Abstract
Prosthetic heart valve (PHV) dysfunction is a rare, but potentially life-threatening, complication. In clinical practice, PHV dysfunction poses a diagnostic dilemma. Echocardiography and fluoroscopy are the imaging techniques of choice and are routinely used in daily practice. However, these techniques sometimes fail to determine the specific cause of PHV dysfunction, which is crucial to the selection of the appropriate treatment strategy. Multidetector-row CT (MDCT) can be of additional value in diagnosing the specific cause of PHV dysfunction and provides valuable complimentary information for surgical planning in case of reoperation. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) has limited value in the evaluation of biological PHV dysfunction. In this Review, we discuss the use of established imaging modalities for the detection of left-sided mechanical and biological PHV dysfunction and discuss the complementary role of MDCT in this context.
Key Points
-
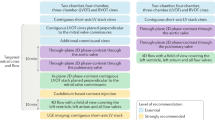
Echocardiography and fluoroscopy are the 'gold standard' for the evaluation of mechanical prosthetic heart valve (PHV) dysfunction
-
Echocardiography is the preferred imaging technique to assess biological PHV dysfunction.
-
Determining the exact cause of PHV dysfunction is essential for optimal patient treatment, but echocardiography and fluoroscopy sometimes fail to identify the exact cause of the PHV dysfunction
-
Multislice CT can complement echocardiography and fluoroscopy particularly in patients with mechanical heart valve obstruction and infective PHV endocarditis
-
Multislice CT can provide specific anatomical information assisting the cardiothoracic surgeon during the planning of reoperation
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yacoub, M. H. & Takkenberg, J. J. Will heart valve tissue engineering change the world? Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2, 60–61 (2005).
Cannegieter, S. C., Rosendaal, F. R. & Briet, E. Thromboembolic and bleeding complications in patients with mechanical heart valve prostheses. Circulation 89, 635–641 (1994).
Khan, S. Long-term outcomes with mechanical and tissue valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 11, S8–S14 (2002).
Grunkemeier, G. L., Li, H. H., Naftel, D. C., Starr, A. & Rahimtoola, S. H. Long-term performance of heart valve prostheses. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 25, 73–154 (2000).
Hammermeister, K. et al. Outcomes 15 years after valve replacement with a mechanical versus a bioprosthetic valve: final report of the Veterans Affairs randomized trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36, 1152–1158 (2000).
Akins, C. W. et al. Guidelines for reporting mortality and morbidity after cardiac valve interventions. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 135, 732–738 (2008).
Girard, S. E. et al. Reoperation for prosthetic aortic valve obstruction in the era of echocardiography: trends in diagnostic testing and comparison with surgical findings. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 37, 579–584 (2001).
Tsai, I. C. et al. Correctness of multi-detector-row computed tomography for diagnosing mechanical prosthetic heart valve disorders using operative findings as a gold standard. Eur. Radiol. 19, 857–867 (2009).
Teshima, H. et al. Usefulness of a multidetector-row computed tomography scanner for detecting pannus formation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 77, 523–526 (2004).
Symersky, P., Budde, R. P., de Mol, B. A. & Prokop, M. Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography to echocardiography and fluoroscopy for evaluation of patients with mechanical prosthetic valve obstruction. Am. J. Cardiol. 104, 1128–1134 (2009).
LaBounty, T. M. et al. Evaluation of mechanical heart valve size and function with ECG-gated 64-MDCT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 193, W389–W396 (2009).
Konen, E. et al. The role of ECG-gated MDCT in the evaluation of aortic and mitral mechanical valves: initial experience. Am. J. Roentgenol. 191, 26–31 (2008).
Feuchtner, G. M. et al. Multislice computed tomography in infective endocarditis: comparison with transesophageal echocardiography and intraoperative findings. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 53, 436–444 (2009).
Chenot, F. et al. Evaluation of anatomic valve opening and leaflet morphology in aortic valve bioprosthesis by using multidetector CT: comparison with transthoracic echocardiography. Radiology 255, 377–385 (2010).
