Abstract
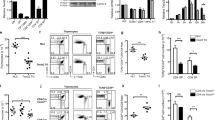
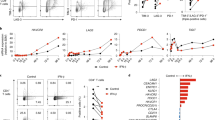
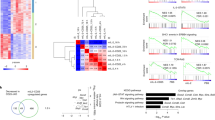
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) drive T helper type 1 (TH1) differentiation, but the mechanisms underlying the regulation of the complicated gene networks involved in this differentiation are not fully understood. Here we show that the IFN-γ-induced transcription factor IRF1 was essential in TH1 differentiation by acting on Il12rb1, the gene encoding the IL-12 receptor β1 subunit (IL-12Rβ1). IRF1 directly interacted with and activated the Il12rb1 promoter in CD4+ T cells. Notably, the IRF1-dependent induction of IL-12Rβ1 was essential for IFN-γ–IL-12 signaling but was dispensable for IL-23–IL-17 signaling. Because both IL-12 and IL-23 bind to and transmit signals through IL-12Rβ1, our data suggest that distinct thresholds of IL-12Rβ1 expression are required for TH1 versus TH-17 differentiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 December 2007
In the version of this supplementary file originally posted online, a band in the middle panel of Fig. 4C was not visible; the contrast has been adjusted appropriately. The error has been corrected in the PDF version of the article.
References
Mosmann, T.R. & Coffman, R.L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 7, 145–173 (1989).
Glimcher, L.H. & Murphy, K.M. Lineage commitment in the immune system: the T helper lymphocyte grows up. Genes Dev. 14, 1693–1711 (2000).
Murphy, K.M. et al. Signaling and transcription in T helper development. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 451–494 (2000).
Harrington, L.E. et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1123–1132 (2005).
Park, H. et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1133–1141 (2005).
Weaver, C.T., Hatton, R.D., Mangan, P.R. & Harrington, L.E. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 821–852 (2007).
Langrish, C.L. et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 201, 233–240 (2005).
Murphy, C.A. et al. Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1951–1957 (2003).
Cua, D.J. et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature 421, 744–748 (2003).
Szabo, S.J., Sullivan, B.M., Peng, S.L. & Glimcher, L.H. Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 713–758 (2003).
Lighvani, A.A. et al. T-bet is rapidly induced by interferon-γ in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 15137–15142 (2001).
Afkarian, M. et al. T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 3, 549–557 (2002).
Szabo, S.J. et al. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 100, 655–669 (2000).
Mullen, A.C. et al. Role of T-bet in commitment of TH1 cells before IL-12-dependent selection. Science 292, 1907–1910 (2001).
Murphy, K.M. et al. T helper differentiation proceeds through Stat1-dependent, Stat4-dependent and Stat4-independent phases. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 238, 13–26 (1999).
Szabo, S.J., Dighe, A.S., Gubler, U. & Murphy, K.M. Regulation of the interleukin (IL)-12Rβ2 subunit expression in developing T helper 1 (Th1) and Th2 cells. J. Exp. Med. 185, 817–824 (1997).
Mullen, A.C. et al. Hlx is induced by and genetically interacts with T-bet to promote heritable TH1 gene induction. Nat. Immunol. 3, 652–658 (2002).
Usui, T., Nishikomori, R., Kitani, A. & Strober, W. GATA-3 suppresses Th1 development by downregulation of Stat4 and not through effects on IL-12Rβ2 chain or T-bet. Immunity 18, 415–428 (2003).
Usui, T. et al. T-bet regulates Th1 responses through essential effects on GATA-3 function rather than on IFNG gene acetylation and transcription. J. Exp. Med. 203, 755–766 (2006).
Veldhoen, M., Hocking, R.J., Atkins, C.J., Locksley, R.M. & Stockinger, B. TGFβ in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24, 179–189 (2006).
Oppmann, B. et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13, 715–725 (2000).
Honda, K. & Taniguchi, T. IRFs: master regulators of signalling by Toll-like receptors and cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 644–658 (2006).
Taniguchi, T., Ogasawara, K., Takaoka, A. & Tanaka, N. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 623–655 (2001).
Taki, S. et al. Multistage regulation of Th1-type immune responses by the transcription factor IRF-1. Immunity 6, 673–679 (1997).
Lohoff, M. et al. Interferon regulatory factor-1 is required for a T helper 1 immune response in vivo. Immunity 6, 681–689 (1997).
Liu, J., Cao, S., Herman, L.M. & Ma, X. Differential regulation of interleukin (IL)-12 p35 and p40 gene expression and interferon (IFN)-γ-primed IL-12 production by IFN regulatory factor 1. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1265–1276 (2003).
Maruyama, S. et al. Identification of IFN regulatory factor-1 binding site in IL-12 p40 gene promoter. J. Immunol. 170, 997–1001 (2003).
McElligott, D.L. et al. CD4+ T cells from IRF-1-deficient mice exhibit altered patterns of cytokine expression and cell subset homeostasis. J. Immunol. 159, 4180–4186 (1997).
Elser, B. et al. IFN-γ represses IL-4 expression via IRF-1 and IRF-2. Immunity 17, 703–712 (2002).
Hwang, E.S., Szabo, S.J., Schwartzberg, P.L. & Glimcher, L.H. T helper cell fate specified by kinase-mediated interaction of T-bet with GATA-3. Science 307, 430–433 (2005).
