nonalcoholic diabetic patient with high blood glucose levels. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 2015; 27: e149–e150.
Lechevalier B, Andersson JC, Morin P . Hemispheric disconnection syndrome with a ‘crossed avoiding’ reaction in a case of Marchiafava-Bignami disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1977; 40: 483–497.
Celik Y Marchiafava-Bignami disease in alcoholism. In: Preedy VR, Watso RR (eds). Comprehensive Handbook of Alcohol Related Pathology. Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, 2004; pp 713–718.
Fukumoto J, Suzuki T . Marchiafava-Bignami disease treated by mianserin hydrochloride in short-term evaluated by neuropsychological analysis. Psychogeriatrics 2007; 7: 25–32.
Lucato LT, Freua F, Kok F . Chronic stage of Marchiafava-Bignami disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2015; 73: 890.
Augusto L, Figueiredo R, Costa H, Reis C, Silva ML . Marchiafava-Bignami disease as a cause of visual hallucinations. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 2015; 37: 82–83.
Kumar KS, Challam RJN, Singh WJ . Marchiafava - bignami disease: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res 2014; 8: RD01–RD02.
Friese SA, Bitzer M, Freudenstein D, Voigt K, Küker W . Classification of acquired lesions of the corpus callosum with MRI. Neuroradiology 2000; 42: 795–802.
He X, Sullivan EV, Stankovic RK, Harper CG, Pfefferbaum A . Interaction of thiamine deficiency and voluntary alcohol consumption disrupts rat corpus callosum ultrastructure. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007; 32: 2207–2216.
Bano S, Mehra S, Yadav SN, Chaudhary V . Marchiafava-Bignami disease: role of neuroimaging in the diagnosis and management of acute disease. Neurol India 2009; 57: 649–652.
Nalini A, Kovoor JM, Dawn R, Kallur KG . Marchiafava-Bignami disease: two cases with magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography scan findings. Neurol India 2009; 57: 644–648.
Bhat A, Punia V, Lee HJ, Marks D . Corpus callosum fibre disruption in Marchiafava-Bignami disease. Prac Neurol 2014; 14: 189–190.
Yang L, Qin W, Xu J, Hu W . Marchiafava-Bignami disease with asymmetric extracallosal lesions. Arch Med Sci 2015; 11: 895–898.
Davies SB, Joshua FF, Zagami AS . Wernicke's encephalopathy in a non-alcoholic patient with a normal blood thiamine level. Med J Aust 2011; 194: 483–484.
Kumar N . Neurologic presentations of nutritional deficiencies. Neurol Clin 2010; 28: 107–170.
Guilland JC . Vitamin B1 (thiamine). Rev Prat 2013; 63: 1074–1075. 1077-8.
Brion S Marchiafava-Bignami disease. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds). Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Oxford, Amsterdam: The Netherlands, 1977; pp 317–329.
Hoppe M, Ebner A . Transient lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum: three further cases in epileptic patients and a pathophysiological hypothesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001; 70: 459–463.
Ménégon P, Sibon I, Pachai C, Orgogozo JM, Dousset V . Marchiafava-Bignami disease: diffusion-weighted MRI in corpus callosum and cortical lesions. Neurology 2005; 65: 475–477.
Heinrich A, Runge U, Khaw AV . Clinicoradiologic subtypes of Marchiafava-Bignami disease. J Neurol 2004; 251: 1050–1059.
Martin PR, Singleton CK, Hiller-Sturmhöfel S . The role of thiamine deficiency in alcoholic brain disease. Alcohol Res Health 2003; 27: 134–142.
Depaz I, Ito M, Matsumoto I, Niwa S, Kroon P, Wilce PA . Expression of hNP22 is altered in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of the alcoholic human brain. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2003; 27: 1481–1488.
Zieve L . Influence of magnesium deficiency on the utilization of thiamine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1969; 162: 732–743.
Spector R . Thiamin homeostasis in the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1982; 378: 344–354.
Osiezagha K, Ali S, Freeman C, Barker NC, Jabeen S, Maitra S . Thiamine deficiency and delirium’. Innov Clin Neurosci 2013; 10: 26–32.
Hazell AS, Todd KG, Butterworth RF . Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 1998; 13: 97–122.
Martin PR, Adinoff B, Weingartner H, Mukherjee AB, Eckardt MJ . Alcoholic organic brain disease: nosology and pathophysiologic mechanisms. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1986; 10: 147–164.
Halsted CH . B-Vitamin dependent methionine metabolism and alcoholic liver disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51: 457–465.
Singleton CK, Martin PR . Molecular mechanisms of thiamine utilization. Curr Mol Med 2001; 1: 197–207.
Tallaksen CM, Bell H, Bohmer T . Thiamin and thiamin phosphate ester deficiency assessed by high performance liquid chromatography in four clinical cases of Wernicke encephalopathy. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1993; 17: 712–716.