Soulen, R. L., Budinger, T. F. & Higgins, C. B. Magnetic resonance imaging of prosthetic heart valves. Radiology 154, 705–707 (1985).
von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F., Rudolph, A., Wassmuth, R. & Schulz-Menger, J. Assessment of mitral bioprostheses using cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 12, 36 (2010).
von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F. et al. Feasibility of cardiovascular magnetic resonance to assess the orifice area of aortic bioprostheses. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2, 397–404 (2009).
Zoghbi, W. A. et al. Recommendations for evaluation of prosthetic valves with echocardiography and doppler ultrasound: a report From the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Task Force on Prosthetic Valves, developed in conjunction with the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Imaging Committee, Cardiac Imaging Committee of the American Heart Association, the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, the Japanese Society of Echocardiography and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography, endorsed by the American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association, European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, the Japanese Society of Echocardiography, and Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 22, 975–1014 (2009).
Feigenbaum, H., Armstrong, W. F., Thomas, R. in Feigenbaum's echocardiography (eds. Feigenbaum H., Armstrong W. F., Thomas R.) 11–21 (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2005).
Bitar, J. N., Lechin, M. E., Salazar, G. & Zoghbi, W. A. Doppler echocardiographic assessment with the continuity equation of St Jude Medical mechanical prostheses in the mitral valve position. Am. J. Cardiol. 76, 287–293 (1995).
van den Brink, R. B. Evaluation of prosthetic heart valves by transesophageal echocardiography: problems, pitfalls, and timing of echocardiography. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 10, 89–100 (2006).
Garcia, D. & Kadem, L. What do you mean by aortic valve area: geometric orifice area, effective orifice area, or gorlin area? J. Heart Valve Dis. 15, 601–608 (2006).
Steiner, R. M. et al. The radiology of cardiac valve prostheses. Radiographics 8, 277–298 (1988).
Chambers, J., Coppack, F., Deverall, P., Jackson, G. & Sowton, E. The continuity equation tested in a bileaflet aortic prosthesis. Int. J. Cardiol. 31, 149–154 (1991).
Keser, N. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation of normally functioning Sulzer Carbomedics prosthetic valves. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 29, 649–657 (2003).
Hage, F. G. & Nanda, N. C. Guidelines for the evaluation of prosthetic valves with echocardiography and Doppler ultrasound: value and limitations. Echocardiography 27, 91–93 (2010).
Singh, P. et al. Usefulness of live/real time three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography in evaluation of prosthetic valve function. Echocardiography 26, 1236–1249 (2009).
Feigenbaum, H., Armstrong, W. F., Thomas, R. in Feigenbaum's echocardiography (eds. Feigenbaum H., Armstrong W. F., Thomas R.) 59–61 (Lippincott Williams&Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2005).
Zabalgoitia, M. et al. Improvement in the diagnosis of bioprosthetic valve dysfunction by transesophageal echocardiography. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2, 595–603 (1993).
Daniel, L. B., Grigg, L. E., Weisel, R. D. & Rakowski, H. Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal assessment of prosthetic valve dysfunction. Echocardiography 7, 83–95 (1990).
Karalis, D. G. et al. Single-plane transesophageal echocardiography for assessing function of mechanical or bioprosthetic valves in the aortic valve position. Am. J. Cardiol. 69, 1310–1315 (1992).
Chaudhry, F. A., Herrera, C., DeFrino, P. F., Mehlman, D. J. & Zabalgoitia, M. Pathologic and angiographic correlations of transesophageal echocardiography in prosthetic heart valve dysfunction. Am. Heart J. 122, 1057–1064 (1991).
Cianciulli, T. E. et al. Cinefluoroscopic assessment of mechanical disc prostheses: its value as a complementary method to echocardiography. J. Heart Valve Dis. 14, 664–673 (2005).
Singh, P. et al. Live/real time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of mitral and aortic valve prosthetic paravalvular regurgitation. Echocardiography 26, 980–987 (2009).
Muratori, M. et al. Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of quantitative assessment of mechanical prostheses leaflet motion by transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography in suspected prosthetic valve dysfunction. Am. J. Cardiol. 97, 94–100 (2006).
Faletra, F. F., Alain, M. & Moccetti, T. Blockage of bileaflet mitral valve prosthesis imaged by computed tomography virtual endoscopy. Heart 93, 324 (2007).
Symersky, P., Budde, R. P., Prokop, M. & de Mol, B. A. Multidetector-row computed tomography imaging characteristics of mechanical prosthetic valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 20, 216–222 (2011).
