Abstract
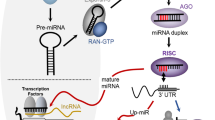
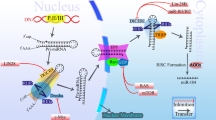
MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are 18–22-nucleotide non-coding RNAs that have emerged as a new paradigm of epigenetic regulation in both normal development and cellular function, and in the pathogenesis of human disease including cancer. This review summarizes the current literature of mechanism of gene regulation by miRNA and their role in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. An understanding of these processes suggests further avenues for research to understand gene regulation and miRNA-based therapeutic approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V . The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993; 75: 843–854.
Berezikov E, Chung WJ, Willis J, Cuppen E, Lai EC . Mammalian mirtron genes. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 328–336.
Rana TM . Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 23–36.
Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, Kumaraswamy E, Norman J, Cooch N, Nishikura K et al. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature 2005; 436: 740–744.
Sontheimer EJ . Assembly and function of RNA silencing complexes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 127–138.
Peters L, Meister G . Argonaute proteins: mediators of RNA silencing. Mol Cell 2007; 26: 611–623.
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM . Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol 2005; 3: e85.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005; 120: 15–20.
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK, Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP, Bartel DP . MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell 2007; 27: 91–105.
Vasudevan S, Tong Y, Steitz JA . Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 2007; 318: 1931–1934.
Doench JG, Sharp PA . Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 504–511.
Vella MC, Choi EY, Lin SY, Reinert K, Slack FJ . The C. elegans microRNA let-7 binds to imperfect let-7 complementary sites from the lin-41 3′UTR. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 132–137.
Wang B, Love TM, Call ME, Doench JG, Novina CD . Recapitulation of short RNA-directed translational gene silencing in vitro. Mol Cell 2006; 22: 553–560.
Lytle JR, Yario TA, Steitz JA . Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 9667–9672.
Olsen PH, Ambros V . The lin-4 regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation of translation. Dev Biol 1999; 216: 671–680.
Maroney PA, Yu Y, Fisher J, Nilsen TW . Evidence that microRNAs are associated with translating messenger RNAs in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2006; 13: 1102–1107.
Chendrimada TP, Finn KJ, Ji X, Baillat D, Gregory RI, Liebhaber SA et al. MicroRNA silencing through RISC recruitment of eIF6. Nature 2007; 447: 823–828.
Schmitter D, Filkowski J, Sewer A, Pillai RS, Oakeley EJ, Zavolan M et al. Effects of Dicer and Argonaute down-regulation on mRNA levels in human HEK293 cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: 4801–4815.
Giraldez AJ, Mishima Y, Rihel J, Grocock RJ, Van Dongen S, Inoue K et al. Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science 2006; 312: 75–79.
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T, Stark A, Bork P, Izaurralde E . mRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping complexes. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 1885–1898.
Liu CG, Calin GA, Meloon B, Gamliel N, Sevignani C, Ferracin M et al. An oligonucleotide microchip for genome-wide microRNA profiling in human and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 9740–9744.
Hammond SM . MicroRNAs as oncogenes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2006; 16: 4–9.
Kim VN, Nam JW . Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet 2006; 22: 165–173.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005; 435: 834–838.
Schmittgen TD, Jiang J, Liu Q, Yang L . A high-throughput method to monitor the expression of microRNA precursors. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: e43.
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: e179.
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R, Diaz Jr LA, Sjoblom T et al. The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3687–3692.
Allawi HT, Dahlberg JE, Olson S, Lund E, Olson M, Ma WP et al. Quantitation of microRNAs using a modified invader assay. RNA 2004; 10: 1153–1161.
Nelson PT, Baldwin DA, Scearce LM, Oberholtzer JC, Tobias JW, Mourelatos Z . Microarray-based, high-throughput gene expression profiling of microRNAs. Nat Methods 2004; 1: 155–161.
