Abstract
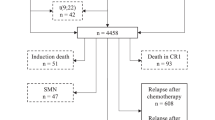
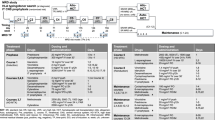
Analysis of 2668 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) treated in two successive Nordic clinical trials (Nordic Society of Paediatric Haematology and Oncology (NOPHO) ALL-92 and ALL-2000) showed that 75% of all patients are cured by first-line therapy, and 83% are long-term survivors. Improvements in systemic and intrathecal chemotherapy have reduced the use of central nervous system (CNS) irradiation to <10% of the patients and provided a 5-year risk of isolated CNS relapse of 2.6%. Improved risk stratification and chemotherapy have eliminated the previous independent prognostic significance of gender, CNS leukemia and translocation t(1;19)(q23;p13), whereas the post-induction level of minimal residual disease (MRD) has emerged as a new risk grouping feature. Infant leukemia, high leukocyte count, T-lineage immunophenotype, translocation t(4;11)(q21;q23) and hypodiploidy persist to be associated with lower cure rates. To reduce the overall toxicity of the treatment, including the risk of therapy-related second malignant neoplasms, the current NOPHO ALL-2008 protocol does not include CNS irradiation in first remission, the dose of 6-mercaptopurine is reduced for patients with low thiopurine methyltransferase activity, and the protocol restricts the use of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in first remission to patients without morphological remission after induction therapy or with high levels of MRD after 3 months of therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pui CH, Robison LL, Look AT . Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2008; 371: 1030–1043.
Schmiegelow K, Gustafsson G . Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In: Voute PA BASM, Caron M (eds) Cancer in Children, 5th edn Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2005, pp 138–170.
Gustafsson G, Garwicz S, Hertz H, Johanesson G, Jonmundsson G, Moe PJ et al. A population-based study of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia diagnosed from July 1981 through June 1985 in the five Nordic countries. Incidence, patient characteristics and treatment results. Acta Paediatr Scand 1987; 76: 781–788.
Gustafsson G, Schmiegelow K, Forestier E, Clausen N, Glomstein A, Jonmundsson G et al. Improving outcome through two decades in childhood ALL in the Nordic countries: the impact of high-dose methotrexate in the reduction of CNS irradiation. Nordic Society of Pediatric Haematology and Oncology (NOPHO). Leukemia 2000; 14: 2267–2275.
Schmiegelow K, Forestier E, Kristinsson J, Soderhall S, Vettenranta K, Weinshilboum R et al. Thiopurine methyltransferase activity is related to the risk of relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results from the NOPHO ALL-92 study. Leukemia 2009; 3: 557–564.
Schmiegelow K, Bjork O, Glomstein A, Gustafsson G, Keiding N, Kristinsson J et al. Intensification of mercaptopurine/methotrexate maintenance chemotherapy may increase the risk of relapse for some children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1332–1339.
Schmiegelow K, Heyman M, Kristinsson J, Mogensen UB, Rosthoj S, Vettenranta K et al. Oral Methotrexate/6-Mercaptopurine may be superior to a multi-drug LSA2L2 maintenance therapy for higher risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2009; 31: 385–392.
Forestier E, Gauffin F, Andersen MK, Autio K, Borgstrom G, Golovleva I et al. Clinical and cytogenetic features of pediatric dic(9;20)(p13.2;q11.2)-positive B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemias: a Nordic series of 24 cases and review of the literature. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2008; 47: 149–158.
Forestier E, Heyman M, Andersen MK, Autio K, Blennow E, Borgstrom G et al. Outcome of ETV6/RUNX1-positive childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the NOPHO-ALL-1992 protocol: frequent late relapses but good overall survival. Br J Haematol 2008; 140: 665–672.
Lonnerholm G, Nordgren A, Frost BM, Jonsson OG, Kanerva J, Nygaard R et al. Dic(9;20)(p13;q11) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is related to low cellular resistance to asparaginase, cytarabine and corticosteroids. Leukemia 2008; 23: 209–212.
Forestier E, Schmiegelow K . The incidence peaks of the childhood acute leukemias reflect specific cytogenetic aberrations. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2006; 28: 486–495.
Karrman K, Forestier E, Andersen MK, Autio K, Borgstrom G, Heim S et al. High incidence of the ETV6/RUNX1 fusion gene in paediatric precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemias with trisomy 21 as the sole cytogenetic change: a Nordic series of cases diagnosed 1989–2005. Br J Haematol 2006; 135: 352–354.
Frost BM, Forestier E, Gustafsson G, Nygren P, Hellebostad M, Jonmundsson G et al. Translocation t(1;19) is related to low cellular drug resistance in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 165–169.
Forestier E, Izraeli S, Beverloo B, Haas O, Pession A, Michalova K et al. Cytogenetic features of acute lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemias in pediatric patients with Down syndrome: an iBFM-SG study. Blood 2008; 111: 1575–1583.
Li AH, Forestier E, Rosenquist R, Roos G . Minimal residual disease quantification in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia by real-time polymerase chain reaction using the SYBR green dye. Exp Hematol 2002; 30: 1170–1177.
Nyvold C, Madsen HO, Ryder LP, Seyfarth J, Svejgaard A, Clausen N et al. Precise quantification of minimal residual disease at day 29 allows identification of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and an excellent outcome. Blood 2002; 99: 1253–1258.
Malec M, van der Velden VH, Bjorklund E, Wijkhuijs JM, Soderhall S, Mazur J et al. Analysis of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: comparison between RQ-PCR analysis of Ig/TcR gene rearrangements and multicolor flow cytometric immunophenotyping. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1630–1636.
