Abstract
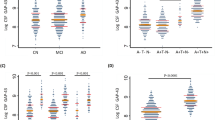
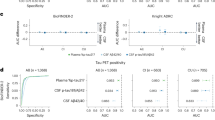
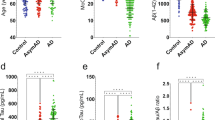
In this report, we present the results of a multicenter study to test analytic and diagnostic performance of soluble forms of amyloid precursor proteins α and β (sAPPα and sAPPβ) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with different forms of dementing conditions. CSF samples were collected from 188 patients with early dementia (mini-mental state examination⩾20 in majority of cases) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in 12 gerontopsychiatric centers, and the clinical diagnoses were supported by neurochemical dementia diagnostic (NDD) tools: CSF amyloidβ peptides, Tau and phospho-Tau. sAPPα and sAPPβ were measured with multiplexing method based on electrochemiluminescence. sAPPα and sAPPβ CSF concentrations correlated with each other with very high correlation ratio (R=0.96, P<0.001). We observed highly significantly increased sAPPα and sAPPβ CSF concentrations in patients with NDD characteristic for Alzheimer's disease (AD) compared to those with NDD negative results. sAPPα and sAPPβ highly significantly separated patients with AD, whose diagnosis was supported by NDD findings (sAPPα: cutoff, 117.4 ng ml−1, sensitivity, 68%, specificity, 85%, P<0.001; sAPPβ: cutoff, 181.8 ng ml−1, sensitivity, 75%, specificity, 85%, P<0.001), from the patients clinically assessed as having other dementias and supported by NDD untypical for AD. We conclude sAPPα and sAPPβ might be regarded as novel promising biomarkers supporting the clinical diagnosis of AD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mayeux R . Evaluation and use of diagnostic tests in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 1998; 19: 139–143.
Klafki HW, Staufenbiel M, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J . Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2006; 129: 2840–2855.
Hull M, Berger M, Heneka M . Disease-modifying therapies in Alzheimer's disease: how far have we come? Drugs 2006; 66: 2075–2093.
The Working Group on: ‘Molecular and Biochemical Markers of Alzheimer's Disease’. Consensus report of the Working Group on: ‘Molecular and Biochemical Markers of Alzheimer's Disease’. The Ronald and Nancy Reagan Research Institute of the Alzheimer's Association and the National Institute on Aging Working Group. Neurobiol Aging 1998; 19: 109–116.
Wiltfang J, Lewczuk P, Riederer P, Grünblatt E, Hock C, Scheltens P et al. Consensus paper of the WFSBP task force on biological markers of dementia: the role of CSF and blood analysis in the early and differential diagnosis of dementia. World J Biol Psychiatry 2005; 6: 69–84.
Lewczuk P, Wiltfang J . Neurochemical dementia diagnostics: state of the art and research perspectives. Proteomics 2008; 8: 1292–1301.
Andreasen N, Minthon L, Davidsson P, Vanmechelen E, Vanderstichele H, Winblad B et al. Evaluation of CSF-tau and CSF-Aβ42 as diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease in clinical practice. Arch Neurol 2001; 58: 373–379.
Blennow K, Wallin A, Hager O . Low frequency of post-lumbar puncture headache in demented patients. Acta Neurol Scand 1993; 88: 221–223.
Olsson A, Vanderstichele H, Andreasen N, De Meyer G, Wallin A, Holmberg B et al. Simultaneous measurement of beta-amyloid(1–42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau (Thr181) in cerebrospinal fluid by the xMAP technology. Clin Chem 2005; 51: 336–345.
Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Esselmann H, Bibl M et al. Multiplexed quantification of dementia biomarkers in the CSF of patients with early dementias and MCI: a multicenter study. Neurobiol Aging 2008; 29: 812–818.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM . Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984; 34: 939–944.
Thalmann B, Monsch AU, Bernasconi F, Berres M, Schneitter M, Ermini-Fuenfschilling D et al. Die CERAD Neuropsychologische Testbatterie—Ein gemeinsames minimales Instrumentarium zur Demenzabklärung. Memory Clinic, Geriatrische Universitätsklinik Basel: Basel, 1998.
Härting C, Markowitsch HJ, Neufeld H, Calabrese P, Deisinger K . Deutsche Adaptation der revidierten Fassung der Wechsler-Memory Scale (WMS-R). Verlag Hans Huber: Bern, Göttingen, 2000.
Reitan RM . Trail Making Test (TMT). Hogrefe Verlag: Bern, Göttingen, 1979.
Shulman KI, Shedletsky R, Silver IL . Challenge of time: clock-drawing and cognitive function in the elderly. Int J Ger Psychiatr 1986; 1: 135–140.