Bar M, Wyman SK, Fritz BR, Qi J, Garg KS, Parkin RK et al. MicroRNA discovery and profiling in human embryonic stem cells by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries. Stem Cells 2008; 26: 2496–2505.
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP . MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004; 303: 83–86.
Neilson JR, Zheng GX, Burge CB, Sharp PA . Dynamic regulation of miRNA expression in ordered stages of cellular development. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 578–589.
Xiao C, Calado DP, Galler G, Thai TH, Patterson HC, Wang J et al. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007; 131: 146–159.
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, Lintault L, Meissner A, Erkeland SJ et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008; 132: 875–886.
Johnnidis JB, Camargo FD . Isolation and functional characterization of side population stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 2008; 430: 183–193.
Fukao T, Fukuda Y, Kiga K, Sharif J, Hino K, Enomoto Y et al. An evolutionarily conserved mechanism for microRNA-223 expression revealed by microRNA gene profiling. Cell 2007; 129: 617–631.
Kasashima K, Nakamura Y, Kozu T . Altered expression profiles of microRNAs during TPA-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 322: 403–410.
Rosa A, Ballarino M, Sorrentino A, Sthandier O, De Angelis FG, Marchioni M et al. The interplay between the master transcription factor PU.1 and miR-424 regulates human monocyte/macrophage differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 19849–19854.
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, Iuliano R, Cimmino A, Aqeilan R et al. MicroRNA fingerprints during human megakaryocytopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 5078–5083.
Lu J, Guo S, Ebert BL, Zhang H, Peng X, Bosco J et al. MicroRNA-mediated control of cell fate in megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors. Dev Cell 2008; 14: 843–853.
Labbaye C, Spinello I, Quaranta MT, Pelosi E, Pasquini L, Petrucci E et al. A three-step pathway comprising PLZF/miR-146a/CXCR4 controls megakaryopoiesis. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 788–801.
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R, Bonci D, Facchiano F et al. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18081–18086.
Bruchova H, Yoon D, Agarwal AM, Mendell J, Prchal JT . Regulated expression of microRNAs in normal and polycythemia vera erythropoiesis. Exp Hematol 2007; 35: 1657–1667.
Masaki S, Ohtsuka R, Abe Y, Muta K, Umemura T . Expression patterns of microRNAs 155 and 451 during normal human erythropoiesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 364: 509–514.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 15524–15529.
Kluiver J, Poppema S, de Jong D, Blokzijl T, Harms G, Jacobs S et al. BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol 2005; 207: 243–249.
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z, Gomez MF et al. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 3627–3632.
Costinean S, Zanesi N, Pekarsky Y, Tili E, Volinia S, Heerema N et al. Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade lymphoma in E(mu)-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 7024–7029.
Rai D, Karanti S, Jung I, Dahia PL, Aguiar RC . Coordinated expression of microRNA-155 and predicted target genes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2008; 181: 8–15.
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2008; 141: 672–675.
Xiao C, Srinivasan L, Calado DP, Patterson HC, Zhang B, Wang J et al. Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased miR-17-92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 405–414.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
Woods K, Thomson JM, Hammond SM . Direct regulation of an oncogenic micro-RNA cluster by E2F transcription factors. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 2130–2134.
Tagawa H, Karube K, Tsuzuki S, Ohshima K, Seto M . Synergistic action of the microRNA-17 polycistron and Myc in aggressive cancer development. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 1482–1490.
Nie K, Gomez M, Landgraf P, Garcia JF, Liu Y, Tan LH et al. MicroRNA-mediated down-regulation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells: a potential pathogenetic lesion in Hodgkin lymphomas. Am J Pathol 2008; 173: 242–252.
Bueno MJ, Perez de Castro I, Gomez de Cedron M, Santos J, Calin GA, Cigudosa JC et al. Genetic and epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 496–506.
Huppi K, Volfovsky N, Runfola T, Jones TL, Mackiewicz M, Martin SE et al. The identification of microRNAs in a genomically unstable region of human chromosome 8q24. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 212–221.
