Abstract
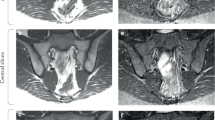
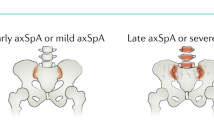
The diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is based on detection of characteristic inflammatory or structural changes (or a combination of both) in the spine and sacroiliac joints. Imaging of the axial skeleton is, therefore, useful for the identification of these pathological changes. Both inflammation (best detected by MRI) and bone formation (best visualized by conventional radiography) can predict the development of future structural changes. In addition, a high degree of spinal inflammation on MRI is predictive of a successful response to anti-TNF therapy. Emerging data indicate that the combination of acute and chronic changes on MRI has an important influence on progression of nonradiographic axSpA to ankylosing spondylitis. This Perspectives article provides an overview of the role of imaging in the diagnosis and management of axSpA, and also discusses open questions and future perspectives in this field.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudwaleit, M. et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 777–783 (2009).
Baraliakos, X. et al. Progression of radiographic damage in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: defining the central role of syndesmophytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 910–915 (2007).
Vander Cruyssen, B. et al. The epidemiology of ankylosing spondylitis and the commencement of anti-TNF therapy in daily rheumatology practice. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 1072–1077 (2007)
Bollow, M. et al. Quantitative analyses of sacroiliac biopsies in spondyloarthropathies: T cells and macrophages predominate in early and active sacroiliitis- cellularity correlates with the degree of enhancement detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 59, 135–140 (2000).
Francois, R. J., Neure, L., Sieper, J. & Braun, J. Immunohistological examination of open sacroiliac biopsies of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: detection of tumour necrosis factor {alpha} in two patients with early disease and transforming growth factor {beta} in three more advanced cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65, 713–720 (2006).
Baraliakos, X., Listing, J., Rudwaleit, M., Sieper, J. & Braun, J. The relationship between inflammation and new bone formation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 10, R104 (2008).
Rudwaleit, M., Listing, J., Brandt, J., Braun, J. & Sieper, J. Prediction of a major clinical response (BASDAI 50) to tumour necrosis factor alpha blockers in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63, 665–670 (2004).
van der Linden, S., Valkenburg, H. A. & Cats, A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 27, 361–368 (1984).
van Tubergen, A. et al. Radiographic assessment of sacroiliitis by radiologists and rheumatologists: does training improve quality? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 62, 519–525 (2003).
Kiltz, U. et al. Do patients with non-radiographic axial spondylarthritis differ from patients with ankylosing spondylitis? Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 64, 1415–1422 (2012).
Rudwaleit, M. et al. Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 1520–1527 (2009).
Weber, U. et al. Assessment of structural lesions in sacroiliac joints enhances diagnostic utility of MRI in early spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 62, 1763–1771 (2010).
Hermann, K. G. et al. Descriptions of spinal MRI lesions and definition of a positive MRI of the spine in axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI study group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 1278–1288 (2012).
Maksymowych, W. P. et al. Inflammatory lesions of the spine on magnetic resonance imaging predict the development of new syndesmophytes in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence of a relationship between inflammation and new bone formation. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 93–102 (2009).
van der Heijde, D. et al. MRI inflammation at the vertebral unit only marginally predicts new syndesmophyte formation: a multilevel analysis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 369–373 (2012).
Bennett, A. N. et al. Severity of baseline magnetic resonance imaging-evident sacroiliitis and HLA-B27 status in early inflammatory back pain predict radiographically evident ankylosing spondylitis at eight years. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 3413–3418 (2008).
Maksymowych, W. P., Morency, N., Conner-Spady, B. & Lambert, R. G. Suppression of inflammation and effects on new bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence for a window of opportunity in disease modification. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 23–28 (2012).
Baraliakos, X. et al. The relationship of inflammation, fatty degeneration and the effect of long-term TNF-blocker treatment on the development of new bone formation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 64, S338 (2012).
Baraliakos, X., Listing, J., von der Recke, A. & Braun, J. The natural course of radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis—evidence for major individual variations in a large proportion of patients. J. Rheumatol. 36, 997–1002 (2009).
Poddubnyy, D. et al. Rates and predictors of radiographic sacroiliitis progression over 2 years in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 1369–1374 (2011).
Baraliakos, X., Listing, J., von der Recke, A. & Braun, J. The natural course of radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis: differences between genders and appearance of characteristic radiographic features. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 13, 383–387 (2011).
Reveille, J. D. et al. for the Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium. Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 42, 123–127 (2010).
Pedersen, S. J. et al. ASDAS, BASDAI and different treatment responses and their relation to biomarkers of inflammation, cartilage and bone turnover in patients with axial spondyloarthritis treated with TNFα inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 1375–1381 (2011).
