Abstract
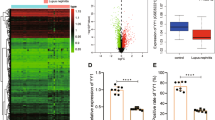
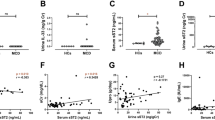
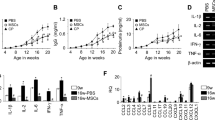
We identified a novel soluble protein, mouse (m)IL-20R1a, generated by alternative splicing of the mIL-20R1 gene, which encodes one subunit of the receptor complex for mIL-19, mIL-20 and mIL-24. mIL-20R1a has 77.14% amino-acid identity with the extracellular domain of mIL-20R1. However, no significant interaction between mIL-20R1a and mIL-19 or mIL-20 was detected. Consequently, we aimed to clarify whether mIL-20R1a might function as a novel effector on certain cells. Competitive binding assays demonstrated that mIL-20R1a bound to cell surfaces and resulted in AKT and JNK phosphorylation in primary mesangial cells (MCs) isolated from either the wild-type mice, DBA/W mice, or the SLE-prone mice, NZB/W mice. NZB/W MCs expressed more mIL-20R1a transcript than DBA/W MCs did. Furthermore, mIL-20R1a-treated NZB/W MCs produced higher level of chemokines, renal fibrogenic factors and ROS than mIL-20R1a-treated DBA/W MCs did. These factors are involved in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Endogenous mIL-20R1a was upregulated in the bladder, colon and spleen tissue of NZB/W mice. Elevated mIL-20R1a in the spleen tissue of NZB/W mice was expressed mainly in monocytes and B cells. mIL-20R1a further induced mIL-10 production by the anti-IgM antibody-stimulated B cells in NZB/W mice. Therefore, mIL-20R1a-mediated effects may exacerbate the disease outcome of lupus nephritis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout












Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Rose-John S, Heinrich PC . Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: generation and biological function. Biochem J 1994; 300 (Part 2): 281–290.
Hooper NM, Karran EH, Turner AJ . Membrane protein secretases. Biochem J 1997; 321 (Part 2): 265–279.
Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, Fisher PB . Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 2004; 22: 929–979.
Fickenscher H, Hor S, Kupers H, Knappe A, Wittmann S, Sticht H . The interleukin-10 family of cytokines. Trends Immunol 2002; 23: 89–96.
Langer JA, Cutrone EC, Kotenko S . The Class II cytokine receptor (CRF2) family: overview and patterns of receptor-ligand interactions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2004; 15: 33–48.
Parrish-Novak J, Xu W, Brender T, Yao L, Jones C, West J et al. Interleukins 19, 20, and 24 signal through two distinct receptor complexes. Differences in receptor-ligand interactions mediate unique biological functions. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 47517–47523.
Liao YC, Liang WG, Chen FW, Hsu JH, Yang JJ, Chang MS . IL-19 induces production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha and results in cell apoptosis through TNF-alpha. J Immunol 2002; 169: 4288–4297.
Hsing CH, Chiu CJ, Chang LY, Hsu CC, Chang MS . IL-19 is involved in the pathogenesis of endotoxic shock. Shock 2008; 29: 7–15.
Hsing CH, Hsu CC, Chen WY, Chang LY, Hwang JC, Chang MS . Expression of IL-19 correlates with Th2 cytokines in uraemic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2007; 22: 2230–2238.
Hsing CH, Hsieh MY, Chen WY, Cheung So E, Cheng BC, Chang MS . Induction of interleukin-19 and interleukin-22 after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg 2006; 81: 2196–2201.
Li HH, Lin YC, Chen PJ, Hsiao CH, Lee JY, Chen WC et al. Interleukin-19 upregulates keratinocyte growth factor and is associated with psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 2005; 153: 591–595.
Liao SC, Cheng YC, Wang YC, Wang CW, Yang SM, Yu CK et al. IL-19 induced Th2 cytokines and was up-regulated in asthma patients. J Immunol 2004; 173: 6712–6718.
