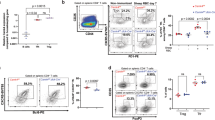
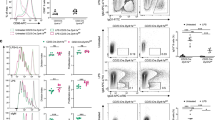
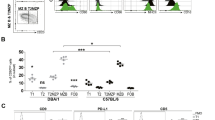
Abstract
Immunoglobulin (Ig) class-switch DNA recombination (CSR) is thought to be highly dependent upon engagement of CD40 on B cells by CD40 ligand on T cells. We show here that dendritic cells up-regulate BLyS and APRIL upon exposure to interferon-α, interferon-γ or CD40 ligand. In the presence of interleukin 10 (IL-10) or transforming growth factor-β, BLyS and APRIL induce CSR from Cμ to Cγ and/or Cα genes in B cells, whereas CSR to Cε requires IL-4. Secretion of class-switched antibodies requires additional stimulation by B cell antigen receptor engagement and IL-15. By eliciting CD40-independent Ig class switching and plasmacytoid differentiation, BLyS and APRIL critically link the innate and adaptive immune responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassing, C.H., Swat, W. & Alt, F.W. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell 109 (Suppl.) 45–55 (2002).
Stavnezer, J. Antibody class switching. Adv. Immunol. 61, 79–146 (1996).
Papavasiliou, F.N. & Schatz, D.G. Somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes: merging mechanisms for genetic diversity. Cell 109 (Suppl.) 35–44 (2002).
Manis, J.P., Tian, M. & Alt, F.W. Mechanism and control of class-switch recombination. Trends Immunol. 23, 31–39 (2002).
MacLennan, I.C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12, 117–139 (1994).
Okazaki, I., Kinoshita, K., Muramatsu, M., Yoshikawa, K. & Honjo, T. The AID enzyme induces class switch recombination in fibroblasts. Nature 416, 340–345 (2002).
Durandy, A. & Honjo, T. Human genetic defects in class-switch recombination (hyper-IgM syndromes). Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 543–548 (2001).
Mond, J.J., Lees, A. & Snapper, C.M. T cell-independent antigens type 2. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 655–692 (1995).
Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E. & Welsh, R.M. T-cell-independent antiviral antibody responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 10, 431–435 (1998).
Cyster, J.G. B cells on the front line. Nature Immunol. 1, 9–10 (2000).
Fagarasan, S. & Honjo, T. T-Independent immune response: new aspects of B cell biology. Science 290, 89–92 (2000).
Fayette, J. et al. Human dendritic cells skew isotype switching of CD40-activated naive B cells towards IgA1 and IgA2. J. Exp. Med. 185, 1909–1918 (1997).
Moore, P.A. et al. BLyS: member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science 285, 260–263 (1999).
Schneider, P. et al. BAFF, a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates B cell growth. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1747–1756 (1999).
Yan, M. et al. Identification of a receptor for BLyS demonstrates a crucial role in humoral immunity. Nature Immunol. 1, 37–41 (2000).
Thompson, J.S. et al. BAFF binds to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-like molecule B cell maturation antigen and is important for maintaining the peripheral B cell population. J. Exp. Med. 192, 129–135 (2000).
Gross, J.A. et al. TACI and BCMA are receptors for a TNF homologue implicated in B-cell autoimmune disease. Nature 404, 995–999 (2000).
Gross, J.A. et al. TACI-Ig neutralizes molecules critical for B cell development and autoimmune disease. Impaired B cell maturation in mice lacking BLyS. Immunity 15, 289–302 (2001).
Thompson, J.S. et al. BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically interacts with BAFF. Science 293, 2108–2111 (2001).
Hahne, M. et al. APRIL, a new ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family, stimulates tumor cell growth. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1185–1190 (1998).
Rennert, P. et al. A soluble form of B cell maturation antigen, a receptor for the tumor necrosis factor family member APRIL, inhibits tumor cell growth. J. Exp. Med. 192, 1677–1684 (2000).
Do, R.K. et al. Attenuation of apoptosis underlies B lymphocyte stimulator enhancement of humoral immune response. J. Exp. Med. 192, 953–964 (2000).
Xu, J. et al. Mice deficient for the CD40 ligand. Immunity 5, 423–431 (1994).
Renshaw, B.R. et al. Humoral immune responses in CD40 ligand-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1889–1900 (1994).
Schiemann, B. et al. An essential role for BAFF in the normal development of B cells through a BCMA-independent pathway. Science 293, 2111–4 (2001).
Yu, G. et al. APRIL and TALL-I and receptors BCMA and TACI: system for regulating humoral immunity. Nature Immunol. 1, 252–256 (2000).
von Bulow, G. U., van Deursen, J. M. & Bram, R. J. Regulation of the T-independent humoral response by TACI. Immunity 14, 573–582 (2001).
Mackay, F. et al. Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1697–1710 (1999).
