Abstract
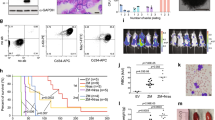
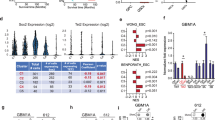
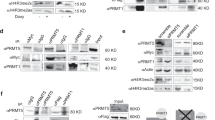
Enzymes that mediate reversible epigenetic modifications have not only been recognized as key in regulating gene expression1 and oncogenesis2,3, but also provide potential targets for molecular therapy4. Although the methylation of arginine 3 of histone 4 (H4R3) by protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) is a critical modification for active chromatin5,6 and prevention of heterochromatin spread7, there has been no direct evidence of any role of PRMTs in cancer. Here, we show that PRMT1 is an essential component of a novel Mixed Lineage Leukaemia (MLL) oncogenic transcriptional complex with both histone acetylation and H4R3 methylation activities, which also correlate with the expression of critical MLL downstream targets. Direct fusion of MLL with PRMT1 or Sam68, a bridging molecule in the complex for PRMT1 interaction, could enhance self-renewal of primary haematopoietic cells. Conversely, specific knockdown of PRMT1 or Sam68 expression suppressed MLL-mediated transformation. This study not only functionally dissects the oncogenic transcriptional machinery associated with an MLL fusion complex, but also uncovers — for the first time — an essential function of PRMTs in oncogenesis and reveals their potential as novel therapeutic targets in human cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128, 693–705 (2007).
Lund, A. H. & van Lohuizen, M. Epigenetics and cancer. Genes Dev. 18, 2315–2335 (2004).
Schneider, R., Bannister, A. J. & Kouzarides, T. Unsafe SETs: histone lysine methyltransferases and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 27, 396–402 (2002).
Minucci, S. & Pelicci, P. G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 6, 38–51 (2006).
Bedford, M. T. & Richard, S. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol. Cell 18, 263–272 (2005).
Lee, D. Y., Teyssier, C., Strahl, B. D. & Stallcup, M. R. Role of protein methylation in regulation of transcription. Endocr. Rev. 26, 147–170 (2005).
Huang, S., Litt, M. & Felsenfeld, G. Methylation of histone H4 by arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 is essential in vivo for many subsequent histone modifications. Genes Dev. 19, 1885–1893 (2005).
Look, A. T. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science 278, 1059–1064 (1997).
Dou, Y. et al. Regulation of MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferase activity by its core components. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 713–719 (2006).
Wysocka, J. et al. WDR5 associates with histone H3 methylated at K4 and is essential for H3 K4 methylation and vertebrate development. Cell 121, 859–872 (2005).
Daser, A. & Rabbitts, T. H. The versatile mixed lineage leukaemia gene MLL and its many associations in leukaemogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 15, 175–188 (2005).
Milne, T. A. et al. MLL targets SET domain methyltransferase activity to Hox gene promoters. Mol. Cell 10, 1107–1117 (2002).
Cozzio, A. et al. Similar MLL-associated leukemias arising from self-renewing stem cells and short-lived myeloid progenitors. Genes Dev. 17, 3029–3035 (2003).
So, C. W. et al. MLL-GAS7 transforms multipotent hematopoietic progenitors and induces mixed lineage leukemias in mice. Cancer Cell 3, 161–171 (2003).
Krivtsov, A. V. et al. Transformation from committed progenitor to leukaemia stem cell initiated by MLL-AF9. Nature 442, 818–822 (2006).
So, C. W. et al. EEN encodes for a member of a new family of proteins containing an Src homology 3 domain and is the third gene located on chromosome 19p13 that fuses to MLL in human leukemia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2563–2568 (1997).
So, C. W. & Cleary, M. L. Dimerization: a versatile switch for oncogenesis. Blood 104, 919–922 (2004).
So, C. W. & Cleary, M. L. Common mechanism for oncogenic activation of MLL by forkhead family proteins. Blood 101, 633–639 (2003).
Lukong, K. E. & Richard, S. Sam68, the KH domain-containing superSTAR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1653, 73–86 (2003).