Hsieh MY, Chen WY, Jiang MJ, Cheng BC, Huang TY, Chang MS . Interleukin-20 promotes angiogenesis in a direct and indirect manner. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 234–242.
Hsing CH, Ho CL, Chang LY, Lee YL, Chuang SS, Chang MS . Tissue microarray analysis of interleukin-20 expression. Cytokine 2006; 35: 44–52.
Hsu YH, Li HH, Hsieh MY, Liu MF, Huang KY, Chin LS et al. Function of interleukin-20 as a proinflammatory molecule in rheumatoid and experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 2722–2733.
Otkjaer K, Kragballe K, Funding AT, Clausen JT, Noerby PL, Steiniche T et al. The dynamics of gene expression of interleukin-19 and interleukin-20 and their receptors in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 2005; 153: 911–918.
Caligiuri G, Kaveri SV, Nicoletti A . IL-20 and atherosclerosis: another brick in the wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 1929–1930.
Chen WY, Cheng BC, Jiang MJ, Hsieh MY, Chang MS . IL-20 is expressed in atherosclerosis plaques and promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 2090–2095.
Wei CC, Hsu YH, Li HH, Wang YC, Hsieh MY, Chen WY et al. IL-20: biological functions and clinical implications. J Biomed Sci 2006; 13: 601–612.
Wei CC, Chen WY, Chen PJ, Lee YJ, Wang DH, Chen WC et al. Detection of IL-20 and its receptors on psoriasis skin. Clin Immunol 2005; 117: 65–72.
Zhao L, Dong A, Gu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang W et al. The antitumor activity of TRAIL and IL-24 with replicating oncolytic adenovirus in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 1011–1022.
Miyahara R, Banerjee S, Kawano K, Efferson C, Tsuda N, Miyahara Y et al. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 (mda-7)/interleukin (IL)-24 induces anticancer immunity in a syngeneic murine model. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 753–761.
Chen WY, Cheng YT, Lei HY, Chang CP, Wang CW, Chang MS . IL-24 inhibits the growth of hepatoma cells in vivo. Genes Immun 2005; 6: 493–499.
Saito Y, Miyahara R, Gopalan B, Litvak A, Inoue S, Shanker M et al. Selective induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through adenoviral transfer of the melanoma differentiation-associated -7 (mda-7)/interleukin-24 (IL-24) gene. Cancer Gene Ther 2005; 12: 238–247.
Yacoub A, Mitchell C, Lebedeva IV, Sarkar D, Su ZZ, McKinstry R et al. mda-7 (IL-24) Inhibits growth and enhances radiosensitivity of glioma cells in vitro via JNK signaling. Cancer Biol Ther 2003; 2: 347–353.
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Valerie K et al. mda-7 (IL-24) mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10054–10059.
Dumoutier L, Lejeune D, Colau D, Renauld JC . Cloning and characterization of IL-22 binding protein, a natural antagonist of IL-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor/IL-22. J Immunol 2001; 166: 7090–7095.
Kotenko SV, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko OV, Esterova E, Dickensheets H, Donnelly RP et al. Identification, cloning, and characterization of a novel soluble receptor that binds IL-22 and neutralizes its activity. J Immunol 2001; 166: 7096–7103.
Xu W, Presnell SR, Parrish-Novak J, Kindsvogel W, Jaspers S, Chen Z et al. A soluble class II cytokine receptor, IL-22RA2, is a naturally occurring IL-22 antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 9511–9516.
Wei CC, Ho TW, Liang WG, Chen GY, Chang MS . Cloning and characterization of mouse IL-22 binding protein. Genes Immun 2003; 4: 204–211.
Blumberg H, Conklin D, Xu WF, Grossmann A, Brender T, Carollo S et al. Interleukin 20: discovery, receptor identification, and role in epidermal function. Cell 2001; 104: 9–19.
Kanegae K, Tamura M, Kabashima N, Serino R, Tokunaga M, Oikawa S et al. Synergistic induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by integrins and platelet-derived growth factor via focal adhesion kinase in MCs. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005; 20: 2080–2088.
