Abstract
The ABCB1 gene encodes the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) that drives the transmembrane efflux of many drugs. The donor ABCB1 polymorphisms have been related with chronic histological damage and long-term renal function among kidney transplanted patients who received cyclosporine A and tacrolimus (Tac). The aim of our study was to determine whether the donor ABCB1 3435 C/T genotype was related with renal function among Tac-treated renal transplanted patients. Kidney donors (n=65) and recipients (n=90) were genotyped for the ABCB1 rs1045642 (c.3435 C/T) and CYP3A5 rs776746 single-nucleotide polymorphisms. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated with the modification of diet in renal disease formulae at five post-transplant times (2 weeks and 1, 3, 6 and 12 months). The recipient ABCB1 and CYP3A5 genotypes had no significant effect on the eGFR at all the post-transplant times. We found significantly lower eGFR values among patients who received a kidney from ABCB1 3435 T carriers (P<0.01). In conclusion, our study confirmed the potential impact of the donor ABCB1 3435 genotype on the post-transplant renal function among patients treated with Tac.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Tacrolimus (Tac, FK-506) is a calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) widely used to avoid organ rejection among kidney transplanted patients. Tac is characterized by a narrow therapeutic index and large interindividual dose requirement variability, which makes necessary the monitoring of blood concentration to adjust the dose in order to prevent rejection and toxicity. The CYP3A5*3 allele (SNP rs776746) is the main genetic determinant of Tac dose requirements: homozygotes for the null CYP3A5*3 allele showed an almost complete absence of enzyme activity and required significantly lower Tac compared with CYP3A5*1 (wild-type allele) carriers.1, 2, 3, 4, 5 The ABCB1 gene (also known as multidrug response-1, MDR1) encodes the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) that drives the transmembrane efflux of many drugs. The effect of ABCB1 variants on Tac dose is controversial: the common c.C3435T SNP (rs1045642) has been related to Tac bioavailability by some authors, but others failed to confirm the association.6, 7, 8, 9
Recent studies suggested that the donor (instead of the recipient) ABCB1 genotype was related with chronic histological damage and low glomerular filtration rate(GFR) in response to CNIs, either cyclosporine A (CsA) or Tac.10, 11, 12, 13 In a large cohort from UK, the donor ABCB1 genotype was associated with long-term graft survival.13 The donor genotype was also linked to differences in the estimated GFRs (eGFRs) at 1 year post transplant (PT).12 These effects on graft function might be explained by a heterogeneous expression of the of P-gp in the renal tubular epithelial cells that could in turn result in differences in Tac or CsA absorption by these cells.11 However, the reported positive effects should be taken with caution because at least one study based on a cohort followed for >2 years did not find differences between the donor ABCB1 genotypes.14
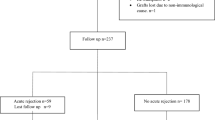
The aim of our study was to determine whether the donor CYP3A5 and ABCB1 genotypes were related with kidney function among Tac-treated renal transplanted patients. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Hospital Universitario Central Asturias (HUCA) and involved a total of 65 deceased donors and 90 patients who received a first graft from these donors in the years 2010–2013. Patients aged >18 years, who had not received a previous organ, who were treated with Tac as primary immunosuppressor and had been followed for at least 1 year PT were included in the study. All the donors and recipients were Caucasians from Spain. The 90 kidney transplanted patients were treated with Tac, micophenolate mofetil (MMF) and prednisone as reported.5, 15 The eGFR was calculated with the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula: eGFR (ml min−1 1.73 m−2)=186 × [plasma creatinin (mg dl−1)]−1.154 × (age)−0.203 × (0.742 if female).16 Some studies reported that among renal transplanted patients the MDRD values showed a better correlation with the true filtration rate (compared with other renal function estimates, such as the raw serum creatinine value or the Cockcroft–Gault formula).17 The diagnosis of acute rejection was based on laboratory and clinical findings, such as decreased urine production and a rise in plasma creatinine that lowered in response to antirejection treatment.18
The DNA from the donors and recipients was obtained and the genotypes for ABCB1 rs1045642 was determined through real-time PCR Taqman (assay C_7586657_20; www.appliedbiosystems.com). We also determined the CYP3A5*3 allele (rs776746, Taqman assay id. C_25201809_30) in recipients and donors. There were no significant effect of the recipient CYP3A5 and ABCB1 genotypes on the eGFR at the five PT times (Table 1). As expected, recipients who were CYP3A5*3 homozygotes required lower Tac dose and showed a significantly higher normalized value (the ratio of Tac blood concentration/Tac dose; Table 1). In reference to the donor genotypes, there were no differences in the recipient Tac dose and Tac blood concentrations (data not shown). The donor ABCB1 3435 T allele was linked to significantly lower eGFR values (P<0.01) at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months PT (Table 2). The eGFR value decreased with the number of T-allele copies (CC>CT>TT; Figure 1).