Batsche, E., Yaniv, M. & Muchardt, C. The human SWI/SNF subunit Brm is a regulator of alternative splicing. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 22–29 (2006).
So, C. W., Karsunky, H., Wong, P., Weissman, I. L. & Cleary, M. L. Leukemic transformation of hematopietic progenitors by MLL-GAS7 in the absence of Hoxa7 or Hoxa9. Blood 103, 3192–3199 (2004).
Ayton, P. M. & Cleary, M. L. Transformation of myeloid progenitors by MLL oncoproteins is dependent on Hoxa7 and Hoxa9. Genes Dev. 17, 2298–2307 (2003).
Wang, H. et al. Methylation of histone H4 at arginine 3 facilitating transcriptional activation by nuclear hormone receptor. Science 293, 853–857 (2001).
Ernst, P., Wang, J., Huang, M., Goodman, R. H. & Korsmeyer, S. J. MLL and CREB bind cooperatively to the nuclear coactivator CREB-binding protein. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 2249–2258 (2001).
So, C. W. & Cleary, M. L. MLL-AFX requires the transcriptional effector domains of AFX to transform myeloid progenitors and transdominantly interfere with forkhead protein function. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 6542–6552 (2002).
Torres-Padilla, M. E., Parfitt, D. E., Kouzarides, T. & Zernicka-Goetz, M. Histone arginine methylation regulates pluripotency in the early mouse embryo. Nature 445, 214–218 (2007).
Ancelin, K. et al. Blimp1 associates with Prmt5 and directs histone arginine methylation in mouse germ cells. Nature Cell Biol. 8, 623–630 (2006).
Kwok, C., Zeisig, B. B., Dong, S. & So, C. W. Forced homo-oligomerization of RARα leads to transformation of primary hematopoietic cells. Cancer Cell 9, 95–108 (2006).
Zeisig, B. B. et al. Recruitment of RXR by homotetrameric RARα fusion proteins is essential for transformation. Cancer Cell 12, 36–51 (2007).
Sternsdorf, T. et al. Forced retinoic acid receptor alpha homodimers prime mice for APL-like leukemia. Cancer Cell 9, 81–94 (2006).
Zhu, J. et al. RXR is an essential component of the oncogenic PML/RARA complex in vivo. Cancer Cell 12, 23–35 (2007).
Villa, R. et al. Role of the polycomb repressive complex 2 in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell 11, 513–525 (2007).
An, W., Kim, J. & Roeder, R. G. Ordered cooperative functions of PRMT1, p300, and CARM1 in transcriptional activation by p53. Cell 117, 735–748 (2004).
Okada, Y. et al. hDOT1L links histone methylation to leukemogenesis. Cell 121, 167–178 (2005).
Cheung, N. et al. Subcellular localization of EEN/endophilin A2, a fusion partner gene in leukemia. Biochem. J. 383, 27–35 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Greaves, P. Workman, A. Ashworth, T. Lappin, S. Armstrong, A. Zelent, S. Huang and D. Shuo for useful discussion; J. Yam, G. McGonigle, B. Zeisig, W. Yue, A. Wilson, M. Boix-Chornet for excellent technical help; A. Thornhill, F. Darling, BSU staff for husbandry of mice; and P. Tse for professional artwork. This work is supported by the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR), and CWE So is an AICR research fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.C. performed most of the experiments; A.T. did the Q–RT–QPCR; L.C.C. and M.L.C. provided critical advice; C.W.E.S. designed and oversaw the project and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1, S2, S3 and S4 (PDF 160 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheung, N., Chan, L., Thompson, A. et al. Protein arginine-methyltransferase-dependent oncogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 9, 1208–1215 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1642
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1642
This article is cited by
-
Phase 1 study of GSK3368715, a type I PRMT inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
PHF6 maintains acute myeloid leukemia via regulating NF-κB signaling pathway
Leukemia (2023)
-
PRMT1-mediated H4R3me2a recruits SMARCA4 to promote colorectal cancer progression by enhancing EGFR signaling
Genome Medicine (2021)
-
Protein arginine methylation: from enigmatic functions to therapeutic targeting
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2021)
-
Interplay between cofactors and transcription factors in hematopoiesis and hematological malignancies
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)