Habets, J. et al. Prosthetic heart valve assessment with multidetector-row CT: imaging characteristics of 91 valves in 83 patients. Eur. Radiol. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2068–8.
Symersky, P., Budde, R. P., Prokop, M. & de Mol, B. A. Abstract 541: prosthetic valve evaluation using prospective triggering with 256-detector row computed tomography reduces radiation dose [abstract]. Circulation 120, S355 (2009).
Vahanian, A. et al. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease: the Task Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 28, 230–268 (2007).
Lin, S. S. et al. Prediction of thrombus-related mechanical prosthetic valve dysfunction using transesophageal echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 86, 1097–1101 (2000).
Licata, A. & Matthai, W. H. Jr Evaluating the etiology of mechanical valve obstruction: use of clinical parameters, fluoroscopy, and echocardiography. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 55, 495–500 (2002).
Teshima, H. et al. Obstruction of St Jude Medical valves in the aortic position: histology and immunohistochemistry of pannus. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 126, 401–407 (2003).
Deviri, E., Sareli, P., Wisenbaugh, T. & Cronje, S. L. Obstruction of mechanical heart valve prostheses: clinical aspects and surgical management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 17, 646–650 (1991).
Barbetseas, J. et al. Differentiating thrombus from pannus formation in obstructed mechanical prosthetic valves: an evaluation of clinical, transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic parameters. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 32, 1410–1417 (1998).
Guiar-Souto, P., Mirelis, J. G. & Silva-Melchor, L. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease. Eur. Heart J. 28, 1267–1268 (2007).
Vitale, N. et al. Obstruction of mechanical mitral prostheses: analysis of pathologic findings. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 63, 1101–1106 (1997).
Kondruweit, M. et al. Early failure of a mechanical bileaflet aortic valve prosthesis due to pannus: a rare complication. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 136, 213–214 (2008).
Daniel, W. G. et al. Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography for detection of abnormalities of prosthetic and bioprosthetic valves in the mitral and aortic positions. Am. J. Cardiol. 71, 210–215 (1993).
Montorsi, P., De, B. F., Muratori, M., Cavoretto, D. & Pepi, M. Role of cine-fluoroscopy, transthoracic, and transesophageal echocardiography in patients with suspected prosthetic heart valve thrombosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 85, 58–64 (2000).
Aoyagi, S. et al. Obstruction of St Jude medical valves in the aortic position: a consideration for pathogenic mechanism of prosthetic valve obstruction. Cardiovasc. Surg. 10, 339–344 (2002).
Chan, J. et al. Images in cardiovascular medicine. Cardiac CT assessment of prosthetic aortic valve dysfunction secondary to acute thrombosis and response to thrombolysis. Circulation 120, 1933–1934 (2009).
Bleiziffer, S. et al. Prediction of valve prosthesis-patient mismatch prior to aortic valve replacement: which is the best method? Heart 93, 615–620 (2007).
Urso, S., Sadaba, R. & Aldamiz-Echevarria, G. Is mismatch an independent risk factor for early and mid-term overall mortality in adult patients undergoing aortic valve replacement? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 9, 510–518 (2009).
Blais, C. et al. Impact of valve prosthesis-patient mismatch on short-term mortality after aortic valve replacement. Circulation 108, 983–988 (2003).
Pibarot, P. & Dumesnil, J. G. Hemodynamic and clinical impact of prosthesis-patient mismatch in the aortic valve position and its prevention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36, 1131–1141 (2000).
Tasca, G. et al. Impact of valve prosthesis-patient mismatch on left ventricular mass regression following aortic valve replacement. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 79, 505–510 (2005).
Pibarot, P. & Dumesnil, J. G. Prevention of valve prosthesis—patient mismatch before aortic valve replacement: does it matter and is it feasible? Heart 93, 549–551 (2007).
Pibarot, P. & Dumesnil, J. G. Prosthesis-patient mismatch in the mitral position: old concept, new evidences. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 133, 1405–1408 (2007).
Yazdanbakhsh, A. P., van den Brink, R. B., Dekker, E. & de Mol, B. A. Small valve area index: its influence on early mortality after mitral valve replacement. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 17, 222–227 (2000).
