Abstract
Background/Objective:
The timing of food intake may be implicated in weight gain. This study tested the hypothesis that symptoms commonly associated with night-eating syndrome are related to measures of weight gain in adults.
Subjects/Methods:
Parents participating in QUALITY (Québec Adipose and Lifestyle InvesTigation in Youth) completed the night eating questionnaire (NEQ) at baseline (2005–2008) and at follow-up (2008–2010). Height and weight were measured and self-report questionnaire data were available for 388 parents (59% female, mean (s.d.) age: 41.8±5.7, mean (s.d.) body mass index (BMI): 29.6±5.7). Linear regression models were used to test the associations between baseline night-eating symptoms (NEQ scores, night-eating behaviours) and percent change in each of BMI and waist circumference (WC).
Results:
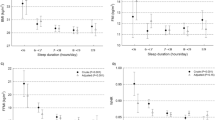
A high NEQ score predicted a small increase in percent change in BMI in nonobese parents but a decrease among those who were severely obese. Nocturnal ingestions of food predicted an increase in percent change in BMI; however, the effect size was small. Morning anorexia predicted an increase in percent change in WC.
Conclusion:
Certain night-eating symptoms may predict measures of weight gain in adults but the effects seem small and the findings need to be confirmed in more symptomatic samples.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison KC, Goel N, Ahima RS . Delayed timing of eating: impact on weight and metabolism. Curr Obes Rep 2014; 3: 91–100.
Garaulet M, Gomez-Abellan P . Timing of food intake and obesity: a novel association. Physiol Behav 2014; 134: 44–50.
Wang JB, Patterson RE, Ang A, Emond JA, Shetty N, Arab L . Timing of energy intake during the day is associated with the risk of obesity in adults. J Hum Nutr Diet 2013; 27: 255–262.
Baron KG, Reid KJ, Kern AS, Zee PC . Role of sleep timing in caloric intake and BMI. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2011; 19: 1374–1381.
Garaulet M, Gomez-Abellan P, Alburquerque-Bejar JJ, Lee YC, Ordovas JM, Scheer FA . Timing of food intake predicts weight loss effectiveness. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013; 37: 604–611.
Jakubowicz D, Barnea M, Wainstein J, Froy O . High Caloric intake at breakfast vs. dinner differentially influences weight loss of overweight and obese women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2013; 21: 2504–2512.
Gallant AR, Lundgren J, Drapeau V . The night-eating syndrome and obesity. Obes Rev 2012; 13: 528–536.
Colles SL, Dixon JB . The relationship of night eating syndrome with obesity, bariatric surgery and physical health Jennifer DL, Allison KC, Stunkard AJ (eds.) Night Eating Syndrome: Research, Assessment and Treatment. The Guilford Press New York, USA, 2012. pp 85–126.
Aronoff NJ, Geliebter A, Zammit G . Gender and body mass index as related to the night-eating syndrome in obese outpatients. J Am Diet Assoc 2001; 101: 102–104.
Tholin S, Lindroos A, Tynelius P, Akerstedt T, Stunkard AJ, Bulik CM et al. Prevalence of night eating in obese and nonobese twins. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009; 17: 1050–1055.
Lundgren JD, Allison KC, Crow S, O'Reardon JP, Berg KC, Galbraith J et al. Prevalence of the night eating syndrome in a psychiatric population. Am J Psychiatry 2006; 163: 156–158.
Grilo CM, Masheb RM . Night-time eating in men and women with binge eating disorder. Behav Res Ther 2004; 42: 397–407.
Morse SA, Ciechanowski PS, Katon WJ, Hirsch IB . Isn't this just bedtime snacking? The potential adverse effects of night-eating symptoms on treatment adherence and outcomes in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 1800–1804.
de Zwaan M, Muller A, Allison KC, Brahler E, Hilbert A . Prevalence and correlates of night eating in the German general population. PLoS One 2014; 9: e97667.
Gallant A, Drapeau V, Allison KC, Tremblay A, Lambert M, O'Loughlin J et al. Night eating behavior and metabolic heath in mothers and fathers enrolled in the QUALITY cohort study. Eat Behav 2014; 15: 186–191.
Colles SL, Dixon JB, O'Brien PE . Night eating syndrome and nocturnal snacking: association with obesity, binge eating and psychological distress. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007; 31: 1722–1730.
Gluck ME, Venti CA, Salbe AD, Krakoff J . Nighttime eating: commonly observed and related to weight gain in an inpatient food intake study. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 88: 900–905.
Andersen GS, Stunkard AJ, Sorensen TI, Petersen L, Heitmann BL . Night eating and weight change in middle-aged men and women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: 1338–1343.
