Abstract
Objective:
Infiltration by macrophages is a hallmark of obesity-related adipose tissue (AT) inflammation that is tightly linked to insulin resistance. Although CD11c+ AT macrophages (ATMs) have recently been shown to promote inflammation in obese mice, the knowledge on phenotype and function of different ATM populations is still very limited. This study aimed at identifying and characterizing ATM populations in obesity.
Methods:
Isolation of ATM populations defined by CD11c and mannose receptor (MR) expression and analysis of gene expression in high-fat diet-induced obese mice.
Results:
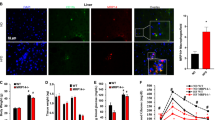
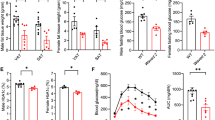
Obesity provoked a shift from a predominant MR+CD11c− population (‘MR-ATM’) to two MR− populations, namely MR−CD11c+ (‘CD11c-ATM’) and MR−CD11c− (double negative, ‘DN-ATM’). Although CD11c-ATMs were of a clear inflammatory M1 phenotype, DN-ATMs expressed few inflammatory mediators and highly expressed genes for alternative activation (M2) markers involved in tissue repair, such as arginase and YM1. In contrast, MR-ATMs marginally expressed M1 and M2 markers but highly expressed chemokines, including Mcp-1 (Ccl2) and Mcp-3 (Ccl7). Both CD11c-ATMs and DN-ATMs, but not MR-ATM, highly expressed a panel of chemokine receptors (namely Ccr2, Ccr5, Ccr3 and Cx3cr1), whereas the expression of Ccr7 and Ccr9 was selective for CD11c-ATMs and DN-ATMs, respectively. Notably, stressed adipocytes upregulated various chemokines capable of attracting CD11c-ATM and DN-ATM.
Conclusion:
This study identifies a novel ATM population with a putatively beneficial role in AT inflammation. This DN-ATM population could be attracted to the obese AT by similar chemokines such as inflammatory CD11c-ATM, on which only Ccr7 is uniquely expressed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Luca C, Olefsky JM . Inflammation and insulin resistance. FEBS Lett 2008; 582: 97–105.
Fain JN . Release of interleukins and other inflammatory cytokines by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity and primarily due to the nonfat cells. Vitam Horm 2006; 74: 443–477.
Zeyda M, Stulnig TM . Adipose tissue macrophages. Immunol Lett 2007; 112: 61–67.
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante Jr AW . Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1796–1808.
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1821–1830.
Curat CA, Wegner V, Sengenes C, Miranville A, Tonus C, Busse R et al. Macrophages in human visceral adipose tissue: increased accumulation in obesity and a source of resistin and visfatin. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 744–747.
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 2004; 306: 457–461.
Cinti S, Mitchell G, Barbatelli G, Murano I, Ceresi E, Faloia E et al. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J Lipid Res 2005; 46: 2347–2355.
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR . Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 175–184.
Gordon S . Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 23–35.
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A . Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol 2002; 23: 549–555.
Lumeng CN, Delproposto JB, Westcott DJ, Saltiel AR . Phenotypic switching of adipose tissue macrophages with obesity is generated by spatiotemporal differences in macrophage subtypes. Diabetes 2008; 57: 3239–3246.
Nguyen MT, Favelyukis S, Nguyen AK, Reichart DD, Scott PA, Jenn A et al. A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 35279–35292.
Zeyda M, Farmer D, Todoric J, Aszmann O, Speiser M, Gyori G et al. Human adipose tissue macrophages are of an anti-inflammatory phenotype but capable of excessive pro-inflammatory mediator production. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007; 31: 1420–1428.
Bourlier V, Zakaroff-Girard A, Miranville A, De Barros S, Maumus M, Sengenes C et al. Remodeling phenotype of human subcutaneous adipose tissue macrophages. Circulation 2008; 117: 806–815.
Huber J, Kiefer FW, Zeyda M, Ludvik B, Silberhumer GR, Prager G et al. CC chemokine and CC chemokine receptor profiles in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue are altered in human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93: 3215–3221.
Moraes RC, Blondet A, Birkenkamp-Demtroeder K, Tirard J, Orntoft TF, Gertler A et al. Study of the alteration of gene expression in adipose tissue of diet-induced obese mice by microarray and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analyses. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 4773–4782.
Wu H, Ghosh S, Perrard XD, Feng L, Garcia GE, Perrard JL et al. T-cell accumulation and regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted upregulation in adipose tissue in obesity. Circulation 2007; 115: 1029–1038.
Kamei N, Tobe K, Suzuki R, Ohsugi M, Watanabe T, Kubota N et al. Overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in adipose tissues causes macrophage recruitment and insulin resistance. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 26602–26614.