LaBounty, T. M. et al. Hemodynamic and functional assessment of mechanical aortic valves using combined echocardiography and multidetector computed tomography. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 3, 161–167 (2009).
Doddamani, S. et al. Demonstration of left ventricular outflow tract eccentricity by 64-slice multi-detector CT. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 25, 175–181 (2009).
Van den Brink, R. B. et al. Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal color Doppler flow imaging in patients with mechanical prostheses in the mitral valve position. Am. J. Cardiol. 63, 1471–1474 (1989).
Daniel, L. B., Grigg, L. E., Weisel, R. D. & Rakowski, H. Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal assessment of prosthetic valve dysfunction. Echocardiography 7, 83–95 (1990).
Bashore, T. M., Cabell, C. & Fowler, V. Jr Update on infective endocarditis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 31, 274–352 (2006).
Li, J. S. et al. Proposed modifications to the Duke criteria for the diagnosis of infective endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 30, 633–638 (2000).
Hanrath, P. Imaging techniques: transoesophageal echo-doppler in cardiology. Heart 86, 586–592 (2001).
Jacob, S. & Tong, A. T. Role of echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of infective endocarditis. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 17, 478–485 (2002).
Bonow, R. O. et al. 2008 focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to revise the 1998 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease). Endorsed by the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 52, e1–e142 (2008).
Daniel, W. G. et al. Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography for detection of abnormalities of prosthetic and bioprosthetic valves in the mitral and aortic positions. Am. J. Cardiol. 71, 210–215 (1993).
Meijboom, W. B. et al. Pre-operative computed tomography coronary angiography to detect significant coronary artery disease in patients referred for cardiac valve surgery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 48, 1658–1665 (2006).
Ro, T. K., Cotter, B. R., Simsir, S. A. & Karlsberg, R. P. Complicated ruptured sinus of Valsalva: cardiac computed tomographic angiography (64 slice) predicts surgical appearance and obviates need for invasive cardiac catheterization. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 9, 888–890 (2009).
Daniel, W. G. et al. Improvement in the diagnosis of abscesses associated with endocarditis by transesophageal echocardiography. N. Engl. J. Med. 324, 795–800 (1991).
Lerakis, S. et al. The role of transesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of patients with aortic perivalvular abscesses. Am. J. Med. Sci. 321, 152–155 (2001).
Leung, D. Y., Cranney, G. B., Hopkins, A. P. & Walsh, W. F. Role of transoesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of aortic root abscess. Br. Heart J. 72, 175–181 (1994).
Daniel, W. G. et al. Comparison of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography for detection of abnormalities of prosthetic and bioprosthetic valves in the mitral and aortic positions. Am. J. Cardiol. 71, 210–215 (1993).
Teoh, K. H. et al. Clinical and Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of bioprosthetic valve failure after 10 years. Circulation 82, IV110–IV116 (1990).
Chen, Y. T. et al. Detection of prosthetic mitral valve leak: a comparative study using transesophageal echocardiography, transthoracic echocardiography, and auscultation. J. Clin. Ultrasound 18, 557–561 (1990).
Mahesh, B., Angelini, G., Caputo, M., Jin, X. Y. & Bryan, A. Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 80, 1151–1158 (2005).
Effron, M. K. & Popp, R. L. Two-dimensional echocardiographic assessment of bioprosthetic valve dysfunction and infective endocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2, 597–606 (1983).
Kirzner, C. F. et al. Hemodynamic performance evaluation of small aortic ATS Medical valves by Doppler echocardiography. J. Heart Valve Dis. 6, 661–665 (1997).
Karpuz, H. et al. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of the new ATS medical prosthetic valve in the aortic position. Am. J. Card Imaging 10, 254–260 (1996).
De Paulis, R. et al. Doppler echocardiography evaluation of the CarboMedics valve in patients with small aortic anulus and valve prosthesis-body surface area mismatch. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 108, 57–62 (1994).
Chakraborty, B., Quek, S., Pin, D. Z., Siong, C. T. & Kheng, T. L. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of normally functioning Starr-Edwards, carbomedics and Carpentier-Edwards valves in aortic position. Angiology 47, 481–489 (1996).