Hindmarch I, Lehfeld H, de Jongh P, Erzigkeit H . The bayer activities of daily living scale (B-ADL). Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 1998; 9 (Suppl 2): 20–26.
Jorm AF . A short form of the informant questionnaire on cognitive decline in the elderly (IQCODE): development and cross-validation. Psychol Med 1994; 24: 145–153.
Morris JC . The clinical dementia rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology 1993; 43: 2412–2414.
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR . Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 1975; 12: 189–198.
Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rabins PV et al. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 2001; 58: 1985–1992.
Lewczuk P, Esselmann H, Otto M, Maler JM, Henkel AW, Henkel MK et al. Neurochemical diagnosis of Alzheimer's dementia by CSF Aβ42, Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio and total tau. Neurobiol Aging 2004; 25: 273–281.
Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J . The German competence net dementias: standard operating procedures for the neurochemical dementia diagnostics. J Neural Transm 2006; 113: 1075–1080.
Lewczuk P, Esselmann H, Bibl M, Beck G, Maler JM, Otto M et al. Tau protein phosphorylated at threonine 181 in CSF as a neurochemical biomarker in Alzheimer's disease: original data and review of the literature. J Mol Neurosci 2004; 23: 115–122.
Ehehalt R, Michel B, De Pietri Tonelli D, Zacchetti D, Simons K, Keller P . Splice variants of the beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme BACE1 in human brain and pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 293: 30–37.
Tampellini D, Magrane J, Takahashi RH, Li F, Lin MT, Almeida CG et al. Internalized antibodies to the Abeta domain of APP reduce neuronal Abeta and protect against synaptic alterations. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 18895–18906.
Hixson JE, Vernier DT . Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 1990; 31: 545–548.
Lewczuk P, Kornhuber J, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Esselmann H, Bibl M et al. Multiplexed quantification of dementia biomarkers in the CSF of patients with early dementias and MCI: a multicenter study. Neurobiol Aging 2008; 29: 812–818.
Lewczuk P, Beck G, Ganslandt O, Esselmann H, Deisenhammer F, Regeniter A et al. International quality control survey of neurochemical dementia diagnostics. Neurosci Lett 2006; 409: 1–4.
Lewczuk P, Esselmann H, Bibl M, Paul S, Svitek J, Miertschischk J et al. Electrophoretic separation of amyloid beta peptides in plasma. Electrophoresis 2004; 25: 3336–3343.
Bibl M, Esselmann H, Otto M, Lewczuk P, Cepek L, Rüther E et al. Cerebrospinal fluid amyloid β peptide patterns in Alzheimer's disease patients and nondemented controls depend on sample pretreatment: indication of carrier-mediated epitope masking of amyloid beta peptides. Electrophoresis 2004; 25: 2912–2918.
Engelborghs S, De Vreese K, Van de Casteele T, Vanderstichele H, Van Everbroeck B, Cras P et al. Diagnostic performance of a CSF-biomarker panel in autopsy-confirmed dementia. Neurobiol Aging 2008; 29: 1143–1159.
Zetterberg H, Wahlund LO, Blennow K . Cerebrospinal fluid markers for prediction of Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 2003; 352: 67–69.
Hansson O, Zetterberg H, Buchhave P, Londos E, Blennow K, Minthon L . Association between CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer's disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a follow-up study. Lancet Neurol 2006; 5: 228–234.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the following grants from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF): Kompetenznetz Demenzen (01 GI 0420), HBPP-NGFN2 (01 GR 0447), and the Forschungsnetz der Früh- und Differenzialdiagnose der Creutzfeldt-Jakob-Krankheit und der neuen Variante der CJK (01 GI 0301), and by the EU grants cNEUPRO (contract no. LSHM-CT-2007-037950), and neuroTAS (contract no. LSHB-CT-2006-037953). We appreciate aliquots of 6E10 and ANGU antibodies provided by Dr R Umek (Meso-Scale Discovery) for western blot experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewczuk, P., Kamrowski-Kruck, H., Peters, O. et al. Soluble amyloid precursor proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid as novel potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease: a multicenter study. Mol Psychiatry 15, 138–145 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.84
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advanced Overview of Biomarkers and Techniques for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Soluble APP-α and APP-β in cerebrospinal fluid as potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research (2022)
-
α-Secretase nonsense mutation (ADAM10 Tyr167*) in familial Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2020)
-
CSF sAPPα and sAPPβ levels in Alzheimer’s Disease and Multiple Other Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Network Meta-Analysis
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2020)
-
Pharmacodynamics of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2018)