Abstract
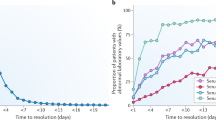
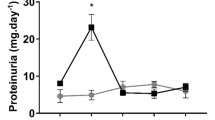
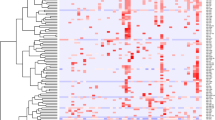
The capacities of urinary trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) and urinary albumin to detect acute renal tubular injury have never been evaluated with sufficient statistical rigor to permit their use in regulated drug development instead of the current preclinical biomarkers serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN). Working with rats, we found that urinary TFF3 protein levels were markedly reduced, and urinary albumin were markedly increased in response to renal tubular injury. Urinary TFF3 levels did not respond to nonrenal toxicants, and urinary albumin faithfully reflected alterations in renal function. In situ hybridization localized TFF3 expression in tubules of the outer stripe of the outer medulla. Albumin outperformed either SCr or BUN for detecting kidney tubule injury and TFF3 augmented the potential of BUN and SCr to detect kidney damage. Use of urinary TFF3 and albumin will enable more sensitive and robust diagnosis of acute renal tubular injury than traditional biomarkers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devarajan, P. Emerging biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Acute Kidney Injury 156, 203–212 (2007).
Bonventre, J.V., Vaidya, V.S., Schmouder, R., Feig, P. & Dieterle, F. Next-generation biomarkers for detecting kidney toxicity. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 436–440 (2010).
Madsen, J., Nielsen, O., Tornoe, I., Thim, L. & Holmskov, U. Tissue localization of human trefoil factors 1, 2, and 3. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 55, 505–513 (2007).
Taupin, D. & Podolsky, D.K. Trefoil factors: initiators of mucosal healing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 721–732 (2003).
Kinoshita, K., Taupin, D.R., Itoh, H. & Podolsky, D.K. Distinct pathways of cell migration and antiapoptotic response to epithelial injury: Structure-function analysis of human intestinal trefoil factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4680–4690 (2000).
LeSimple, P. et al. Trefoil factor family 3 peptide promotes human airway epithelial ciliated cell differentiation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 36, 296–303 (2007).
Suemori, S., Lynchdevaney, K. & Podolsky, D.K. Identification and characterization of rat intestinal trefoil factor—tissue-specific and cell-specific member of the trefoil protein family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 11017–11021 (1991).
Chinery, R., Poulsom, R., Elia, G., Hanby, A.M. & Wright, N.A. Expression and purification of a trefoil peptide motif in A beta-galactosidase fusion protein and its use to search for trefoil-binding sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 212, 557–563 (1993).
Debata, P.R., Panda, H. & Supakar, P.C. Altered expression of trefoil factor 3 and cathepsin L gene in rat kidney during aging. Biogerontology 8, 25–30 (2007).
Venkat, K.K. Proteinuria and microalbuminuria in adults: significance, evaluation, and treatment. South. Med. J. 97, 969–979 (2004).
Christensen, E., Birn, H., Rippe, B. & Maunsbach, A.B. Controversies in nephrology: renal albumin handling, facts, and artifacts!. Kidney Int. 72, 1192–1194 (2007).
Tugay, S., Bircan, Z., Caglayan, C., Arisoy, A.E. & Gokalp, A.S. Acute effects of gentamicin on glomerular and tubular functions in preterm neonates. Pediatr. Nephrol. 21, 1389–1392 (2006).
Koch Nogueira, P.C. et al. Long-term nephrotoxicity of cisplatin, ifosfamide, and methotrexate in osteosarcoma. Pediatr. Nephrol. 12, 572–575 (1998).
Kern, W. et al. Microalbuminuria during cisplatin therapy: relation with pharmacokinetics and implications for nephroprotection. Anticancer Res. 20, 3679–3688 (2000).
Sistare, F. et al. Towards consensus practices to qualify safety biomarkers for use in early drug development. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 446–454 (2010).