Chambers, J., Cross, J., Deverall, P. & Sowton, E. Echocardiographic description of the CarboMedics bileaflet prosthetic heart valve. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 21, 398–405 (1993).
De Paulis, R. et al. Hemodynamic performances of small diameter carbomedics and St Jude valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 5, S339–S343 (1996).
Globits, S. et al. Doppler sonographic evaluation of the CarboMedics bileaflet valve prosthesis: one-year experience. J. Card Surg. 7, 9–16 (1992).
Ihlen, H. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation of the CarboMedics prosthetic heart valve in the aortic position: comparison of noninvasive and invasivse techniques. Am. Heart J. 123, 151–159 (1992).
Izzat, M. B., Birdi, I., Wilde, P., Bryan, A. J. & Angelini, G. D. Evaluation of the hemodynamic performance of small CarboMedics aortic prostheses using dobutamine-stress Doppler echocardiography. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 60, 1048–1052 (1995).
Gibbs, J. L., Wharton, G. A. & Williams, G. J. Doppler echocardiographic characteristics of the Carpentier-Edwards xenograft. Eur. Heart J. 7, 353–356 (1986).
Wiseth, R. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation by Doppler echocardiography of small (less than or equal to 21 mm) prostheses and bioprostheses in the aortic valve position. Am. J. Cardiol. 70, 240–246 (1992).
Gioia, G. & Rutsch, W. Normal echo-Doppler values in Duromedics valvular prostheses [Italian]. G. Ital. Cardiol. 18, 213–217 (1988).
Chambers, J. & Ely, J. L. Early postoperative echocardiographic hemodynamic performance of the On-X prosthetic heart valve: a multicenter study. J. Heart Valve Dis. 7, 569–573 (1998).
Noera, G. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation of the Carbomedics R, St Jude Medical HP and Sorin-Bicarbon valve in patients with small aortic annulus. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 11, 473–475 (1997).
Badano, L. et al. Normal echocardiographic characteristics of the Sorin Bicarbon bileaflet prosthetic heart valve in the mitral and aortic positions. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 10, 632–643 (1997).
Flameng, W. et al. Postoperative hemodynamics of two bileaflet heart valves in the aortic position. J. Heart Valve Dis. 6, 269–273 (1997).
Bech-Hanssen, O., Wallentin, I., Larsson, S. & Caidahl, K. Reference Doppler echocardiographic values for St Jude Medical, Omnicarbon, and Biocor prosthetic valves in the aortic position. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 11, 466–477 (1998).
Aris, A. et al. The 20 mm Medtronic Hall prosthesis in the small aortic root. J. Heart Valve Dis. 5, 459–462 (1996).
Henneke, K. H., Pongratz, G., Pohlmann, M. & Bachmann, K. Doppler echocardiographic determination of geometric orifice areas in mechanical aortic valve prostheses. Cardiology 86, 508–513 (1995).
Cooper, D. M. et al. Evaluation of normal prosthetic valve function by Doppler echocardiography. Am. Heart J. 114, 576–582 (1987).
Chafizadeh, E. R. & Zoghbi, W. A. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of the St Jude Medical prosthetic valve in the aortic position using the continuity equation. Circulation 83, 213–223 (1991).
Kadir, I. et al. Hemodynamics of St Jude Medical prostheses in the small aortic root: in vivo studies using dobutamine Doppler echocardiography. J. Heart Valve Dis. 6, 123–129 (1997).
Panidis, I. P., Ross, J. & Mintz, G. S. Normal and abnormal prosthetic valve function as assessed by Doppler echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 8, 317–326 (1986).
Perin, E. C., Jin, B. S., de Castro, C. M., Ferguson, J. J. & Hall, R. J. Doppler echocardiography in 180 normally functioning St Jude Medical aortic valve prostheses. Early and late postoperative assessments. Chest 100, 988–990 (1991).
Ren, J. F. et al. Effect of depressed left ventricular function on hemodynamics of normal St Jude Medical prosthesis in the aortic valve position. Am. J. Cardiol. 65, 1004–1009 (1990).
Carrel, T., Zingg, U., Jenni, R., Aeschbacher, B. & Turina, M. I. Early in vivo experience with the Hemodynamic Plus St Jude Medical heart valves in patients with narrowed aortic annulus. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 61, 1418–1422 (1996).