The P-gp is expressed in renal tubular epithelial cells and would contribute to exporting Tac out of the cells. The ABCB1 3435 C/T is a silent polymorphism (p.I1145I) and therefore it was not expected to change the function of the protein. This SNP was in linkage disequilibrium with other polymorphisms, including missense changes that might have functional consequences on P-gp activity and the ability of the protein to drive the efflux of Tac.19 Studies that determined the P-gp expression and function in the duodenum by western blots and quantitative immunohistology found that the homozygous T-allele was associated with more than twofold lower protein expression levels compared with homozygous CC samples. Heterozygous individuals display an intermediate phenotype.20 Moreover, after receiving an oral dose of digoxin (an indicator of Pg-P activity) individuals homozygous for the T allele showed significantly highest digoxin plasma levels.20
Interestingly, the ABCB1 3435 C>T was associated with differences in Tac concentrations in peripheral blood cells (PBCs) from renal transplanted patients, and the T allele was also linked to increased intracellular levels of CsA.21, 22 The reported differences between the genotypes in Pg-P level and activity might also result in heterogeneous intrarenal accumulation, and the increased accumulation of CNI in ABCB1 3435 T kidneys could result in an increased apoptotic stress in tubular cells and the subsequent reduction of graft function. This would explain the reported higher risk of CsA-related nephrotoxicity and Tac-chronic damage among patients receiving a kidney bearing the low P-gp expression genotype.11, 23
In conclusion, our study showed a potential impact of ABCB1 3435 donor genotype on the post-transplant renal function among patients treated with Tac. Although our results confirm previous studies, it should be taken with caution due to the limited sample size.
References
MacPhee, I. A. M., Fredericks, S., Maha, M., Moreton, M., Carter, N. D., Johnston, A. et al. Tacrolimus pharmacogenetics: the CYP3A5*1 allele predicts low dose-normalized tacrolimus blood concentrations in Whites and South Asians. Transplantation 79, 499–502 (2005).
Thervet, E., Anglicheau, D., King, B., Schlageter, M. H., Cassinat, B., Beaune, P. et al. Impact of cytochrome p450 3A5 genetic polymorphism on tacrolimus doses and concentration-to-dose ratio in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 76, 1233–1235 (2003).
Tsuchiya, N., Satoh, S., Tada, H., Li, Z., Ohyama, C., Sato, K. et al. Influence of CYP3A5 and MDR1 (ABCB1) polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 78, 1182–1187 (2004).
Dai, Y., Hebert, M. F., Isoherranen, N., Davis, C. L., Marsh, C., Shen, D. D. et al. Effect of CYP3A5 polymorphism on tacrolimus metabolic clearance in vitro. Drug Metab. Dispos. 34, 836–847 (2006).
Tavira, B., Coto, E., Díaz-Corte, C., Ortega, F., Arias, M., Torres, A. et al. Pharmacogenetics of tacrolimus after renal transplantation: Analysis of polymorphisms in genes encoding 16 drug metabolizing enzymes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 49, 825–833 (2011).
Anglicheau, D., Verstuyft, C., Laurent-Puig, P., Becquemont, L., Schlageter, M. H., Cassinat, B. et al. Association of the multidrug resistance-1 gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms with the tacrolimus dose requirements in renal transplant recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 14, 1889–1896 (2003).
Zhang, X., Liu, Z. H., Zheng, J. M., Chen, Z. H., Tang, Z., Chen, J. S. et al. Influence of CYP3A5 and MDR1 polymorphisms on tacrolimus concentration in the early stage after renal transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 19, 638–643 (2005).
Mai, I., Perloff, E. S., Bauer, S., Goldammer, M., Johne, A., Filler, G. et al. MDR1 haplotypes derived from exons 21 and 26 do not affect the steady-state pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in renal transplant patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 58, 548–553 (2004).