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa KI, Kitazawa R et al. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 1494–1505.
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ma FY, Ozols E, Rollins BJ, Tesch GH . Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-induced tissue inflammation is critical for the development of renal injury but not type 2 diabetes in obese db/db mice. Diabetologia 2007; 50: 471–480.
Inouye KE, Shi H, Howard JK, Daly CH, Lord GM, Rollins BJ et al. Absence of CC chemokine ligand 2 does not limit obesity-associated infiltration of macrophages into adipose tissue. Diabetes 2007; 56: 2242–2250.
Kirk EA, Sagawa ZK, McDonald TO, O’Brien KD, Heinecke JW . Macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 deficiency fails to restrain macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue. Diabetes 2008; 57: 1254–1261.
Lumeng CN, Deyoung SM, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR . Increased inflammatory properties of adipose tissue macrophages recruited during diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 2007; 56: 16–23.
Weisberg SP, Hunter D, Huber R, Lemieux J, Slaymaker S, Vaddi K et al. CCR2 modulates inflammatory and metabolic effects of high-fat feeding. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 115–124.
Ito A, Suganami T, Yamauchi A, Degawa-Yamauchi M, Tanaka M, Kouyama R et al. Role of CC chemokine receptor 2 in bone marrow cells in the recruitment of macrophages into obese adipose tissue. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 35715–35723.
Kiefer FW, Zeyda M, Todoric J, Huber J, Geyeregger R, Weichhart T et al. Osteopontin expression in human and murine obesity: extensive local up-regulation in adipose tissue but minimal systemic alterations. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 1350–1357.
Nomiyama T, Perez-Tilve D, Ogawa D, Gizard F, Zhao Y, Heywood EB et al. Osteopontin mediates obesity-induced adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and insulin resistance in mice. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2877–2888.
Patsouris D, Li PP, Thapar D, Chapman J, Olefsky JM, Neels JG . Ablation of CD11c-positive cells normalizes insulin sensitivity in obese insulin resistant animals. Cell Metab 2008; 8: 301–309.
Yang SJ, Iglayreger HB, Kadouh HC, Bodary PF . Inhibition of the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2/chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 pathway attenuates hyperglycaemia and inflammation in a mouse model of hepatic steatosis and lipoatrophy. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 972–981.
Maury E, Ehala-Aleksejev K, Guiot Y, Detry R, Vandenhooft A, Brichard SM . Adipokines oversecreted by omental adipose tissue in human obesity. Am J Physiol 2007; 293: E656–E665.
Kiefer FW, Zeyda M, Gollinger K, Pfau B, Neuhofer A, Weichhart T et al. Neutralization of osteopontin inhibits obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2010; 59: 935–946.
Lee HS, Park JH, Kang JH, Kawada T, Yu R, Han IS . Chemokine and chemokine receptor gene expression in the mesenteric adipose tissue of KKAy mice. Cytokine 2009; 46: 160–165.
Winer S, Chan Y, Paltser G, Truong D, Tsui H, Bahrami J et al. Normalization of obesity-associated insulin resistance through immunotherapy. Nat Med 2009; 15: 921–929.
Feuerer M, Herrero L, Cipolletta D, Naaz A, Wong J, Nayer A et al. Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat Med 2009; 15: 930–939.
Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K, Yamashita H, Ohsugi M et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med 2009; 15: 914–920.
Hadeiba H, Sato T, Habtezion A, Oderup C, Pan J, Butcher EC . CCR9 expression defines tolerogenic plasmacytoid dendritic cells able to suppress acute graft-versus-host disease. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 1253–1260.
Fujisaka S, Usui I, Bukhari A, Ikutani M, Oya T, Kanatani Y et al. Regulatory mechanisms for adipose tissue M1 and M2 macrophages in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 2009; 58: 2574–2582.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (project no. P18776-B11 and as part of the CCHD doctoral program W1205-B09), and the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) under grant agreement no. 201608 (TOBI—Targeting OBesity-driven Inflammation; all to TMS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeyda, M., Gollinger, K., Kriehuber, E. et al. Newly identified adipose tissue macrophage populations in obesity with distinct chemokine and chemokine receptor expression. Int J Obes 34, 1684–1694 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.103
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Attenuated TGFB signalling in macrophages decreases susceptibility to DMBA-induced mammary cancer in mice
Breast Cancer Research (2021)
-
Tissue-infiltrating macrophages mediate an exosome-based metabolic reprogramming upon DNA damage
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Targeting ERβ in Macrophage Reduces Crown-like Structures in Adipose Tissue by Inhibiting Osteopontin and HIF-1α
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
FoxK1 and FoxK2 in insulin regulation of cellular and mitochondrial metabolism
Nature Communications (2019)
-
The effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: an overview of molecular mechanisms
Inflammation Research (2019)