Abstract
Cancers of the oesophagus, gastro-oesophageal junction and stomach (upper gastrointestinal tract cancers; UGICs) pose a major health risk around the world. Collectively, the 5-year survival rate has remained <15%, and therapeutic improvements have been very slow and small. Novel molecules for early diagnosis, prognosis and therapy are, therefore, urgently needed. The role that microRNA (miRNA) molecules have in UGICs are worth pursuing to this end. miRNAs are small noncoding RNA molecules that regulate ∼60% of coding genes in humans and, therefore, are pivotal in mediating and regulating many physiologic processes. miRNAs are deregulated in many disease states, particularly in cancer, making them important targets. Here, we review the growing body of evidence regarding the alterations of miRNAs in UGICs. By suppressing translation and/or promoting degradation of mRNAs, miRNAs can contribute to carcinogenesis and progression of UGICs. In-depth studies of miRNAs in UGICs might yield novel insights and potential novel therapeutic strategies.
Key Points
-
Cancers of the oesophagus, gastro-oesophageal junction and stomach (UGICs) are common worldwide, and outcomes for patients with these cancers have remained dismal
-
miRNAs are noncoding, single-stranded RNAs ∼22 nucleotides in length; they comprise a novel class of gene regulators that negatively regulate their targets
-
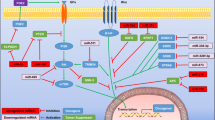
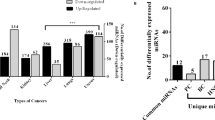
Many miRNA that act as oncogenes, tumour suppressors and important modulators in the process of invasion and metastasis of UGICs have been identified
-
Increased activity of oncogenic miRNAs leads to inhibition of tumour suppressor genes, facilitating cell proliferation and tumour progression; decreased activity of tumour-suppressor miRNAs leads to increased oncogene translation, contributing to tumour progression
-
Certain miRNAs are involved in the regulation of metastasis as well as in modulation of chemoresistance in UGICs
-
Circulating miRNAs provide potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis in patients with UGICs; further research could lead to exploitation of miRNAs as therapeutic or diagnostic targets for these cancers
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, L. M., Devesa, S. S. & Chow, W. H. Incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus among white Americans by sex, stage, and age. J. Natl Cancer Inst 100, 1184–1187 (2008).
Siegel, R., Naishadham, D. & Jemal, A Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 62, 10–29 (2012).
Jemal, A. et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 69–90 (2011).
Croce, C. M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 704–714 (2009).
Wu, W. K. K. et al. MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: a new player enters the game. Oncogene 29, 5761–5771 (2010).
Liu, C. et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat. Med. 17, 211–215 (2011).
Iorio, M. V. & Croce, C. M. microRNA involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis 33, 1126–1133 (2012).
Iorio, M. V. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol. Med. 4, 143–159 (2012)
Lewis, B. P., Burge, C. B. & Bartel, D. P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120, 15–20 (2005).
Calin, G. A. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 857–866 (2006).
Moretti, F., Thermann, R. & Hentze, M. W. Mechanism of translational regulation by miR-2 from sites in the 5′ untranslated region or the open reading frame. RNA 16, 2493–2502 (2010).
Eiring, A. M. et al. miR-328 functions as an RNA decoy to modulate hnRNP E2 regulation of mRNA translation in leukemic blasts. Cell 140, 652–665 (2010).
Garzon, R., Marcucci, G. & Croce, C. M. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 775–789 (2010).
Lopez-Camarillo, C. et al. MetastamiRs: non-coding microRNAs driving cancer invasion and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 1347–1379 (2012).
Hurst, D. R., Edmonds, M. D. & Welch, D. R. Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res. 69, 7495–7498 (2009).
Kota, J. et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 137, 1005–1017 (2009).
Haussecker, D. & Kay, M. A. miR-122 continues to blaze the trail for microRNA therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 18, 240–242 (2010).
Ichikawa, D., Komatsu, S., Konishi, H. & Otsuji, E. Circulating microRNA in digestive tract cancers. Gastroenterology 142, 1074–1078 (2012).
Valadi, H. et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 654–659 (2007).