Dijstelbloem HM, van de Winkel JG, Kallenberg CG . Inflammation in autoimmunity: receptors for IgG revisited. Trends Immunol 2001; 22: 510–516.
Cooke MS, Mistry N, Wood C, Herbert KE, Lunec J . Immunogenicity of DNA damaged by reactive oxygen species--implications for anti-DNA antibodies in lupus. Free Radic Biol Med 1997; 22: 151–159.
Klahr S, Morrissey JJ . The role of vasoactive compounds, growth factors and cytokines in the progression of renal disease. Kidney Int Suppl 2000; 75: S7–S14.
Suzuki Y, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J . Angiotensin II: a double-edged sword in inflammation. J Nephrol 2000; 13 (Suppl 3): S101–S110.
Abboud HE . Role of platelet-derived growth factor in renal injury. Annu Rev Physiol 1995; 57: 297–309.
Handwerger BS, Rus V, da Silva L, Via CS . The role of cytokines in the immunopathogenesis of lupus. Springer Semin Immunopathol 1994; 16: 153–180.
Theofilopoulos AN, Lawson BR . Tumour necrosis factor and other cytokines in murine lupus. Ann Rheum Dis 1999; 58 (Suppl 1): I49–I55.
Iida H, Seifert R, Alpers CE, Gronwald RG, Phillips PE, Pritzl P et al. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF receptor are induced in mesangial proliferative nephritis in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 6560–6564.
Nakamura T, Ebihara I, Nagaoka I, Tomino Y, Koide H . Renal platelet-derived growth factor gene expression in NZB/W F1 mice with lupus and ddY mice with IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1992; 63: 173–181.
Jackson M, Ahmad Y, Bruce IN, Coupes B, Brenchley PE . Activation of transforming growth factor-beta1 and early atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 2006; 8: R81.
Zhang ZG, Liu XG, Chen GP, Zhang XR, Guo MY . Significance of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 mRNA expressions on glomerular cells in the development of glomerulosclerosis. Chin Med Sci J 2004; 19: 84–88.
Linker-Israeli M, Honda M, Nand R, Mandyam R, Mengesha E, Wallace DJ et al. Exogenous IL-10 and IL-4 downregulate IL-6 production by SLE-derived PBMC. Clin Immunol 1999; 91: 6–16.
Strand V . Monoclonal antibodies and other biologic therapies. Lupus 2001; 10: 216–221.
Harris RC, Martinez-Maldonado M . Angiotensin II-mediated renal injury. Miner Electrolyte Metab 1995; 21: 328–335.
Dean GS, Tyrrell-Price J, Crawley E, Isenberg DA . Cytokines and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2000; 59: 243–251.
Ishida H, Muchamuel T, Sakaguchi S, Andrade S, Menon S, Howard M . Continuous administration of anti-interleukin 10 antibodies delays onset of autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 305–310.
Ka SM, Cheng CW, Shui HA, Wu WM, Chang DM, Lin YC et al. Mesangial cells of lupus-prone mice are sensitive to chemokine production. Arthritis Res Ther 2007; 9: R67.
Song SW, Fuller GN, Khan A, Kong S, Shen W, Taylor E et al. IIp45, an insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) binding protein, antagonizes IGFBP-2 stimulation of glioma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 13970–13975.
Wei CC, Chen WY, Wang YC, Chen PJ, Lee JY, Wong TW et al. Detection of IL-20 and its receptors on psoriatic skin. Clin Immunol 2005; 117: 65–72.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the National Science Council (NSC 96-2628-B-006 -055 -MY3), Taiwan, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, CC., Chang, MS. A novel transcript of mouse interleukin-20 receptor acts on glomerular mesangial cells as an aggravating factor in lupus nephritis. Genes Immun 9, 668–679 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.61
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Interleukin-20 Promotes Airway Remodeling in Asthma
Inflammation (2014)
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates inflammation in MRL/lpr mouse mesangial cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2010)
-
Mouse interleukin-20 receptor 1a targets renal epithelial cells and is associated with renal calcium deposition
Genes & Immunity (2009)