Lambert M, Van Hulst A, O'Loughlin J, Tremblay A, Barnett TA, Charron H et al. Cohort profile: the Quebec adipose and lifestyle investigation in youth cohort. Int J Epidemiol 2011; 41: 1533–1544.
Lohman T . Anthropometric Standardizationi Reference Manual. Human Kinetics Champaign, IL, USA, 1988.
NIH. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults—The Evidence Report. National Institutes of Health. Obes Res 1998; 6: 51S–209S.
Allison KC, Lundgren JD, O'Reardon JP, Martino NS, Sarwer DB, Wadden TA et al. The night eating questionnaire (NEQ): psychometric properties of a measure of severity of the night eating syndrome. Eat Behav 2008; 9: 62–72.
Dalle Grave R, Calugi S, Ruocco A, Marchesini G . Night eating syndrome and weight loss outcome in obese patients. Int J Eat Disord 2011; 44: 150–156.
Meule A, Allison KC, Platte P . Emotional eating moderates the relationship of night eating with binge eating and body mass. Eur Eat Disord Rev 2014; 22: 147–151.
Runfola CD, Allison KC, Hardy KK, Lock J, Peebles R . Prevalence and clinical significance of night eating syndrome in university students. J Adolesc Health 2014; 55: 41–48.
Elsadek AM, Hamid MS, Allison KC . Psychometric characteristics of the Night Eating Questionnaire in a Middle East population. Int J Eat Disord 2014; 47: 660–665.
Harb A, Levandovski R, Oliveira C, Caumo W, Allison KC, Stunkard A et al. Night eating patterns and chronotypes: a correlation with binge eating behaviors. Psychiatry Res 2012; 200: 489–493.
Moize V, Gluck ME, Torres F, Andreu A, Vidal J, Allison K . Transcultural adaptation of the Night Eating Questionnaire (NEQ) for its use in the Spanish population. Eat Behav 2012; 13: 260–263.
Lundgren JD, Smith BM, Spresser C, Harkins P, Zolton L, Williams K . The relationship of night eating to oral health and obesity in community dental clinic patients. Gen Dent 2010; 58: e134–e139.
Shafiee G, Kelishadi R, Qorbani M, Motlagh ME, Taheri M, Ardalan G et al. Association of breakfast intake with cardiometabolic risk factors. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2013; 89: 575–582.
Deshmukh-Taskar PR, Nicklas TA, O'Neil CE, Keast DR, Radcliffe JD, Cho S . The relationship of breakfast skipping and type of breakfast consumption with nutrient intake and weight status in children and adolescents: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2006. J Am Diet Assoc 2010; 110: 869–878.
Farshchi HR, Taylor MA, Macdonald IA . Deleterious effects of omitting breakfast on insulin sensitivity and fasting lipid profiles in healthy lean women. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 81: 388–396.
Cappuccio FP, Taggart FM, Kandala NB, Currie A, Peile E, Stranges S et al. Meta-analysis of short sleep duration and obesity in children and adults. Sleep 2008; 31: 619–626.
Allison KC, Lundgren JD, O'Reardon JP, Geliebter A, Gluck ME, Vinai P et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria for night eating syndrome. Int J Eat Disord 2010; 43: 241–247.
Acknowledgements
This research was conducted by members of TEAM PRODIGY, an inter-university research team including Université de Montréal, Concordia University, Université Laval and McGill University. The QUALITY cohort is funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada and Fonds de la Recherche en Santé du Québec. AR Gallant is funded by the Quebec Heart and Lung Research Institute. Dr Marie Lambert (July 1952—February 2012), pediatric geneticist and researcher, initiated the QUALITY cohort. Her leadership and devotion to QUALITY will always be remembered and appreciated. Finally, we are grateful to all the families that participate in the QUALITY cohort. We thank Dr Albert Stunkard, the pioneer of NES, for his help with translating the NEQ. JOL holds a Canada Research Chair in the Early Determinants of Chronic Disease. MH holds a research scholar award (Junior 1) from the Fonds de Recherche du Québec—Santé (FRQS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallant, A., Lundgren, J., O'Loughlin, J. et al. Night-eating symptoms and 2-year weight change in parents enrolled in the QUALITY cohort. Int J Obes 39, 1161–1165 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.36
This article is cited by
-
A Review of the Relationship between Night Eating Syndrome and Body Mass Index
Current Obesity Reports (2019)
-
Understanding the risk and protective factors associated with obesity amongst Libyan adults - a qualitative study
BMC Public Health (2018)