Nana-Sinkam, P. & Croce, C. M. MicroRNAs in diagnosis and prognosis in cancer: what does the future hold? Pharmacogenomics 11, 667–669 (2010).
Song, J. H. & Meltzer, S. J. MicroRNAs in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of gastroesophageal cancers. Gastroenterology 143, 35–47 (2012).
Zhang, T. et al. MicroRNA-1322 regulates ECRG2 allele specifically and acts as a potential biomarker in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mc.21880
Kan, T. et al. The miR-106b-25 polycistron, activated by genomic amplification, functions as an oncogene by suppressing p21 and Bim. Gastroenterology 136, 1689–1700 (2009).
Luthra, R. et al. MicroRNA-196a targets annexin A1: a microRNA-mediated mechanism of annexin A1 downregulation in cancers. Oncogene 27, 6667–6678 (2008).
Maru, D. M. et al. MicroRNA-196a is a potential marker of progression during Barrett's metaplasia-dysplasia-invasive adenocarcinoma sequence in esophagus. Am. J. Pathol. 174, 1940–1948 (2009).
Fassan, M. et al. PDCD4 nuclear loss inversely correlates with miR-21 levels in colon carcinogenesis. Virchows Arch. 458, 413–419 (2011).
Mathe, E. A. et al. MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 6192–6200 (2009).
Fassan, M. et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in human Barrett's carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 129, 1661–1670 (2011).
Leidner, R. S. et al. The microRNAs, MiR-31 and MiR-375, as candidate markers in Barrett's esophageal carcinogenesis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 51, 473–479 (2012).
Smith, C. M. et al. miR-200 family expression is downregulated upon neoplastic progression of Barrett's esophagus. World J. Gastroenterol. 17, 1036–1044 (2011).
Feber, A. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 135, 255–260 (2008).
Luzna, P. et al. Changes of microRNAs-192, 196a and 203 correlate with Barrett's esophagus diagnosis and its progression compared to normal healthy individuals. Diagn. Pathol. 6, 114 (2011).
Wijnhoven, B. P. et al. MicroRNA profiling of Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 97, 853–861 (2010).
Yang, H. et al. MicroRNA expression signatures in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 5744–5752 (2009).
Akagi, I. et al. Relationship between altered expression levels of MIR21, MIR143, MIR145, and MIR205 and clinicopathologic features of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 24, 523–530 (2011).
Ma, W. J. et al. Role of microRNA-21 and effect on PTEN in Kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 38, 3253–3260 (2011).
Hiyoshi, Y. et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 1915–1922 (2009).
Xu, X. et al. MicroRNA-25 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 421, 640–645 (2012).
Chen, Z. L. et al. microRNA-92a promotes lymph node metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via E-cadherin. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 10725–10734 (2011).
Tian, Y. et al. MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 7986–7994 (2010).
Lee, K. H. et al. MicroRNA-373 (miR-373) post-transcriptionally regulates large tumor suppressor, homolog 2 (LATS2) and stimulates proliferation in human esophageal cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 2529–2538 (2009).
Kurashige, J. et al. Overexpression of microRNA-223 regulates the ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 106, 182–188 (2012).
Zhang, T. et al. The oncogenetic role of microRNA-31 as a potential biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 121, 437–447 (2011).
Hong, L. et al. The prognostic and chemotherapeutic value of miR-296 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 251, 1056–1063 (2010).
Ogawa, R. et al. Expression profiling of micro-RNAs in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using RT-PCR. Med. Mol. Morphol. 42, 102–109 (2009).
Liu, M. et al. TNF-alpha is a novel target of miR-19a. Int. J. Oncol. 38, 1013–1022 (2011).
Hamano, R. et al. Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 3029–3038 (2011).
Wu, Y. et al. A miR-200b/200c/429-binding site polymorphism in the 3′ untranslated region of the AP-2alpha gene is associated with cisplatin resistance. PLoS ONE 6, e29043 (2011).
Kong, K. L. et al. MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through repressing insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Gut 61, 33–42 (2012).
Komatsu, S. et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 105, 104–111 (2011).
Li, X., Lin, R. & Li, J. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-375 regulates PDK1 expression in esophageal cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 56, 2849–2856 (2011).
Suzuki, S. et al. CD47 expression regulated by the miR-133a tumor suppressor is a novel prognostic marker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 28, 465–472 (2012).