Yamane, H., Igarashi, O., Kato, T. & Nariuchi, H. Positive and negative regulation of IL-12 receptor expression of naive CD4+ T cells by CD28/CD152 co-stimulation. Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 3171–3180 (2000).
Szabo, S.J. et al. Distinct effects of T-bet in TH1 lineage commitment and IFN-γ production in CD4 and CD8 T cells. Science 295, 338–342 (2002).
Aggarwal, S., Ghilardi, N., Xie, M.H., de Sauvage, F.J. & Gurney, A.L. Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 1910–1914 (2003).
Mangan, P.R. et al. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the TH17 lineage. Nature 441, 231–234 (2006).
Powrie, F. et al. Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells. Immunity 1, 553–562 (1994).
Wenner, C.A., Guler, M.L., Macatonia, S.E., O'Garra, A. & Murphy, K.M. Roles of IFN-γ and IFN-α in IL-12-induced T helper cell-1 development. J. Immunol. 156, 1442–1447 (1996).
Musikacharoen, T. et al. Interleukin-15 induces IL-12 receptor β1 gene expression through PU.1 and IRF 3 by targeting chromatin remodeling. Blood 105, 711–720 (2005).
Zhang, F. & Boothby, M. T helper type 1-specific Brg1 recruitment and remodeling of nucleosomes positioned at the IFN-γ promoter are Stat4 dependent. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1493–1505 (2006).
Avni, O. et al. TH cell differentiation is accompanied by dynamic changes in histone acetylation of cytokine genes. Nat. Immunol. 3, 643–651 (2002).
te Velde, A.A. et al. Comparative analysis of colonic gene expression of three experimental colitis models mimicking inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 13, 325–330 (2007).
Silverberg, M.S. et al. Refined genomic localization and ethnic differences observed for the IBD5 association with Crohn's disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 15, 328–335 (2007).
Clavell, M. et al. Detection of interferon regulatory factor-1 in lamina propria mononuclear cells in Crohn's disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 30, 43–47 (2000).
Matsuyama, T. et al. Targeted disruption of IRF-1 or IRF-2 results in abnormal type I IFN gene induction and aberrant lymphocyte development. Cell 75, 83–97 (1993).
Meraz, M.A. et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell 84, 431–442 (1996).
Huang, S. et al. Immune response in mice that lack the interferon-γ receptor. Science 259, 1742–1745 (1993).
Wu, C., Ferrante, J., Gately, M.K. & Magram, J. Characterization of IL-12 receptor β1 chain (IL-12Rβ1)-deficient mice: IL-12Rβ1 is an essential component of the functional mouse IL-12 receptor. J. Immunol. 159, 1658–1665 (1997).
Honda, K. et al. Selective contribution of IFN-α/β signaling to the maturation of dendritic cells induced by double-stranded RNA or viral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 10872–10877 (2003).
Ouyang, W. et al. Inhibition of Th1 development mediated by GATA-3 through an IL-4-independent mechanism. Immunity 9, 745–755 (1998).
Takayanagi, H. et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev. Cell 3, 889–901 (2002).
Martin-Fontecha, A. et al. Induced recruitment of NK cells to lymph nodes provides IFN-γ for TH1 priming. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1260–1265 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Flavell, R. Medzhitov, M. Feldmann, A. Rao and G. Nunez for discussions; L. Glimcher (Harvard School of Public Health) for the T-bet retrovirus vector and Tbx21−/− mice; R. Kastelein (DNAX Research Institute) for the IL-12Rβ1 bicistronic retrovirus vector; S. Hida and S. Taki (Shinshu University Graduate School of Medicine) for Rag1−/− mice; K. Ogasawara, A. Takaoka, H. Takayanagi, Y. Ohba, T. Tamura, H. Yanai, H. Katoh, C. Nakajima, K. Tsushima and H. Negishi for advice; Y. Matsuno and M. Shishido for technical assistance; D. Savitsky for critically reading the manuscript; and T. Yokochi and A. Sawa for encouragement. Supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (grant for Advanced Research on Cancer and a Grant-In-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas), the Ishidu Shun Memorial Foundation (S.K.) and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (S.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.-i.K. designed and did the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper; K.S. provided some of the initial results and ideas; Y.M. did the histological analysis of colitis; S.V. and S.K. did some of the experiments and analyzed the data; K.B., K.H. and M.K. generated key materials and analyzed some of the critical data; and T.T. supervised all the work and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5, Table 1 and Methods (PDF 2072 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kano, Si., Sato, K., Morishita, Y. et al. The contribution of transcription factor IRF1 to the interferon-γ–interleukin 12 signaling axis and TH1 versus TH-17 differentiation of CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 9, 34–41 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1538
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1538
This article is cited by
-
Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) promotes intestinal group 3 innate lymphoid responses during Citrobacter rodentium infection
Nature Communications (2022)
-
An atlas of alternative polyadenylation quantitative trait loci contributing to complex trait and disease heritability
Nature Genetics (2021)
-
The essential functions of mitochondrial dynamics in immune cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
Host–parasite interaction associated with major mental illness
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)
-
Inhibition of PARP1 Increases IRF-dependent Gene Transcription in Jurkat Cells
Current Medical Science (2019)