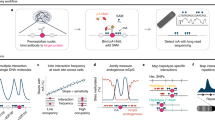
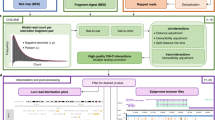
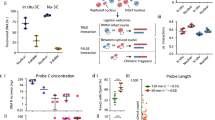
Abstract
Regulatory DNA elements can control the expression of distant genes via physical interactions. Here we present a cost-effective methodology and computational analysis pipeline for robust characterization of the physical organization around selected promoters and other functional elements using chromosome conformation capture combined with high-throughput sequencing (4C-seq). Our approach can be multiplexed and routinely integrated with other functional genomics assays to facilitate physical characterization of gene regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Change history
21 September 2012
In the version of this article initially published online, the name of Christian Valdes-Quezada was misspelled as Christian Valdes Quezada. The error has been corrected for the print, PDF and HTML version of this article.
References
Shen, Y. et al. Nature 488, 116–120 (2012).
Dekker, J., Rippe, K., Dekker, M. & Kleckner, N. Science 295, 1306–1311 (2002).
de Wit, E. & de Laat, W. Genes Dev. 26, 11–24 (2012).
Lieberman-Aiden, E. et al. Science 326, 289–293 (2009).
Sexton, T. et al. Cell 148, 458–472 (2012).
Dixon, J.R. et al. Nature 485, 376–380 (2012).
Li, G. et al. Cell 148, 84–98 (2012).
Simonis, M. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 1348–1354 (2006).
Zhao, Z. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 1341–1347 (2006).
Splinter, E. et al. Genes Dev. 25, 1371–1383 (2011).
Lower, K.M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 21771–21776 (2009).
de Wit, E., Braunschweig, U., Greil, F., Bussemaker, H.J. & van Steensel, B. PLoS Genet. 4, e1000045 (2008).
Tolhuis, B., Palstra, R.J., Splinter, E., Grosveld, F. & de Laat, W. Mol. Cell 10, 1453–1465 (2002).
Dostie, J. et al. Genome Res. 16, 1299–1309 (2006).
Splinter, E. et al. Genes Dev. 20, 2349–2354 (2006).
Vernimmen, D., De Gobbi, M., Sloane-Stanley, J.A., Wood, W.G. & Higgs, D.R. EMBO J. 26, 2041–2051 (2007).
Zhou, G.L. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 5096–5105 (2006).
Baù, D. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 107–114 (2011).
Yeom, Y.I. et al. Development 122, 881–894 (1996).
Yaffe, E. & Tanay, A. Nat. Genet. 43, 1059–1065 (2011).
Simonis, M., Kooren, J. & de Laat, W. Nat. Methods 4, 895–901 (2007).
Rozen, S. & Skaletsky, H. Methods Mol. Biol. 132, 365–386 (2000).
Zhang, Z., Schwartz, S., Wagner, L. & Miller, W. J. Comput. Biol. 7, 203–214 (2000).
Di Stefano, B. et al. PLoS ONE 5, e16092 (2010).
Kooren, J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 16544–16552 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank R. Palstra, E. Yaffe and other members of our labs for help and input, G. Geeven for testing the 4C-seq pipeline and H.T. Timmers (Netherlands Proteomics Centre and University Medical Center Utrecht) and J.P.P. Meijerink (Erasmus Medical Center-Sophia Children′s Hospital) for providing cells. This work was supported by grants from the Modelling Hepatocellular Carcinoma (MODHEP) Seventh Framework Program (FP7) collaborative project to W.d.L. and A.T., grants from the Dutch Scientific Organization (NWO) (91204082 and 935170621), a European Research Council Starting Grant (209700, '4C') and InteGeR FP7 Marie Curie Initial Training Networks contract (no. PITN-GA-2007-214902) to W.d.L., and the Israeli Science Foundation integrated technologies grant to A.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.J.G.v.d.W. designed, performed and analyzed experiments and wrote the manuscript; E.S. helped design experiments; G.L. helped design and analyze experiments and wrote the manuscript; P.K., S.J.B.H., B.A.M.B., M.J.A.M.V., Y.Ö. and C.V.-Q. performed experiments; M.H., R.C. and E.d.W. helped analyze experiments; and A.T. and W.d.L. designed experiments, supervised the project and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–15 and Supplementary Tables 1–4 (PDF 15411 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van de Werken, H., Landan, G., Holwerda, S. et al. Robust 4C-seq data analysis to screen for regulatory DNA interactions. Nat Methods 9, 969–972 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2173
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2173
This article is cited by
-
Revisiting characteristics of oncogenic extrachromosomal DNA as mobile enhancers on neuroblastoma and glioma cancers
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
CTCF blocks antisense transcription initiation at divergent promoters
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2022)
-
The zinc finger protein CLAMP promotes long-range chromatin interactions that mediate dosage compensation of the Drosophila male X-chromosome
Epigenetics & Chromatin (2021)
-
Extrachromosomal circular DNA: a new potential role in cancer progression
Journal of Translational Medicine (2021)
-
HOXBLINC long non-coding RNA activation promotes leukemogenesis in NPM1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia
Nature Communications (2021)