Kano, M. et al. miR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 127, 2804–2814 (2010).
Matsushima, K. et al. MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Transl. Med. 9, 30 (2011).
Matsushima, K., Isomoto, H., Kohno, S. & Nakao, K. MicroRNAs and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Digestion 82, 138–144 (2010).
Li, J. et al. Transcriptional activation of microRNA-34a by NF-kappa B in human esophageal cancer cells. BMC Mol. Biol. 13, 4 (2012).
Chen, X. et al. CpG island methylation status of miRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 130, 1607–1613 (2012).
Liu, Q. et al. Role of microRNA let-7 and effect to HMGA2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 39, 1239–1246 (2012).
Ding, D. P. et al. miR-29c induces cell cycle arrest in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating cyclin E expression. Carcinogenesis 32, 1025–1032 (2011).
Tsuchiya, S. et al. MicroRNA-210 regulates cancer cell proliferation through targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1). J. Biol. Chem. 286, 420–428 (2011).
Li, S. et al. miR-223 regulates migration and invasion by targeting Artemin in human esophageal carcinoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 18, 24 (2011).
Liu, R. et al. The cluster of miR-143 and miR-145 affects the risk for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through co-regulating fascin homolog 1. PLoS ONE 7, e33987 (2012).
Zhang, X. et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes gastric cancer by negatively regulating tumor suppressor KLF6. Tumour Biol. 33, 1589–1597 (2012).
Zhang, B. G. et al. microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol. Rep. 27, 1019–1026 (2012).
Cao, Z., Yoon, J. H., Nam, S. W., Lee, J. Y. & Park, W. S. PDCD4 expression inversely correlated with miR-21 levels in gastric cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 138, 611–619 (2012).
Yamanaka, S. et al. MicroRNA-21 inhibits Serpini1, a gene with novel tumour suppressive effects in gastric cancer. Dig. Liver Dis. 44, 589–596 (2012).
Tsai, K. W. et al. Aberrant expression of miR-196a in gastric cancers and correlation with recurrence. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 51, 394–401 (2012).
Tsai, K. W. et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-196b expression in gastric cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 49, 969–980 (2010).
Xiao, B. et al. Increased miR-146a in gastric cancer directly targets SMAD4 and is involved in modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 27, 559–566 (2012).
Shi, X., Su, S., Long, J., Mei, B. & Chen, Y. MicroRNA-191 targets N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 and promotes cell growth in human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 43, 849–856 (2011).
Lo, S. S. et al. Overexpression of miR-370 and downregulation of its novel target TGFbeta-RII contribute to the progression of gastric carcinoma. Oncogene 31, 226–237 (2012).
Otsubo, T. et al. MicroRNA-126 inhibits SOX2 expression and contributes to gastric carcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 6, e16617 (2011).
Chen, L., Jiang, M., Yuan, W. & Tang, H. Prognostic value of miR-93 overexpression in resectable gastric adenocarcinomas. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 75, 22–27 (2012).
Li, N. et al. Increased miR-222 in H. pylori-associated gastric cancer correlated with tumor progression by promoting cancer cell proliferation and targeting RECK. FEBS Lett. 586, 722–728 (2012).
Yi, C. et al. MiR-663, a microRNA targeting p21(WAF1/CIP1), promotes the proliferation and tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene 31, 4421–4433 (2012).
Ahn, S. M. et al. Smad3 regulates E-cadherin via miRNA-200 pathway. Oncogene 31, 3051–3059 (2012).
Wang, M. et al. Circulating miR-17-5p and miR-20a: molecular markers for gastric cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 5, 1514–1520 (2012).
Inoue, T., Iinuma, H., Ogawa, E., Inaba, T. & Fukushima, R. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of microRNA-107 and its relationship to DICER1 mRNA expression in gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 27, 1759–1764 (2012).
Chen, L. et al. MicroRNA-181b targets cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 in gastric adenocarcinomas. IUBMB Life 64, 628–635 (2012).
Kong, W. Q. et al. MicroRNA-182 targets cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 and suppresses cell growth in human gastric adenocarcinoma. FEBS J. 279, 1252–1260 (2012).