Cravo ML, Glória LM, Selhub J . Hyperhomocysteinemia in chronic alcoholism: correlation with folate, vitamin B-12, and vitamin B-6 status. Am J Clin Nutr 1996; 63: 220–224.
Panchenko LF, Pirozhkov SV, Popova SV, Antonenkov VD . Effect of chronic ethanol treatment on peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase activity and lipid peroxidation in rat liver and heart. Experientia 1987; 43: 580–581.
Galter D, Carmine A, Buervenich S, Duester G, Olson L . Distribution of class I, III and IV alcohol dehydrogenase mRNAs in the adult rat, mouse and human brain. Eur J Biochem 2003; 270: 1316–1326.
Zimatkin SM, Pronko SP, Vasiliou V, Gonzalez FJ, Deitrich RA . Enzymatic mechanisms of ethanol oxidation in the brain. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2006; 30: 1500–1555.
Vasiliou V, Ziegle TL, Bludeau P, Petersen DR, Gonzalez FJ, Deitrich RA . CYP2E1 and catalase influence ethanol sensitivity in the central nervous system. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2006; 16: 51–58.
Norberg A, Jones AW, Hahn RG, Gabrielsson JL . Role of variability in explaining ethanol pharmacokinetics: research and forensic applications. Clin Pharmacokinet 2003; 42: 1–31.
Manzo-Avalos S, Saavedra-Molina A . Cellular and mitochondrial effects of alcohol consumption. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2010; 7: 4281–4304.
Haorah J, Ramirez SH, Floreani N, Gorantla S, Morsey B, Persidsky Y . Mechanism of alcohol-induced oxidative stress and neuronal injury. Free Radic Biol Med 2008; 45: 1542–1550.
Aragon C, Stotland L, Amit Z . Studies on ethanol–brain catalase interaction: evidence for central ethanol oxidation. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 15: 165–169.
Person RE, Chen H, Fantel AG, Juchau MR . Enzymic catalysis of the accumulation of acetaldehyde from ethanol in human prenatal cephalic tissues: evaluation of the relative contributions of CYP2E1, alcohol dehydrogenase, and catalase/peroxidases. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2000; 24: 1433–1442.
Correa M, Sanchis-Segura C, Pastor R, Aragon CM . Ethanol intake and motor sensitization: the role of brain catalase activity in mice with different genotypes. Physiol Behav 2004; 82: 231–240.
Weiner H . Subcellular localization of acetaldehyde oxidation on liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1987; 492: 25–34.
Somani SM, Husain K, Diaz-Phillips L, Lanzotti DJ, Kareti KR, Trammell GL . Interaction of exercise and ethanol on antioxidant enzymes in brain regions of the rat. Alcohol 1996; 13: 603–610.
Calabrese V, Renis M, Calderone A, Russo A, Reale S, Barcellona ML et al. Stress proteins and SH-groups in oxidant-induced cellular injury after chronic ethanol administration in rat. Free Radic Biol Med 1998; 24: 1159–1167.
Kumar A, Singh CK, Lavoie HA, Dipette DJ, Singh US . Resveratrol restores Nrf2 level and prevents ethanol-induced toxic effects in the cerebellum of a rodent model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Mol Pharmacol 2011; 80: 446–457.
Reddy SK, Husain K, Schlorff EC, Scott RB, Somani SM . Dose response of ethanol ingestion on antioxidant defense system in rat brain subcellular fractions. Neurotoxicology 1999; 20: 977–987.
Aggarwal A, Khandelwal A, Jiloha RC . A case of Marchiafava-Bignami disease: complete recovery with thiamine. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 2011; 23: E28.
Heit C, Dong H, Chen Y, Thompson DC, Deitrich RA, Vasiliou VK . The role of CYP2E1 in alcohol metabolism and sensitivity in the central nervous system. Subcell Biochem 2013; 67: 2352–47.
Haorah J, Knipe B, Leibhart J, Ghorpade A, Persidsky Y . Alcohol-induced oxidative stress in brain endothelial cells causes blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J Leukoc Biol 2005; 78: 1223–1232.
Albano E . Alcohol, oxidative stress and free radical damage. Proc Nutr Soc 2006; 65: 278–290.
Liangpunsakul S, Kolwankar D, Pinto A, Gorski JC, Hall SD, Chalasani N . Activity of CYP2E1 and CYP3A enzymes in adults with moderate alcohol consumption: a comparison with nonalcoholics. Hepatology 2005; 41: 1144–1150.
Kumar A, Lavoie HA, Dipette DJ, Singh US . Ethanol neurotoxicity in the developing cerebellum: underlying mechanisms and implications. Brain Sci 2013; 3: 941–963.
