Abstract
Objective:
To investigate fetal antigen 1 (FA1) protein within the context of human obesity and its relation with insulin sensitivity.
Subjects:
Cross-sectional study that analyses circulating levels of FA1 in two selected human cohorts: n=127 men for the study of FA1 circulating levels in the context of obesity and insulin sensitivity (Si); and n=61 severely obese women before and after bariatric surgery. The response in vitro to FA1 protein on human cell lines of monocytes, preadipocytes and mature adipocytes was studied.
Measurements:
Anthropometrical parameters: body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, waist circumference, fat-free mass and fat mass. Clinical parameters: lipid profile (high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides), glycemic profile (fasting glucose, insulin, Si, HOMA-IR (Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance), cytokines (sIL-6), adipokines (adiponectin) and circulating soluble fractions of tumor necrosis factor-α receptors 1 and 2 (sTNFR1 and sTNFR2).
Results:
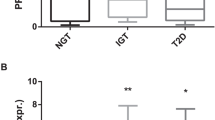
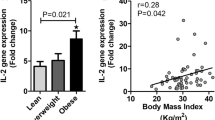
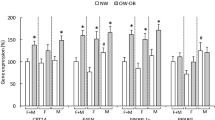
In the obesity study, levels of FA1 in serum were found to increase with obesity. The Si index was negatively dependent on FA1 levels. In severe obesity, serum levels of FA1 decreased 1.4-fold 6 months after bariatric surgery. In vitro assays with FA1 protein on human monocytes and adipocytes cell lines modified the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipokines (tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), IL-6 (interleukin-6) and adiponectin).
Conclusion:
FA1 serum levels were increased in obese subjects and might influence Si. The stimulatory effect of FA1 protein on pro-inflammatory cytokines on both immune and adipose cell types could contribute to worsening the inflammatory environment observed in obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah BM, Jensen CH, Gutierrez G, Leslie GQ, Jensen TG, Kassem M . Regulation of human skeletal stem cells differentiation by Dlk1/Pref-1. J Bone Miner Res 2004; 19: 841–852.
Wang Y, Sul HS . Ectodomain shedding of preadipocyte factor 1 (Pref-1) by tumor necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme (TACE) and inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 5421–5435.
Baladron V, Ruiz-Hidalgo MJ, Nueda ML, Diaz-Guerra MJ, Garcia-Ramirez JJ, Bonvini E et al. dlk acts as a negative regulator of Notch1 activation through interactions with specific EGF-like repeats. Exp Cell Res 2005; 303: 343–359.
Moore KA, Pytowski B, Witte L, Hicklin D, Lemischka IR . Hematopoietic activity of a stromal cell transmembrane protein containing epidermal growth factor-like repeat motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 4011–4016.
Carlsson C, Tornehave D, Lindberg K, Galante P, Billestrup N, Michelsen B et al. Growth hormone and prolactin stimulate the expression of rat preadipocyte factor-1/delta-like protein in pancreatic islets: molecular cloning and expression pattern during development and growth of the endocrine pancreas. Endocrinology 1997; 138: 3940–3948.
Crameri RM, Langberg H, Magnusson P, Jensen CH, Schroder HD, Olesen JL et al. Changes in satellite cells in human skeletal muscle after a single bout of high intensity exercise. J Physiol 2004; 558: 333–340.
Tanimizu N, Nishikawa M, Saito H, Tsujimura T, Miyajima A . Isolation of hepatoblasts based on the expression of Dlk/Pref-1. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 1775–1786.
Jensen P, Bauer M, Jensen CH, Widmer HR, Gramsbergen JB, Blaabjerg M et al. Expansion and characterization of ventral mesencephalic precursor cells: Effect of mitogens and investigation of FA1 as a potential dopaminergic marker. J Neurosci Res 2007; 85: 1884–1893.
Floridon C, Jensen CH, Thorsen P, Nielsen O, Sunde L, Westergaard JG et al. Does fetal antigen 1 (FA1) identify cells with regenerative, endocrine and neuroendocrine potentials? A study of FA1 in embryonic, fetal, and placental tissue and in maternal circulation. Differentiation 2000; 66: 49–59.
Jensen CH, Teisner B, Hojrup P, Rasmussen HB, Madsen OD, Nielsen B et al. Studies on the isolation, structural analysis and tissue localization of fetal antigen 1 and its relation to a human adrenal-specific cDNA, pG2. Hum Reprod 1993; 8: 635–641.
Jensen CH, Krogh TN, Hojrup P, Clausen PP, Skjodt K, Larsson LI et al. Fetal antigen 1 (FA1), a circulating member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) superfamily: ELISA development, physiology and metabolism in relation to renal function. Clin Chim Acta 1997; 268: 1–20.