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, Yang Q, Aris V, Soteropoulos P et al. MicroRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 9762–9770.
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Kitade Y, Kinoshita T, Naoe T . Downregulation of microRNAs-143 and -145 in B-cell malignancies. Cancer Sci 2007; 98: 1914–1920.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Calin GA, Cimmino A, Fabbri M, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Shimizu M et al. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 5166–5171.
Marton S, Garcia MR, Robello C, Persson H, Trajtenberg F, Pritsch O et al. Small RNAs analysis in CLL reveals a deregulation of miRNA expression and novel miRNA candidates of putative relevance in CLL pathogenesis. Leukemia 2008; 22: 330–338.
Fulci V, Chiaretti S, Goldoni M, Azzalin G, Carucci N, Tavolaro S et al. Quantitative technologies establish a novel microRNA profile of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2007; 109: 4944–4951.
Pekarsky Y, Santanam U, Cimmino A, Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V et al. Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11590–11593.
Sonoki T, Iwanaga E, Mitsuya H, Asou N . Insertion of microRNA-125b-1, a human homologue of lin-4, into a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus in a patient with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 2009–2010.
Zanette DL, Rivadavia F, Molfetta GA, Barbuzano FG, Proto-Siqueira R, Silva-Jr WA et al. miRNA expression profiles in chronic lymphocytic and acute lymphocytic leukemia. Braz J Med Biol Res 2007; 40: 1435–1440.
Mi S, Lu J, Sun M, Li Z, Zhang H, Neilly MB et al. MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 19971–19976.
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG, Fernandez-Cymering C, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F et al. MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 3183–3189.
Marcucci G, Radmacher MD, Maharry K, Mrozek K, Ruppert AS, Paschka P et al. MicroRNA expression in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1919–1928.
Dixon-McIver A, East P, Mein CA, Cazier JB, Molloy G, Chaplin T et al. Distinctive patterns of microRNA expression associated with karyotype in acute myeloid leukaemia. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e2141.
O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, Boldin MP, Taganov KD, Nicoll J et al. Sustained expression of microRNA-155 in hematopoietic stem cells causes a myeloproliferative disorder. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 585–594.
Garzon R, Garofalo M, Martelli MP, Briesewitz R, Wang L, Fernandez-Cymering C et al. Distinctive microRNA signature of acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 3945–3950.
Nakamura T, Canaani E, Croce CM . Oncogenic All1 fusion proteins target Drosha-mediated microRNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 10980–10985.
Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M, Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU et al. Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood 2007; 109: 4399–4405.
Chiorazzi N, Ferrarini M . Evolving view of the in-vivo kinetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2006; 512: 273–278.
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1793–1801.
Calin GA, Pekarsky Y, Croce CM . The role of microRNA and other non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2007; 20: 425–437.
Acknowledgements
Dr Calin is supported as a Fellow of The University of Texas MD Anderson Research Trust, as a Fellow of University of Texas System Regents Research Scholar and as a Ladjevardian Regents Research Scholar Fund. This study was also funded by an Institutional Research Grant and by a CCSG Award to George A Calin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yendamuri, S., Calin, G. The role of microRNA in human leukemia: a review. Leukemia 23, 1257–1263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.382
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.382
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A coordinated function of lncRNA HOTTIP and miRNA-196b underpinning leukemogenesis by targeting FAS signaling
Oncogene (2022)
-
Micro-RNA-125a mediates the effects of hypomethylating agents in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Clinical Epigenetics (2021)
-
CCN2 (Cellular Communication Network factor 2) in the bone marrow microenvironment, normal and malignant hematopoiesis
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Global expression of noncoding RNome reveals dysregulation of small RNAs in patients with HTLV-1–associated adult T-cell leukemia: a pilot study
Infectious Agents and Cancer (2021)
-
Inducing Apoptosis and Decreasing Cell Proliferation in Human Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Through Regulation Expression of CASP3 by Let-7a-5p Blockage
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2018)