Stein, J.V. et al. APRIL modulates B and T cell immunity. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1587–1598 (2002).
Kinoshita, K., Harigai, M., Fagarasan, S., Muramatsu, M. & Honjo, T. A hallmark of active class switch recombination: transcripts directed by I promoters on looped-out circular DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 12620–12623 (2001).
Cerutti, A. et al. CD40 ligand and appropriate cytokines induce switching to IgG, IgA, and IgE and coordinated germinal center and plasmacytoid phenotypic differentiation in a human monoclonal IgM+IgD+ B cell line. J. Immunol. 160, 2145–2157 (1998).
Matsumoto, M. et al. Role of lymphotoxin and the type I TNF receptor in the formation of germinal centers. Science 271, 1289–1291 (1996).
Cerutti, A. et al. CD30 is a CD40-inducible molecule that negatively regulates CD40-mediated immunoglobulin class switching in non-antigen-selected human B cells. Immunity 9, 247–256 (1998).
de Vinuesa, C. G. et al. Germinal centers without T cells. J. Exp. Med. 191, 485–494 (2000).
Nardelli, B. et al. Synthesis and release of B-lymphocyte stimulator from myeloid cells. Blood 97, 198–204 (2001).
Arpin, C. et al. Generation of memory B cells and plasma cells in vitro. Science 268, 720–722 (1995).
Armitage, R.J., Macduff, B.M., Eisenman, J., Paxton, R. & Grabstein, K.H. IL-15 has stimulatory activity for the induction of B cell proliferation and differentiation. J. Immunol. 154, 483–490 (1995).
Le Bon, A. et al. Type I interferons potently enhance humoral immunity and can promote isotype switching by stimulating dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity 14, 461–470 (2001).
Blanco, P., Palucka, A.K., Gill, M., Pascual, V. & Banchereau, J. Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-α in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 294, 1540–1543 (2001).
Siegal, F.P. et al. The nature of the principal type 1 interferon-producing cells in human blood. Science 284, 1835–1837 (1999).
Banchereau, J. et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 767–811 (2000).
Lanzavecchia, A. & Sallusto, F. Regulation of T cell immunity by dendritic cells. Cell 106, 263–266 (2001).
Macpherson, A.J. et al. A primitive T cell-independent mechanism of intestinal mucosal IgA responses to commensal bacteria. Science 288, 2222–2226 (2000).
Fagarasan, S., Kinoshita, K., Muramatsu, M., Ikuta, K. & Honjo, T. In situ class switching and differentiation to IgA-producing cells in the gut lamina propria. Nature 413, 639–643 (2001).
Life, P. et al. T cell clones from an X-linked hyper-immunoglobulin (IgM) patient induce IgE synthesis in vitro despite expression of nonfunctional CD40 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1775–1784 (1994).
Macpherson, A.J. et al. IgA production without μ or δ chain expression in developing B cells. Nature Immunol. 2, 625–631 (2001).
von Bulow, G. U. & Bram, R. J. NF-AT activation induced by a CAML-interacting member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. Science 278, 138–141 (1997).
Xia, X.Z. et al. TACI is a TRAF-interacting receptor for TALL-1, a tumor necrosis factor family member involved in B cell regulation. J. Exp. Med. 192, 137–143 (2000).
Cerutti, A. et al. Dysregulation of CD30+ T cells by leukemia impairs isotype switching in normal B cells. Nature Immunol. 2, 150–156 (2001).
Sallusto, F. & Lanzavecchia, A. Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor α. J. Exp. Med. 179, 1109–1118 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. S. Picha (Immunex Corp.) for recombinant soluble CD40L and S. Narula (Schering-Plough) for IL-4 and IL-10. Supported by a New Investigator Grant from The Leukemia Research Foundation (to A. C.), research grants from The SLE Foundation (to A. C. and P. C.) and grants from the National Institutes of Health AR 47872 (to A. C.), AR 40908 and AI 45011 (to P. C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
B. N. and D. M. H. are employed by Human Genome Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Litinskiy, M., Nardelli, B., Hilbert, D. et al. DCs induce CD40-independent immunoglobulin class switching through BLyS and APRIL. Nat Immunol 3, 822–829 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni829
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni829
This article is cited by
-
Intestinal Peyer’s Patches: Structure, Function, and In Vitro Modeling
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2023)
-
Clinical research progress of novel biologics for the treatment of lupus nephritis
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2023)
-
The role of retinoic acid in the production of immunoglobulin A
Mucosal Immunology (2022)
-
Partial RAG deficiency in humans induces dysregulated peripheral lymphocyte development and humoral tolerance defect with accumulation of T-bet+ B cells
Nature Immunology (2022)
-
Cenerimod, a selective S1P1 receptor modulator, improves organ-specific disease outcomes in animal models of Sjögren’s syndrome
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2021)