Carvalho, J. et al. Lack of microRNA-101 causes E-cadherin functional deregulation through EZH2 up-regulation in intestinal gastric cancer. J. Pathol. 228, 31–44 (2012).
Xia, J. et al. miR-124 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer through down-regulation of SPHK1. J. Pathol. 227, 470–480 (2012).
Li, C. et al. MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PHF10 in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 320, 189–197 (2012).
Sun, T., Wang, C., Xing, J. & Wu, D. miR-429 modulates the expression of c-myc in human gastric carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 2552–2559 (2011).
Vaira, V. et al. miR-296 regulation of a cell polarity-cell plasticity module controls tumor progression. Oncogene 31, 27–38 (2012).
Ding, L. et al. MiR-375 frequently downregulated in gastric cancer inhibits cell proliferation by targeting JAK2. Cell Res. 20, 784–793 (2010).
Tsukamoto, Y. et al. MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer Res. 70, 2339–2349 (2010).
Oh, H. K. et al. Genomic loss of miR-486 regulates tumor progression and the OLFM4 antiapoptotic factor in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 2657–2667 (2011).
Yang, Q. et al. Low-level expression of let-7a in gastric cancer and its involvement in tumorigenesis by targeting RAB40C. Carcinogenesis 32, 713–722 (2011).
Golestaneh, A. F. et al. miRNAs expressed differently in cancer stem cells and cancer cells of human gastric cancer cell line MKN-45. Cell Biochem. Funct. 30, 411–418 (2012).
Zhu, Y., Zhong, Z. & Liu, Z. Lentiviral vector-mediated upregulation of let-7a inhibits gastric carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 46, 53–59 (2011).
Chen, Q. et al. miR-137 is frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer and is a negative regulator of Cdc42. Dig. Dis. Sci. 56, 2009–2016 (2011).
Bou Kheir, T. et al. miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 10, 29 (2011).
Cui, Y. et al. MiR-29a inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest through the downregulation of p42.3 in human gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 6, e25872 (2011).
Kogo, R., Mimori, K., Tanaka, F., Komune, S. & Mori, M. Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 4277–4284 (2011).
Kim, K. et al. Epigenetic regulation of microRNA-10b and targeting of oncogenic MAPRE1 in gastric cancer. Epigenetics 6, 740–751 (2011).
Guo, X. B. et al. Down-regulation of miR-622 in gastric cancer promotes cellular invasion and tumor metastasis by targeting ING1 gene. World J. Gastroenterol. 17, 1895–1902 (2011).
Feng, L., Xie, Y., Zhang, H. & Wu, Y. miR-107 targets cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in gastric cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 29, 856–863 (2012).
Zhu, W. et al. miR-497 modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2. Med. Oncol. 29, 384–391 (2012).
Li, Z. et al. miR-495 and miR-551a inhibit the migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by directly interacting with PRL-3. Cancer Lett. 323, 41–47 (2012).
Zhu, W. et al. miR-200bc/429 cluster modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2 and XIAP. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 69, 723–731 (2012).
Kim, C. H. et al. miRNA signature associated with outcome of gastric cancer patients following chemotherapy. BMC Med. Genom. 4, 79 (2011).
Geiger, T. R. & Peeper, D. S. Metastasis mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1796, 293–308 (2009).
Feber, A. et al. MicroRNA prognostic signature for nodal metastases and survival in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 91, 1523–1530 (2011).
Liao, Y. L. et al. Transcriptional regulation of miR-196b by ETS2 in gastric cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 33, 760–769 (2012).
Liu, Z., Zhu, J., Cao, H., Ren, H. & Fang, X. miR-10b promotes cell invasion through RhoC-AKT signaling pathway by targeting HOXD10 in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 40, 1553–1560 (2012).
Zhang, Z., Liu, S., Shi, R. & Zhao, G. miR-27 promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204, 486–491 (2011).
Zhao, X. et al. MicroRNA-7 functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA in gastric cancer by targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncogene http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.156.
Gao, P. et al. The molecular mechanism of microRNA-145 to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer. Oncogene http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.61
Zheng, B. et al. MicroRNA-409 suppresses tumour cell invasion and metastasis by directly targeting radixin in gastric cancers. Oncogene http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.581
Xu, Y. et al. MicroRNA-335 acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and specificity protein 1. Oncogene 31, 1398–1407 (2012).