Laske, A. et al. Pressure gradients across bileaflet aortic valves by direct measurement and echocardiography. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 61, 48–57 (1996).
Kenny, A. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation of the Monostrut and spherical disc Bjork-Shiley aortic valve prosthesis with Doppler echocardiography. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 104, 1025–1028 (1992).
Sagar, K. B., Wann, L. S., Paulsen, W. H. & Romhilt, D. W. Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of Hancock and Bjork-Shiley prosthetic values. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 7, 681–687 (1986).
Gibbs, J. L., Wharton, G. A. & Williams, G. J. Doppler ultrasound of normally functioning mechanical mitral and aortic valve prostheses. Int. J. Cardiol. 18, 391–398 (1988).
Habib, G. et al. Contribution of Doppler echocardiography in the evaluation of normal and pathologic aortic valve prosthesis [abstract]. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 83, 937–945 (1990).
Mikhail, A. A hemodynamic comparison of Omniscience and Medtronic Hall aortic prostheses. J. Heart Valve Dis. 5, 675–677 (1996).
Raisaro, A. et al. Doppler evaluation of the Sorin and Medtronic-Hall prostheses in the aortic position [Italian]. G. Ital. Cardiol. 18, 206–212 (1988).
Badano, L. et al. Doppler haemodynamic assessment of clinically and echocardiographically normal mitral and aortic Allcarbon valve prostheses. Valve Prostheses Ligurian Cooperative Doppler Study. Eur. Heart J. 14, 1602–1609 (1993).
Soo, C. S. et al. Doppler-echocardiographic assessment of Carbomedics prosthetic values in the mitral position. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 7, 159–164 (1994).
Bjørnerheim, R., Ihlen, H., Simonsen, S., Sire, S. & Svennevig, J. Hemodynamic characterization of the CarboMedics mitral valve prosthesis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 6, 115–122 (1997).
Mohan, J. C., Agrawal, R., Arora, R. & Khalilullah, M. Improved Doppler assessment of the Bjork-Shiley mitral prosthesis using the continuity equation. Int. J. Cardiol. 43, 321–326 (1994).
Eriksson, M., Brodin, L. A., Ericsson, A. & Lindblom, D. Doppler-derived pressure differences in normally functioning aortic valve prostheses. Studies in Bjork-Shiley monostrut and Biocor porcine prostheses. Scand. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 27, 93–97 (1993).
Myken, P. S. et al. Long-term Doppler echocardiographic results of aortic or mitral valve replacement with Biocor porcine bioprosthesis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 116, 599–608 (1998).
Eriksson, M. J., Brodin, L. A., Dellgren, G. N. & Radegran, K. Rest and exercise hemodynamics of an extended stentless aortic bioprosthesis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 6, 653–660 (1997).
Gonzalez-Juanatey, J. R. et al. Hemodynamics of various designs of 19 mm pericardial aortic valve bioprosthesis. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 10, 201–206 (1996).
Gonzalez-Juanatey, J. R. et al. Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of the Bioflo pericardial bioprosthesis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2, 315–319 (1993).
Ramirez, M. L., Wong, M., Sadler, N. & Shah, P. M. Doppler evaluation of bioprosthetic and mechanical aortic valves: data from four models in 107 stable, ambulatory patients. Am. Heart J. 115, 418–425 (1988).
Habib, G. et al. Contribution of Doppler echocardiography in the evaluation of normal and pathologic aortic valve prosthesis [French]. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 83, 937–945 (1990).
Chakraborty, B., Quek, S., Pin, D. Z., Siong, C. T. & Kheng, T. L. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of normally functioning Starr-Edwards, carbomedics and Carpentier-Edwards valves in aortic position. Angiology 47, 481–489 (1996).
Bojar, R. M., Rastegar, H., Payne, D. D., Mack, C. A. & Schwartz, S. L. Clinical and hemodynamic performance of the 19-mm Carpentier-Edwards porcine bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 56, 1141–1147 (1993).
Gibbs, J. L., Wharton, G. A. & Williams, G. J. Doppler echocardiographic characteristics of the Carpentier-Edwards xenograft. Eur. Heart J 7, 353–356 (1986).