Adam-Vizi V . Production of reactive oxygen species in brain mitochondria: contribution by electron transport chain and non-electron transport chain sources. Antioxidants Redox Signal 2005; 7: 1140–1149.
Wang X, Ke Z, Chen G, Xu M, Bower KA, Frank JA et al. Cdc42-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase is involved in ethanol-induced neuronal oxidative stress. PLoS One 2012; 7: e38075.
Kim TE, Lee EJ, Young JB, Shin DJ, Kim JH . Wernicke encephalopathy and ethanol-related syndromes. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2014; 35: 85–96.
Kashem MA, Etages HD, Kopitar-Jerala N . Differential protein expression in the corpus callosum (body) of human alcoholic brain. J Neurochem 2009; 110: 486–495.
Ledig M, M’Paria JR, Mandel P . Superoxide dismutase activity in rat brain during acute and chronic alcohol intoxication. Neurochem Res 1981; 6: 385–390.
Ansari KA, Bigelow D, Kaplan E . Glutathione peroxidase activity in surgical and autopsied human brains. Neurochem Res 1985; 10: 703–711.
Bosch-Morell F, Martínez-Soriano F, Colell A, Fernández-Checa JC, Romero FJ . Chronic ethanol feeding induces cellular antioxidants decrease and oxidative stress in rat peripheral nerves. Effect of S-adenosyl-L-methionine and N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Free Radic Biol Med 1998; 25: 365–368.
Knollema S, Hom HW, Schirmer H, Korf J, Ter Horst GJ . Immunolocalization of glutathione reductase in the murine brain. J Comp Neurol 1996; 373: 157–172.
Dringen R . Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol 2000; 62: 649–671.
Iwai T, Matsuo K, Morii-Kitani F, Azuma F, Matsuo H, Takada M et al. Marchiafava-Bignami disease with hyperintensity on late diffusion-weighted imaging. Acta Radiol Short Rep 2014; 3: 1–4.
Hillbom M, Saloheimo P, Fujioka S, Wszolek ZK, Juvela S, Leone MA . Diagnosis and management of Marchiafava-Bignami disease: a review of CT/MRI confirmed cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2014; 85: 168–173.
Staszewski J, Macek K, Stepien A . A reversible demyelinisation of corpus callosum in the course of Marchiafava-Bignami disease. Neurol Neurochir Pol 2006; 40: 156–161.
Consoli A, Pirritano D, Bosco D, Postorino P, Consoli D . Corticosteroid treatment in a patient with Marchiafava–Bignami Disease. Neurol Sci 2014; 35: 1143–1145.
Dujmović I, Nikolić I, Gavrić-Kezić M, Dačković J, Mesaroš Š, Drulović J . Teaching neuroImages: reversible widespread brain MRI lesions in Marchiafava-Bignami disease’. Neurology 2015; 84: e81–e82.
Ruiz-Martínez J, Martínez Pérez-Balsa A, Ruibal M, Urtasun M, Villanua J, Martí Massó JF . Marchiafava-Bignami disease with widespread extracallosal lesions and favourable course. Neuroradiology 1999; 41: 40–43.
Wilby MJ, Hutchinson PJ . The pharmacology of chlormethiazole: a potential neuroprotective agent? CNS Drug Rev 2004; 10: 281–294.
Kashem MA, Harper C, Matsumoto I . Differential protein expression in the corpus callosum (genu) of human alcoholics’. Neurochem Int 2008; 53: 1–11.
Uchiyama M, Kasai H, Kurokawa S, Sakae Y, Kinno R . Relationship between callosal lesions and cerebral microhemorrhage in Marchiafava-Bignami disease. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi 2014; 49: 238–248.
WHO 2014. Global status report on alcohol and health 2014. World Health Organization http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/global_alcohol_report/en/. Accessed on October 15 2015.
Acknowledgements
FRB and FRO received scholarship from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, Brazil). MCM is supported by a research fellowship from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, L., Bezerra, F., Monteiro, M. et al. Thiamine deficiency, oxidative metabolic pathways and ethanol-induced neurotoxicity: how poor nutrition contributes to the alcoholic syndrome, as Marchiafava–Bignami disease. Eur J Clin Nutr 71, 580–586 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2016.267
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2016.267
This article is cited by
-
Clinico-radiologic subtypes and therapeutic observation of acute Marchiafava-Bignami disease
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Randomised trial of intravenous thiamine and/or magnesium sulphate administration on erythrocyte transketolase activity, lactate concentrations and alcohol withdrawal scores
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Response to: “Before blaming a COVID vaccine for cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum all other differentials must be ruled out”
Neuroradiology (2022)
-
Radiologische Merkmale einer seltenen, alkoholassoziierten, neurologischen Erkrankung
Die Radiologie (2022)
-
Alcohol-Related Central Nervous System Disorders Associated with Vitamin B Deficiency
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine (2021)