Zheng, B. et al. MicroRNA-148a suppresses tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 7574–7583 (2011).
Liang, S. et al. MicroRNA let-7f inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting MYH9 in human gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 6, e18409 (2011).
Hutvagner, G. & Zamore, P. D. A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 297, 2056–2060 (2002).
Hossain, A., Kuo, M. T. & Saunders, G. F. Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting translation of AIB1 mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 8191–8201 (2006).
Krutzfeldt, J. et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with 'antagomirs'. Nature 438, 685–689 (2005).
Pramanik, D. et al. Restitution of tumor suppressor microRNAs using a systemic nanovector inhibits pancreatic cancer growth in mice. Mol. Cancer Ther. 10, 1470–1480 (2011).
Ma, L. et al. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 341–347 (2010).
Seki, N. A commentary on MicroRNA-141 confers resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by targeting YAP1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 56, 339–340 (2011).
Hummel, R. et al. Chemotherapy-induced modification of microRNA expression in esophageal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 26, 1011–1017 (2011).
Hummel, R. et al. Mir-148a improves response to chemotherapy in sensitive and resistant oesophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 15, 429–438 (2011).
Song, M. Y. et al. Identification of serum microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 7, e33608 (2012).
Konishi, H. et al. Detection of gastric cancer-associated microRNAs on microRNA microarray comparing pre- and post-operative plasma. Br. J. Cancer 106, 740–747 (2012).
Liu, H. et al. Genome-wide microRNA profiles identify miR-378 as a serum biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 316, 196–203 (2012).
Liu, R. et al. A five-microRNA signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis. Eur. J. Cancer 47, 784–791 (2011).
Mori, Y. et al. MicroRNA-21 induces cell proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2, 235–239 (2009).
Zheng, Y. et al. MicroRNA-21 is a new marker of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. 10, 71–77 (2011).
Hashiguchi, Y. et al. Down-regulation of miR-125a-3p in human gastric cancer and its clinicopathological significance. Int. J. Oncol. 40, 1477–1482 (2012).
Yu, F. et al. let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131, 1109–1123 (2007).
Yu, F. et al. Mir-30 reduction maintains self-renewal and inhibits apoptosis in breast tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene 29, 4194–4204 (2010).
Godlewski, J. et al. Targeting of the Bmi-1 oncogene/stem cell renewal factor by microRNA-128 inhibits glioma proliferation and self-renewal. Cancer Res. 68, 9125–9130 (2008).
Ecker, J. R. et al. Genomics: ENCODE explained. Nature 489, 52–55 (2012).
Birney, E. The making of ENCODE: Lessons for big-data projects. Nature 489, 49–51 (2012).
Schadt, E. & Chang, R. Genetics. A GPS for navigating DNA. Science 337, 1179–1180 (2012).
Pennisi, E. Genomics. ENCODE project writes eulogy for junk DNA. Science 337, 1159–1161 (2012).
Yuan, Y. et al. MicroRNA-203 inhibits cell proliferation by repressing ΔNp63 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 11, 57 (2011).
Li, X. et al. miRNA-223 promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol. Cancer Res. 9, 824–833 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Dallas, Park, Smith, and Cantu family funds; the Kevin Fund; the Sultan Fund; the River Creek Foundation; and the Aaron and Martha Schecter Private Foundation. This work was also supported by the Multidisciplinary Research Program at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and by the National Institutes of Health through MD Anderson Cancer Center Support Grants CA016672 and CA138671 (J.Ajani).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to all aspects of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S., Ajani, J. The role of microRNAs in cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10, 109–118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.210
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.210
This article is cited by
-
Targeting non-coding RNAs to overcome cancer therapy resistance
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
Microarray profile analysis identifies ETS1 as potential biomarker regulated by miR-23b and modulates TCF4 in gastric cancer
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2021)
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0009172 suppresses gastric cancer by regulation of microRNA-485-3p-mediated NTRK3
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
Dysregulated miRNA in a cancer-prone environment: A study of gastric non-neoplastic mucosa
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
The role of hedgehog signaling in gastric cancer: molecular mechanisms, clinical potential, and perspective
Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)