Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate the incidence, onset, duration, characteristics and importance of late-onset neutropenia (defined as absolute neutrophil count<1500 μl−1 at 3 weeks of age or later) in a group of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants.
Study design:
Routine complete blood cell counts (CBCs) obtained from VLBW infants over a period of 7 years were gathered retrospectively, including those of newborns with weekly CBCs taken over a duration of at least 3 weeks. Data were obtained from between January 2003 and December 2009.
Result:
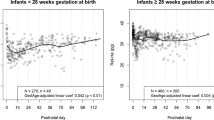
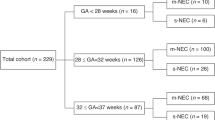
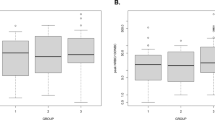
CBCs of 399 newborns were included. Values were obtained from birth to 36 weeks of postnatal age. Late-onset neutropenia was observed in 259 cases (65%). Neutropenic infants had a mean of 0.5 weeks lower gestational age. Late-onset neutropenia was more frequent in children with intraventricular hemorrhage but not in patients who received erythropoietin. The median age of neutropenia onset was 7 weeks in extremely low birth weight infants and 6 weeks in VLBW infants. The fifth percentile of neutrophils between weeks 3 and 4 was 1280 μl−1 and between weeks 13 and 15 was 500 μl−1. The average duration was 2 weeks with normalized values after 18 weeks.
Conclusion:
A neutrophil count <1500 μl−1 after the third week of life is frequently observed in VLBW infants and should not be used as a lower reference limit. The fifth percentile varies according to postnatal age from around 1300 μl−1 in week 4 of life, decreasing to a nadir of 500 μl−1 between 3 and 4 months of age. Values normalize in the first year of life.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Omar SA, Salhadar A, Wooliever DE, Alsgaard PK . Late-onset neutropenia in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2000; 106: 55–72.
Mouzhino A . Revised reference ranges for circulating neutrophils in very low birth weight neonates. Pediatrics 1994; 94: 76–82.
Coulombel L, Denhan M, Tchernia G . The number of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in relation to gestational age in the newborn. Acta Paediatr Scand 1979; 68: 709–711.
Lloyd BW, Oto A . Normal values for mature and immature neutrophils in very preterm babies. Arch Dis Child 1982; 57: 233–235.
Nash PL, Kwon IG . CBC and differential in VLBW infants. Neonatal Netw 1998; 17: 17–21.
Christensen RD . Expected hematologic values for term and preterm neonates In: Christensen RD (eds). Hematologic Problems of the Neonate. WB Saunders Co: Philadelphia, PA, 2000 pp 117–136.
Christensen RD, Henry E, Wiedmeier SE, Stoddard RA, Lambert DK . Low blood neutrophil concentrations among extremely low birth weight neonates: data from a multihospital health-care system. J Perinatol 2006; 26: 682–687.
Obladen M, Diepold K, Maier R . Venous and arterial hematologic profiles of very low birth weight Infants. European Multicenter rhEPO Study Group. Pediatrics 2000; 106: 707–711.
Christensen RD, Henry E, Jopling J, Wiedmeier SE . The CBC: reference ranges for neonates. Semin Perinatol 2009; 33: 3–11.
Schibler K . Leukocyte development and disorders during the neonatal period In: Christensen RD (eds.) Hematologic Problems of the Neonate. WB Saunders Co: Philadelphia, PA, 2000 pp 311–342.
Gillan ER, Christensen R, Suen Y, Ellis R, Van de Ven C, Cairo MS . A randomized placebo controlled trial of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration in newborn infants with presumed sepsis: significant induction of peripheral and bone marrow neutrophilia. Blood 1994; 84: 1427–1433.
Mouzhino A, Rosenfeld CR, Sanchez PJ, Risser R . Effect of maternal hypertension on neonatal neutropenia and risk of nosocomial infection. Pediatrics 1992; 90: 430–435.