Braun, J. et al. 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 896–904 (2011).
Sieper, J. et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, 28-week trial of efficacy and safety of infliximab plus naproxen vs. naproxen alone in patients with early, active axial spondyloarthritis treated with a submaximal dose of NSAIDs: preliminary results of INFAST, Part 1. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71 (Suppl. 3), 247 (2012).
Jarrett, S. J. et al. MRI and clinical findings in patients with ankylosing spondylitis eligible for anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy after a short course of etoricoxib. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 68, 1466–1469 (2009).
Poddubnyy, D. et al. Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on radiographic spinal progression in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: results from the German Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 1616–1622 (2012).
Kroon, F., Landewe, R., Dougados, M. & van der Heijde, D. Continuous NSAID use reverts the effects of inflammation on radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 1623–1629 (2012).
van der Heijde, D. et al. 2010 Update of the international ASAS recommendations for the use of anti-TNF agents in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 905–908 (2011).
Braun, J. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 1126–1136 (2003).
Baraliakos, X., Davis, J., Tsuji, W. & Braun, J. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor α receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 52, 1216–1223 (2005).
Rudwaleit, M. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis before and during therapy with etanercept. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 1305–1310 (2005).
Baraliakos, X. et al. Radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 2 years of treatment with the tumour necrosis factor α antibody infliximab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64, 1462–1466 (2005).
van der Heijde, D. et al. Radiographic findings following two years of infliximab therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 3063–3070 (2008).
van der Heijde, D. et al. Radiographic progression of ankylosing spondylitis after up to two years of treatment with etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 1324–1331 (2008).
van der Heijde, D. et al. Assessment of radiographic progression in the spines of patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with adalimumab for up to 2 years. Arthritis Res. Ther. 11, R127 (2009).
Haibel, H. et al. Efficacy of adalimumab in the treatment of axial spondylarthritis without radiographically defined sacroiliitis: results of a twelve-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial followed by an open-label extension up to week fifty-two. Arthritis Rheum. 58, 1981–1991 (2008).
Barkham, N. et al. Clinical and imaging efficacy of infliximab in HLA-B27-Positive patients with magnetic resonance imaging-determined early sacroiliitis. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 946–954 (2009).
Vastesaeger, N. et al. Predicting the outcome of ankylosing spondylitis therapy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 973–981 (2011).
Rudwaleit, M. et al. MRI in predicting a major clinical response to anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 1276–1281 (2008).
Braun, J. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 1126–1136 (2003).
Machado, P. et al. MRI inflammation and its relation with measures of clinical disease activity and different treatment responses in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 2002–2005 (2012).
Machado, P. et al. Both structural damage and inflammation of the spine contribute to impairment of spinal mobility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 1465–1470 (2010).
Sieper, J. et al. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial (ABILITY-1). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72, 815–822 (2012).
Lubrano, E., D'Angelo, S., Spadaro, A., Palazzi, C. & Olivieri, I. Rehabilitation for ankylosing spondylitis in the era of biologics: any room left for this treatment? J. Rheumatol. 38, 1228–1230 (2011).
Braun, J., Bollow, M. & Sieper, J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 24, 697–735 (1998).
Gong, Y. et al. Ten years' experience with needle biopsy in the early diagnosis of sacroiliitis. Arthritis Rheum. 64, 1399–1406 (2012).
Heldmann, F. et al. The European ankylosing spondylitis infliximab cohort (EASIC): a European multicentre study of long term outcomes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with infliximab. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 29, 672–680 (2011).
Bruijnen, S. T. et al. Bone formation rather than inflammation reflects Ankylosing Spondylitis activity on PET-CT: a pilot study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 14, R71 (2012).
Appel, H. et al. Immunohistologic analysis of zygapophyseal joints in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2845–2851 (2006).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Christian Buchbender, MD, Prof. Benedict Ostendorf, MD, and Thorsten Poeppel, MD, for their cooperation in producing the PET-MRI images shown in this Perspectives.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X. Baraliakos and J. Braun both contributed equally to researching data, discussion of article content, writing and editing of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baraliakos, X., Braun, J. Opinion: Perspectives on imaging in axial spondyloarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 9, 498–502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2013.83
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2013.83
This article is cited by
-
Value-Based Healthcare in Rheumatology: Axial Spondyloarthritis and Beyond
Current Rheumatology Reports (2021)
-
Histographic analysis of oedema and fat in inflamed bone marrow based on quantitative MRI
European Radiology (2020)
-
Radiologic approach to axial spondyloarthritis: where are we now and where are we heading?
Rheumatology International (2018)
-
Andersson lesions of whole spine magnetic resonance imaging compared with plain radiography in ankylosing spondylitis
Rheumatology International (2016)
-
Magnetresonanztomographie in der Rheumatologie
Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie (2016)