McDonald, M. L. et al. Hemodynamic performance of small aortic valve bioprostheses: is there a difference? Ann. Thorac. Surg. 63, 362–366 (1997).
Mullany, C. J., Schaff, H. V., Orszulak, T. A. & Miller, F. A. Early clinical and hemodynamic evaluation of the aortic intact porcine bioprosthesis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 3, 641–647 (1994).
Wiseth, R. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation by Doppler echocardiography of small (less than or equal to 21 mm) prostheses and bioprostheses in the aortic valve position. Am. J. Cardiol. 70, 240–246 (1992).
Cooper, D. M. et al. Evaluation of normal prosthetic valve function by Doppler echocardiography. Am. Heart J. 114, 576–582 (1987).
Lesbre, J. P. et al. Evaluation of new pericardial bioprostheses by pulsed and continuous Doppler ultrasound [French]. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 79, 1439–1448 (1986).
Sagar, K. B., Wann, L. S., Paulsen, W. H. & Romhilt, D. W. Doppler echocardiographic evaluation of Hancock and Bjork-Shiley prosthetic values. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 7, 681–687 (1986).
David, T. E., Armstrong, S. & Sun, Z. Clinical and hemodynamic assessment of the Hancock II bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 54, 661–667 (1992).
Eichinger, W. B. et al. The mosaic bioprosthesis in the aortic position: hemodynamic performance after 2 years. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 66, S126–S129 (1998).
Ius, P. et al. Hemodynamic evaluation of 23 mm Pericarbon and 23 mm Hancock II bioprostheses in the aortic position at mid-term follow up. J. Heart Valve Dis. 5, 656–661 (1996).
Bojar, R. M. et al. Clinical and hemodynamic performance of the Ionescu-Shiley valve in the small aortic root. Results in 117 patients with 17 and 19 mm valves. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 98, 1087–1095 (1989).
Simpson, I. A. et al. Non-invasive assessment by Doppler ultrasound of 155 patients with bioprosthetic valves: a comparison of the Wessex porcine, low profile Ionescu-Shiley, and Hancock pericardial bioprostheses. Br. Heart J. 56, 83–88 (1986).
Gonzalez-Juanatey, J. R. et al. The influence of the design on the medium to long-term hemodynamic behavior of 19 mm pericardial aortic valve prostheses. J. Heart Valve Dis. 5, S317–S323 (1996).
Bojar, R. M. et al. Clinical and hemodynamic performance of the Ionescu-Shiley valve in the small aortic root. Results in 117 patients with 17 and 19 mm valves. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 98, 1087–1095 (1989).
Cartier, P. C. et al. Clinical and hemodynamic performance of the Freestyle aortic root bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 67, 345–349 (1999).
Baur, L. H. et al. Echocardiographic parameters of the freestyle stentless bioprosthesis in aortic position: the European experience. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 12, 729–735 (1999).
Yun, K. L. et al. Prosthesis-patient mismatch: hemodynamic comparison of stented and stentless aortic valves. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 11, 98–102 (1999).
Dumesnil, J. G. et al. Hemodynamic features of the freestyle aortic bioprosthesis compared with stented bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 66, S130–S133 (1998).
Dagenais, F. et al. A single center experience with the freestyle bioprosthesis: midterm results at the Quebec Heart Institute. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 13, 156–162 (2001).
Yun, K. L. et al. Aortic valve replacement with the freestyle stentless bioprosthesis: five-year experience. Circulation 100, II17–II23 (1999).
Kappetein, A. P. et al. Outcome and follow-up of aortic valve replacement with the freestyle stentless bioprosthesis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 71, 601–607 (2001).
Baur, L. H. et al. Echocardiographic parameters of the freestyle stentless bioprosthesis in aortic position: the European experience. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 12, 729–735 (1999).
Del Rizzo, D. F. & Abdoh, A. Clinical and hemodynamic comparison of the Medtronic Freestyle and Toronto SPV stentless valves. J. Card. Surg. 13, 398–407 (1998).
Fries, R., Wendler, O., Schieffer, H. & Schafers, H. J. Comparative rest and exercise hemodynamics of 23-mm stentless versus 23-mm stented aortic bioprostheses. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 69, 817–822 (2000).