Russel ARB, Davies EG, Ball SE, Gordon-Smith E . Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment for neonatal neutropenia. Arch Dis Child 1995; 72: 53–54.
Bilgin K, Yaramis A, Haspolat K, Tas A, Günbey S, Derman O . A randomized trial of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in neonates with sepsis and neutropenia. Pediatrics 2001; 107: 36–41.
Funke A, Berner R, Traichel B, Schmeisse D, Jecabs U, Niemeyer CM et al. Frequency, natural course, and outcome of neonatal neutropenia. Pediatrics 2000; 106: 46–51.
Carr R, Brocklehurst P, Doré CJ, Modi N . Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor administered as prophylaxis for reduction of sepsis in extremely preterm, small for gestational age neonates: a single-blind, multicenter randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2009; 17: 188–190.
Chirico G, Motta M, Villani P, Couzza A . Late-onset neutropenia in very low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2002; 91: 104–108.
Halperin DS, Wacker P, Lacount G . Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin in infants with anemia of prematurity. J Pediatr 1990; 116: 779–786.
Christensen RD . Hematopoiesis in the fetus and neonate. Pediatr Res 1989; 26: 531–535.
Van Zant G, Goldwasser E . Simultaneous effects of erythropoietin and colony-stimulating factors on bone marrow cells. Science 1977; 198: 733–735.
Christensen RD, Liechty KW, Koenig JM, Schibler KR, Ohls RK . Administration of erythropoietin to newborn rats results in diminished neutrophil production. Blood 1991; 78: 1241–1246.
Aher SM, Ohlsson A . Early versus late erythropoietin for preventing red blood cell transfusion in preterm and/or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; 3: CD004865.
Christensen RD, Rothstein G . Erythropoietin affects the maturation pattern of fetal G-CSF-responsive progenitors. Am J Hematol 1992; 39: 108–112.
Latini G, Rosati E . Transient neutropenia may be a risk of treating preterm neonates with high doses of recombinant erythropoietin. Eur J Pediatr 1998; 157: 443–444.
Donato H, Bacciedoni V, Garcia C, Schvartzman G, Vain N . Recombinant erythropoietin as treatment for hyporegenerative anemia following hemolytic disease of the newborn. Arch Argent Pediatr 2009; 107: 119–125.
Mizuno S, Sasaki J, Suzuki C, Kono H, Kojima S . Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin administration on peripheral blood neutrophil count of premature infants. J Pediatr 1994; 124: 467–470.
Maier RF, Obladen M, Scigalla P et al. The effect of epoetin beta (recombinant human erythropoietin) on the need for transfusion in very-low-birth weight infants. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 1173–1178.
Gessler P, Luders R, Konig S, Haas N, Lasch P, Kachel W . Neonatal neutropenia in low birth weight premature infants. Am J Perinatal 1995; 12: 34–38.
Palta M, Sadek-Badawi M, Carlton DP . Association of BPD and IVH with early neutrophil and white counts in VLBW neonates with gestational age <32 weeks. J Perinatol 2008; 28: 604–610.
Manroe BL, Weinberg AG, Rosenfeld CR, Browne R . The neonatal blood count in health and disease. Reference values for neutrophilic cells. J Pediatr 1979; 95: 89–98.
Schmutz N, Henry E, Jopling J, Christensen RD . Expected ranges for blood neutrophil concentrations in neonates: the Manroe and Mouzhino charts revisited. J Perinatol 2008; 28: 275–281.
Sarkar S, Bhagat I, Hieber S, Donn SM . Can neutrophil response in very low birth weight infants predict the organism responsible for late-onset bacterial or fungal sepsis? J Perinatol 2006; 26: 501–505.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Gerard Laracy for his editorial assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vetter-Laracy, S., Balliu, PR., Salinas, J. et al. Late-onset neutropenia: defining limits of neutrophil count in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 34, 22–26 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2013.111
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
C-reactive protein for late-onset sepsis diagnosis in very low birth weight infants
BMC Pediatrics (2018)