Safirstein, R., Winston, J., Moel, D., Dikman, S. & Guttenplan, J. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity—insights into mechanism. Int. J. Androl. 10, 325–346 (1987).
Winston, J.A. & Safirstein, R. Reduced renal blood-flow in early cisplatin-induced acute renal-failure in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 249, F490–F496 (1985).
Martinez-Salgado, C., Lopez-Hernandez, F.J. & Lopez-Novoa, J.M. Glomerular nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 223, 86–98 (2007).
Feldman, S., Wang, M.Y. & Kaloyanides, G.J. Aminoglycosides induce a phospholipidosis in the renal cortex of the rat—an early manifestation of nephrotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 220, 514–520 (1982).
Tune, B.M. & Hsu, C.Y. Mechanisms of beta-lactam antibiotic nephrotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 53, 81–86 (1990).
Tune, B.M. Renal tubular transport and nephrotoxicity of beta-lactam antibiotics—structure-activity-relationships. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 20, 221–231 (1994).
Yamano, T. et al. Hepatotoxicity of geniposide in rats. Am. J. Pathol. 74, 575–519 (1974).
York, M. et al. Characterization of troponin responses in isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury in the Hanover Wistar rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 35, 606–617 (2007).
Harrell, F.E., Lee, K.L., Califf, R.M., Pryor, D.B. & Rosati, R.A. Regression modeling strategies for improved prognostic prediction. Stat. Med. 3, 143–152 (1984).
Ozer, J. et al. A panel of urinary biomarkers to monitor reversibility of renal injury and a serum marker with improved potential to assess renal function. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 486–494 (2010).
Brooks, D.P., Drutz, D.J. & Ruffolo, R.R. Prevention and complete reversal of cyclosporine a-induced renal vasoconstriction and nephrotoxicity in the rat by fenoldopam. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 254, 375–379 (1990).
Goldman, L. & Bennett, C. . Cecil Texbook of Medicine, edn. 21 (W.B. Saunders, 2000).
Loeb, F.W. & Quimby, W.F.P. Clinical Chemistry of Laboratory Animals, edn. 2 (CRC, 1999).
Schwab, S.J., Christensen, R.L., Dougherty, K. & Klahr, S. Quantitation of proteinuria by the use of protein-to-creatinine ratios in single urine samples. Arch. Intern. Med. 147, 943–944 (1987).
Ginsberg, J.M., Chang, B.S., Matarese, R.A. & Garella, S. Use of single voided urine samples to estimate quantitative proteinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 309, 1543–1546 (1983).
Ramesh, G. & Reeves, W.B. Inflammatory cytokines in acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 66, S56–S61 (2004).
Zhang, B., Ramesh, G., Norbury, C.C. & Reeves, W.B. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha produced by renal parenchymal cells. Kidney Int. 72, 37–44 (2007).
Dossinger, V., Kayademir, T., Blin, N. & Gott, P. Down-regulation of TFF expression in gastrointestinal cell lines by cytokines and nuclear factors. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 12, 197–206 (2002).
Loncar, M.B. et al. Tumour necrosis factor alpha and nuclear factor kappa B inhibit transcription of human TFF3 encoding a gastrointestinal healing peptide. Gut 52, 1297–1303 (2003).
Sarafidis, P.A. Proteinuria: natural course, prognostic implications and therapeutic considerations. Minerva Med. 98, 693–711 (2007).
Barker, E.A. & Smuckler, E.A. Nonhepatic thioacetamide injury. II. The morphologic features of proximal renal tubular injury. Hepatogastroenterology 54, 1339–1344 (2007).
Boroushaki, M. Development of resistance against hexachlorobutadiene in the proximal tubules of young male rat. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 136, 367–375 (2003).
Ansari, N.H. & Rajaraman, S. Allopurinol-induced nephrotoxicity - protection by the antioxidant, butylated hydroxytoluene. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 75, 221–229 (1992).
Nguyen, T.K.T., Obatomi, D.K. & Bach, P.H. Increased urinary uronic acid excretion in experimentally-induced renal papillary necrosis in rats. Ren. Fail. 23, 31–42 (2001).