Jaffe, W. M. et al. Early follow-up of patients with the Medtronic Intact porcine valve. A new cardiac bioprosthesis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 98, 181–192 (1989).
Etienne, Y. et al. Evaluation of the normal bioprosthetic Intact aortic valve by Doppler echocardiography [French]. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 83, 2039–2044 (1990).
Ricou, F., Brun, A. & Lerch, R. Hemodynamic comparison of Medtronic intact bioprostheses and bileaflet mechanical prostheses in aortic position. Cardiology 87, 212–215 (1996).
Dumesnil, J. G., Honos, G. N., Lemieux, M. & Beauchemin, J. Validation and applications of indexed aortic prosthetic valve areas calculated by Doppler echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 16, 637–643 (1990).
Thomson, D. J. et al. Medtronic mosaic porcine bioprosthesis satisfactory early clinical performance. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 66, S122–S125 (1998).
Jamieson, W. R., Janusz, M. T., MacNab, J. & Henderson, C. Hemodynamic comparison of second- and third-generation stented bioprostheses in aortic valve replacement. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 71, S282–S284 (2001).
Eichinger, W. et al. The Mosaic bioprosthesis in the aortic position at five years. J. Heart Valve Dis. 9, 653–660 (2000).
Corbineau, H., Lelong, B., Langanay, T., Verhoye, J. P. & Leguerrier, A. Echocardiographic assessment and preliminary clinical results after aortic valve replacement with the Medtronic Mosaic bioprosthesis. J. Heart Valve Dis. 10, 171–176 (2001).
Fradet, G. J., Bleese, N., Burgess, J. & Cartier, P. C. Mosaic valve international clinical trial: early performance results. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 71, S273–S277 (2001).
Fradet, G. et al. The mosaic valve clinical performance at seven years: results from a multicenter prospective clinical trial. J. Heart Valve Dis. 13, 239–246 (2004).
Yun, K. L. et al. Prosthesis-patient mismatch: hemodynamic comparison of stented and stentless aortic valves. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 11, 98–102 (1999).
Wong, S. P. et al. Early experience with the mosaic bioprosthesis: a new generation porcine valve. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 69, 1846–1850 (2000).
Gansera, B. et al. The Mosaic bioprosthesis in the aortic position: seven years' results. J. Heart Valve Dis. 12, 354–361 (2003).
Nardi, C., Scioti, G., Milano, A. D., De, C. M. & Bortolotti, U. Hemodynamic assessment of the Medtronic Mosaic bioprosthesis in the aortic position. J. Heart Valve Dis. 10, 100–104 (2001).
Milano, A. D. et al. Hemodynamic performance of stented and stentless aortic bioprostheses. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 72, 33–38 (2001).
Eichinger, W. B. et al. Exercise hemodynamics of bovine versus porcine bioprostheses: a prospective randomized comparison of the mosaic and perimount aortic valves. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 129, 1056–1063 (2005).
Habib, G. et al. Contribution of Doppler echocardiography to the evaluation and monitoring of normal and pathologic mitral valve prostheses [French]. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 83, 469–477 (1990).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. A. Rijnbach (Department of Radiology, University Medical Center Utrecht) for her help with the final editing of the Figures and I. G. Janssen (Department of Multimedia Productions, University Medical Center Utrecht) for designing Figure 1b. This work was supported by a grant of the Netherlands Heart Foundation (grant number 2009B014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habets, J., Budde, R., Symersky, P. et al. Diagnostic evaluation of left-sided prosthetic heart valve dysfunction. Nat Rev Cardiol 8, 466–478 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2011.71
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2011.71
This article is cited by
-
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Analysis of the Flow Downstream of a Dysfunctional Bileaflet Mechanical Aortic Valve
Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology (2021)
-
Imaging infective endocarditis: Adherence to a diagnostic flowchart and direct comparison of imaging techniques
Journal of Nuclear Cardiology (2020)
-
Advanced CT acquisition protocol with a third-generation dual-source CT scanner and iterative reconstruction technique for comprehensive prosthetic heart valve assessment
European Radiology (2018)
-
Utility of cardiac computed tomography for evaluation of pannus in mechanical aortic valve
The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging (2015)
-
Echocardiographic assessment of prosthetic valves
Journal of Echocardiography (2015)