Abstract
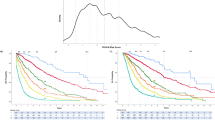
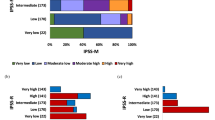
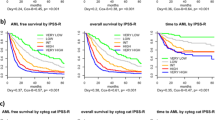
The Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) was developed for untreated myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients based on clinical data. We created and validated a new model that incorporates mutational data to improve the predictive capacity of the IPSS-R in treated MDS patients. Clinical and mutational data from treated MDS patients diagnosed between January 2000 and January 2012 were used to develop the new prognostic system. A total of 508 patients were divided into training (n=333) and validation (n=175) cohorts. Independent significant prognostic factors for survival included age, IPSS-R, EZH2, SF3B1 and TP53. Weighted coefficients for each factor were used to build the new linear predictive model, which produced four prognostic groups: low, intermediate-1, intermediate-2 and high with a median overall survival of 37.4, 23.2, 19.9 and 12.2 months, respectively, P<0.001. Significant improvement in the C-index of the new model (0.73) was observed compared with the IPSS-R (0.69). The new model predicted outcome both in a separate validation cohort and in another cohort of patients with paired samples at different time points during their disease course. The addition of mutational data to the IPSS-R makes it dynamic and enhances its predictive ability in treated MDS patients regardless of their initial or subsequent therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia-Manero G . Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2014 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 2014; 89: 97–108.
Sekeres MA, Cutler C . How we treat higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2014; 123: 829–836.
Greenberg PL, Attar E, Bennett JM, Bloomfield CD, Borate U, De Castro CM et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes: clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2013; 11: 838–874.
Cogle CR, Craig BM, Rollison DE, List AF . Incidence of the myelodysplastic syndromes using a novel claims-based algorithm: high number of uncaptured cases by cancer registries. Blood 2011; 117: 7121–7125.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, Della Porta MG, Pascutto C, Invernizzi R et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3503–3510.
Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Ravandi F, Cortes J, Shan J, Bennett JM et al. Proposal for a new risk model in myelodysplastic syndrome that accounts for events not considered in the original International Prognostic Scoring System. Cancer 2008; 113: 1351–1361.
Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Sole F et al. Revised International Prognostic Scoring System for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012; 120: 2454–2465.
Sekeres MA, Swern AS, Fenaux P, Greenberg PL, Sanz GF, Bennett JM et al. Validation of the IPSS-R in lenalidomide-treated, lower-risk myelodysplastic syndrome patients with del(5q). Blood Cancer J 2014; 4: e242.
Neukirchen J, Lauseker M, Blum S, Giagounidis A, Lubbert M, Martino S et al. Validation of the Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a multicenter study. Leuk Res 2014; 38: 57–64.
Nazha A, Seastone D, Keng M, Hobson S, Kalaycio M, Maciejewski JP et al. The Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) is not predictive of survival in patients with secondary myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma 2015; 24: 1–12.
Lindsley RC, Ebert BL . The biology and clinical impact of genetic lesions in myeloid malignancies. Blood 2013; 122: 3741–3748.
Bejar R, Levine R, Ebert BL . Unraveling the molecular pathophysiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 504–515.
Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Malcovati L, Tauro S, Gundem G, Van Loo P et al. Clinical and biological implications of driver mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013; 122: 3616–3627; quiz 99.
Haferlach T, Nagata Y, Grossmann V, Okuno Y, Bacher U, Nagae G et al. Landscape of genetic lesions in 944 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2014; 28: 241–247.
Bejar R, Stevenson K, Abdel-Wahab O, Galili N, Nilsson B, Garcia-Manero G et al. Clinical effect of point mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2496–2506.
Malcovati L, Papaemmanuil E, Ambaglio I, Elena C, Galli A, Della Porta MG et al. Driver somatic mutations identify distinct disease entities within myeloid neoplasms with myelodysplasia. Blood 2014; 124: 1513–1521.
Bejar R, Stevenson KE, Caughey B, Lindsley RC, Mar BG, Stojanov P et al. Somatic mutations predict poor outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 2691–2698.
Bejar R, Stevenson KE, Caughey BA, Abdel-Wahab O, Steensma DP, Galili N et al. Validation of a prognostic model and the impact of mutations in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 3376–3382.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood 2009; 114: 937–951.
Schanz J, Tuchler H, Sole F, Mallo M, Luno E, Cervera J et al. New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia after MDS derived from an international database merge. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 820–829.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The study was presented as an oral presentation at the 57th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, Orlando, 2015.
Author contributions
NA, JPM and MAS designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data, wrote and approved the manuscript. MN, TR, DJS, BP and BP collected the data, analyzed the samples, performed statistical analysis, reviewed and approved the manuscript. MK, AA and HEC contributed patients, analyzed the data, reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazha, A., Narkhede, M., Radivoyevitch, T. et al. Incorporation of molecular data into the Revised International Prognostic Scoring System in treated patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 30, 2214–2220 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.138
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.138
This article is cited by
-
Clinical and genetic features of Japanese cases of MDS associated with VEXAS syndrome
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Validation of the molecular international prognostic scoring system in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes defined by international consensus classification
Blood Cancer Journal (2023)
-
TP53 mutation variant allele frequency of ≥10% is associated with poor prognosis in therapy-related myeloid neoplasms
Blood Cancer Journal (2023)
-
IPSS-M has greater survival predictive accuracy compared with IPSS-R in persons ≥ 60 years with myelodysplastic syndromes
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2022)
-
Comprehensive analysis of genetic factors predicting overall survival in Myelodysplastic syndromes
Scientific Reports (2022)