Abdallah BM, Boissy P, Tan Q, Dahlgaard J, Traustadottir GA, Kupisiewicz K et al. dlk1/FA1 regulates the function of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by modulating gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and immune response-related factors. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 7339–7351.
Abdallah BM, Ding M, Jensen CH, Ditzel N, Flyvbjerg A, Jensen TG et al. Dlk1/FA1 is a novel endocrine regulator of bone and fat mass and its serum level is modulated by growth hormone. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 3111–3121.
Ansell PJ, Zhou Y, Schjeide BM, Kerner A, Zhao J, Zhang X et al. Regulation of growth hormone expression by Delta-like protein 1 (Dlk1). Mol Cell Endocrinol 2007; 271: 55–63.
Moon YS, Smas CM, Lee K, Villena JA, Kim KH, Yun EJ et al. Mice lacking paternally expressed Pref-1/Dlk1 display growth retardation and accelerated adiposity. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 5585–5592.
Lee K, Villena JA, Moon YS, Kim KH, Lee S, Kang C et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis and development of glucose intolerance by soluble preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1). J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 453–461.
. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 1997; 20: 1183–1197.
World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. In: WHO (eds.). WHO Technical Report Series 894. WHO: Geneva, 2000, pp 8–9.
Fernandez-Real JM, Broch M, Richart C, Vendrell J, Lopez-Bermejo A, Ricart W . CD14 monocyte receptor, involved in the inflammatory cascade, and insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 1780–1784.
Vendrell J, Broch M, Vilarrasa N, Molina A, Gomez JM, Gutierrez C et al. Resistin, adiponectin, ghrelin, leptin, and pro-inflammatory cytokines: relationships in obesity. Obes Res 2004; 12: 962–971.
Chacon MR, Fernandez-Real JM, Richart C, Megia A, Gomez JM, Miranda M et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Insulin sensitivity study. Obesity 2007; 15: 664–672.
Jensen CH, Schroder HD, Teisner B, Laursen I, Brandrup F, Rasmussen HB . Fetal antigen 1, a member of the epidermal growth factor superfamily, in neurofibromas and serum from patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Br J Dermatol 1999; 140: 1054–1059.
Andersen M, Jensen CH, Stoving RK, Larsen JB, Schroder HD, Teisner B et al. Fetal antigen 1 in healthy adults and patients with pituitary disease: relation to physiological, pathological, and pharmacological GH levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 5465–5470.
Vilarrasa N, Vendrell J, Maravall J, Broch M, Estepa A, Megia A et al. Distribution and determinants of adiponectin, resistin and ghrelin in a randomly selected healthy population. Clin Endocrinol 2005; 63: 329–335.
Hotamisligil GS . Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006; 444: 860–867.
Blanco-Colio LM, Martin-Ventura JL, de Teresa E, Farsang C, Gaw A, Gensini G et al. Elevated ICAM-1 and MCP-1 plasma levels in subjects at high cardiovascular risk are diminished by atorvastatin treatment. Atorvastatin on Inflammatory Markers study: a substudy of Achieve Cholesterol Targets Fast with Atorvastatin Stratified Titration. Am Heart J 2007; 153: 881–888.
Wu X, Mahadev K, Fuchsel L, Ouedraogo R, Xu SQ, Goldstein BJ . Adiponectin suppresses I{kappa}B kinase activation induced by tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} or high glucose in endothelial cells: role of cAMP and AMP kinase signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007; 293: E1836–E1844.
Friedrichsen BN, Carlsson C, Moldrup A, Michelsen B, Jensen CH, Teisner B et al. Expression, biosynthesis and release of preadipocyte factor-1/ delta-like protein/fetal antigen-1 in pancreatic beta-cells: possible physiological implications. J Endocrinol 2003; 176: 257–266.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr M Wabitsch for kindly providing with the SGBS cell line. This study was supported by the following grants: FIS 04-0377, CIBERDEM (CB07/08/0012). Dr Matilde R Chacón is supported by a fellowship from the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria CP06/00119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chacón, M., Miranda, M., Jensen, C. et al. Human serum levels of fetal antigen 1 (FA1/Dlk1) increase with obesity, are negatively associated with insulin sensitivity and modulate inflammation in vitro. Int J Obes 32, 1122–1129 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.40
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of paternal exposure to cigarette smoke on sperm DNA methylation and long-term metabolic syndrome in offspring
Epigenetics & Chromatin (2022)
-
Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2021)
-
Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Serum Inflammatory Factors of Obese Patients: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Obesity Surgery (2019)
-
The role of adipokines in skeletal muscle inflammation and insulin sensitivity
Journal of Inflammation (2018)
-
Preadipocyte factor 1 induces pancreatic ductal cell differentiation into insulin-producing cells
Scientific Reports (2016)