Kurzawski, M., Dabrowska, J., Dziewanowski, K., Domański, L., Perużyńska, M. & Droździk, M. CYP3A5 and CYP3A4, but not ABCB1 polymorphisms affect tacrolimus dose-adjusted trough concentrations in kidney transplant recipients. Pharmacogenomics 15, 179–188 (2014).
Woillard, J. B., Rerolle, J. P., Picard, N., Rousseau, A., Guillaudeau, A., Munteanu, E. et al. P-gp polymorphisms strongly influence renal function and graft loss in a cohort of renal transplant recipients on cyclosporine therapy in a long-term follow-up. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 88, 95–100 (2010).
Naesens, M., Lerut, E., de Jonge, H., Van Damme, B., Vanrenterghem, Y. & Kuypers, D. R. Donor age and renal P-glycoprotein expression associate with chronic histological damage in renal allografts. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 20, 2468–2480 (2009).
De Meyer, M., Haufroid, V., Elens, L., Fusaro, F., Patrono, D., De Pauw, L. et al. Donor age and ABCB1 1199G>A genetic polymorphism are independent factors affecting long-term renal function after kidney transplantation. J. Surg. Res. 178, 988–995 (2012).
Moore, J., McKnight, A. J., Döhler, B., Simmonds, M. J., Courtney, A. E., Brand, O. J. et al. ABCB1 variant associates with increased risk for kidney allograft failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 23, 1891–1899 (2012).
Glowacki, F., Lionet, A., Buob, D., Labalette, M., Allorge, D., Provôt, F. et al. CYP3A5 and ABCB1 polymorphisms in donor and recipient: impact on Tacrolimus dose requirements and clinical outcome after renal transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 26, 3046–3050 (2011).
Tavira, B., Coto, E., Diaz-Corte, C., Alvarez, V., López-Larrea, C. & Ortega, F. A search for new CYP3A4 variants as determinants of tacrolimus dose requirements in renal-transplanted patients. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 23, 445–448 (2013).
Levey, A. S., Bosch, J. P., Lewis, J. B., Greene, T., Rogers, N. & Roth, D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann. Intern. Med. 130, 461–470 (1999).
Pöge, U., Gerhardt, T., Palmedo, H., Klehr, H. U., Sauerbruch, T. & Woitas, R. P. MDRD equations for estimation of GFR in renal transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 5, 1306–1311 (2005).
Joosten, S. A., Sijpkens, Y. W., van Kooten, C. & Paul, L. C. Chronic renal allograft rejection: pathophysiologic considerations. Kidney Int. 68, 1–13 (2005).
Dessilly, G., Elens, L., Panin, N., Capron, A., Decottignies, A., Demoulin, J. B. et al. ABCB1 1199G>A genetic polymorphism (Rs2229109) influences the intracellular accumulation of tacrolimus in HEK293 and K562 recombinant cell lines. PLoS ONE 9, e91555 (2014).
Hoffmeyer, S., Burk, O., von Richter, O., Arnold, H. P., Brockmöller, J., Johne, A. et al. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3473–3478 (2000).
Capron, A., Mourad, M., De Meyer, M., De Pauw, L., Eddour, D. C., Latinne, D. et al. CYP3A5 and ABCB1 polymorphisms influence tacrolimus concentrations in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the early phase after renal transplantation. Pharmacogenomics 11, 703–714 (2010).
Crettol, S., Venetz, J. P., Fontana, M., Aubert, J. D., Ansermot, N., Fathi, M. et al. Influence of ABCB1 genetic polymorphisms on cyclosporine intracellular concentration in transplant recipients. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 18, 307–315 (2008).
Hauser, I. A., Schaeffeler, E., Gauer, S., Scheuermann, E. H., Wegner, B., Gossmann, J. et al. ABCB1 genotype of the donor but not of the recipient is a major risk factor for cyclosporine-related nephrotoxicity after renal transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 1501–1511 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Red de Investigación Renal-European Feder funds. BT is a FICYT predoctoral fellow.
Author Contributions
All the authors participated in the study design and contributed to the study by recruiting the patients, obtaining the patient’s data or performing the laboratory work. EC had full access to the data and took the responsibility for the accuracy of the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavira, B., Gómez, J., Díaz-Corte, C. et al. The donor ABCB1 (MDR-1) C3435T polymorphism is a determinant of the graft glomerular filtration rate among tacrolimus treated kidney transplanted patients. J Hum Genet 60, 273–276 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.12
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacogenetics of Membrane Transporters of Tacrolimus in Solid Organ Transplantation
Clinical Pharmacokinetics (2019)