Malec M, Bjorklund E, Soderhall S, Mazur J, Sjogren AM, Pisa P et al. Flow cytometry and allele-specific oligonucleotide PCR are equally effective in detection of minimal residual disease in ALL. Leukemia 2001; 15: 716–727.
Bjorklund E, Mazur J, Soderhall S, Porwit-MacDonald A . Flow cytometric follow-up of minimal residual disease in bone marrow gives prognostic information in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2003; 17: 138–148.
Pieters R, Schrappe M, De LP, Hann I, De RG, Felice M et al. A treatment protocol for infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Interfant-99): an observational study and a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2007; 370: 240–250.
Mitelman F . An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. S Karger: Basel, 1995.
Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Gustafsson G, Carlsen N, Flaegstad T, Forestier E, Glomstein A et al. Outcome of children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia (HR-ALL): Nordic results on an intensive regimen with restricted central nervous system irradiation. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2004; 42: 8–23.
Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Lanning M, Perkkio M, Makipernaa A, Salmi TT, Hovi L et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor support in therapy of high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Med Pediatr Oncol 2000; 34: 319–327.
Relling MV, Rubnitz JE, Rivera GK, Boyett JM, Hancock ML, Felix CA et al. High incidence of secondary brain tumours after radiotherapy and antimetabolites. Lancet 1999; 354: 34–39.
Cox DR . Regression models and life-tables (with discussion). J R Stat Soc (B) 1972; 34: 187–220.
Andersen PK, Borgan Ø, Gill RD, Keiding N . Statistical Models Based on Counting Processes. Springer-Verlag: New York, 1993.
Siegel S, Castellan NJ . Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd edn McGraw-Hill Publishing: Singapore, 1988, 1–330.
Kaplan EJ, Meier P . Non-parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Schmiegelow K, Al-Modhwahi I, Andersen MK, Behrendtz M, Forestier E, Hasle H et al. Methotrexate/6-mercaptopurine maintenance therapy influences the risk of a second malignant neoplasm after childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia - results from the NOPHO ALL-92 study. Blood 2009; 113: 6077–6084.
Smith M, Arthur D, Camitta B, Carroll AJ, Crist W, Gaynon P et al. Uniform approach to risk classification and treatment assignment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [see comments]. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 18–24.
Pui CH, Howard SC . Current management and challenges of malignant disease in the CNS in paediatric leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 2008; 9: 257–268.
Benesch M, Sovinz P, Krammer B, Lackner H, Mann G, Schwinger W et al. Feasibility and toxicity of intrathecal liposomal cytarabine in 5 children and young adults with refractory neoplastic meningitis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2007; 29: 222–226.
Mullighan CG, Goorha S, Radtke I, Miller CB, Coustan-Smith E, Dalton JD et al. Genome-wide analysis of genetic alterations in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2007; 446: 758–764.
Nachman JB, Heerema NA, Sather H, Camitta B, Forestier E, Harrison CJ et al. Outcome of treatment in children with hypodiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2007; 110: 1112–1115.
Pui CH, Gaynon PS, Boyett JM, Chessells JM, Baruchel A, Kamps W et al. Outcome of treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with rearrangements of the 11q23 chromosomal region. Lancet 2002; 359: 1909–1915.
Mehta PA, Davies SM . Allogeneic transplantation for childhood ALL. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 133–139.
Schmiegelow K, Nyvold C, Seyfarth J, Pieters R, Madsen HO, Knabe N et al. Post-induction residual leukemia in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia quantified by PCR correlates with in-vitro prednisolone resistance. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1066–1071.
Campana D . Minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Semin Hematol 2009; 46: 100–106.
Stanulla M, Schaeffeler E, Flohr T, Cario G, Schrauder A, Zimmermann M et al. Thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) genotype and early treatment response to mercaptopurine in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. JAMA 2005; 293: 1485–1489.
Davidsen ML, Dalhoff K, Schmiegelow K . Pharmacogenetics influence treatment efficacy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008; 30: 831–849.
Nygaard U, Schmiegelow K . Dose reduction of coadministered 6-mercaptopurine decreases myelotoxicity following high-dose methotrexate in childhood leukemia. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1344–1348.
Evans WE, Relling MV, Rodman JH, Crom WR, Boyett JM, Pui CH . Conventional compared with individualized chemotherapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 499–505.
Hallbook H, Gustafsson G, Smedmyr B, Soderhall S, Heyman M . Treatment outcome in young adults and children >10 years of age with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Sweden: a comparison between a pediatric protocol and an adult protocol. Cancer 2006; 107: 1551–1561.
Moorman AV, Richards SM, Robinson HM, Strefford JC, Gibson BE, Kinsey SE et al. Prognosis of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21). Blood 2007; 109: 2327–2330.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Childhood Cancer Foundation, Denmark; The Childhood Cancer Foundation, Sweden; The University Hospital Rigshospitalet; Michael Goldschmidt Holding A/S; the Nona and Kullervo Väre Foundation. Kjeld Schmiegelow holds the Childhood Cancer Foundation Research Professorship in Pediatric Oncology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmiegelow, K., Forestier, E., Hellebostad, M. et al. Long-term results of NOPHO ALL-92 and ALL-2000 studies of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 24, 345–354 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.251
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.251
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prospective use of molecular minimal residual disease for risk stratification in children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift (2023)
-
Multimodal classification of molecular subtypes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
npj Precision Oncology (2023)
-
Early vascular toxicity after pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
Temporal changes in incidence of relapse and outcome after relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia over three decades; a Nordic population-based cohort study
Leukemia (2022)
-
Central nervous system involvement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: challenges and solutions
Leukemia (2022)