Williams, R.E. & Lock, E.A. D-serine-induced nephrotoxicity: possible interaction with tyrosine metabolism. Toxicology 201, 231–238 (2004).
Halman, J., Miller, J., Fowler, J.S.L. & Price, R.G. Renal toxicity of propyleneimine—assessment by noninvasive techniques in the rat. Toxicology 41, 43–59 (1986).
Zoja, C., Perico, N. & Remuzzi, G. Abnormalities in arachidonic-acid metabolites in nephrotoxic glomerular injury. Toxicol. Lett. 46, 65–75 (1989).
Sirica, A.E. Biliary proliferation and adaptation in furan-induced rat liver injury and carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Pathol. 24, 90–99 (1996).
Kaufmann, P. et al. Toxicity of statins on rat skeletal muscle mitochondria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 2415–2425 (2006).
Masuda, Y. Learning toxicology from carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Yakugaku Zasshi 126, 885–899 (2006).
Mehendale, H.M. Mechanism of the lethal interaction of chlordecone and CCl4 at non-toxic doses. Toxicol. Lett. 49, 215–241 (1989).
Thulesen, J., Jorgensen, P.E., Torffvit, O., Nexo, E. & Poulsen, S.S. Urinary excretion of epidermal growth factor and Tamm-Horsfall protein in three rat models with increased renal excretion of urine. Regul. Pept. 72, 179–186 (1997).
Croxatto, H.R., Huidrobro, R., Rojas, M., Roblero, J. & Albertini, R. Effect of water sodium overloading and diuretics upon urinary kallikrein. Agents Actions 6, 420 (1976).
Baracho, N.C.V., Simoes-e-Silva, Khosla, M.C. & Santos, R.A.S. Effect of selective angiotensin antagonists on the antidiuresis produced by angiotensin-(1–7) in water-loaded rats. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 31, 1221–1227 (1998).
Mattes, W.B. & Walker, E.G. Translational toxicology and the work of the predictive safety testing consortium. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 85, 327–330 (2009).
Ky, B. & Shughrue, P.J. Methods to enhance signal using isotopic in situ hybridization. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 50, 1031–1037 (2002).
DeLong, E.R., Delong, D.M. & Clarkepearson, D.I. Comparing the areas under 2 or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44, 837–845 (1988).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the participants in the Nephrotoxicity Predictive Safety Testing Consortium and the Merck Kidney Biomarker Working Group. We thank J. Mardi, J. Flor, A. Smith and D. Harner for photographic and editorial assistance in assembling the histopathology supplement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y., D.H., J.S.O., P.S., S.P.T., W.B., A.G.A., F.D.S. and D.L.G. designed and analyzed experiments. Y.Y., H.J., S.V., D.J.F., H.C., M.S., J.S., N.M., S.P.T. and S.S. performed experiments. Y.Y., D.H., J.S.O., P.S., A.G.A., D.T., F.D.S. and D.L.G. wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors are employees of Merck, with the exception of J.S., who works for Charles River Laboaratories.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Tables 1–3, Supplementary Fig. 1, Supplementary Data, Supplementary Assay Validation and Supplementary Results (PDF 34182 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Jin, H., Holder, D. et al. Urinary biomarkers trefoil factor 3 and albumin enable early detection of kidney tubular injury. Nat Biotechnol 28, 470–477 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1624
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1624
This article is cited by
-
Clinical usefulness of urinary biomarkers for early prediction of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing transaortic valve implantation
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Early transcriptomic signatures and biomarkers of renal damage due to prolonged exposure to embedded metal
Cell Biology and Toxicology (2023)
-
Intestinal Trefoil Factor 3: a new biological factor mediating gut-kidney crosstalk in diabetic kidney disease
Endocrine (2023)
-
Epidemiology and renal injury following 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) poisoning
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Perioperative albuminuria and clinical model to predict acute kidney injury in paediatric cardiac surgery
Pediatric Nephrology (2022)