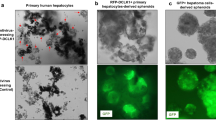
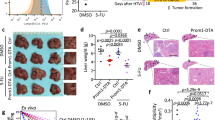
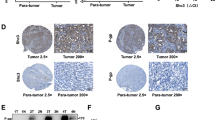
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, with few effective therapeutic options for advanced disease. At least 40% of HCCs are clonal, potentially arising from STAT3+, NANOG+ and OCT3/4+ liver progenitor/stem cell transformation, along with inactivation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling. Here we report significantly greater signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and tyrosine phosphorylated STAT3 in human HCC tissues (P<0.0030 and P<0.0455, respectively) than in human normal liver. Further, in HCC cells with loss of response to TGF-β, NSC 74859, a STAT3-specific inhibitor, markedly suppresses growth. In contrast, CD133+ status did not affect the response to STAT3 inhibition: both CD133+ Huh-7 cells and CD133– Huh-7 cells are equally sensitive to NSC 74859 treatment and STAT3 inhibition, with an IC50 of 100 μM. Thus, the TGF-β/beta2 spectrin (β2SP) pathway may reflect a more functional ‘stem/progenitor’ state than CD133. Furthermore, NSC 74859 treatment of Huh-7 xenografts in nude mice significantly retarded tumor growth, with an effective dose of only 5 mg/kg. Moreover, NSC 74859 inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in HCC cells in vivo. We conclude that inhibiting interleukin 6 (IL6)/STAT3 in HCCs with inactivation of the TGF-β/β2SP pathway is an effective approach in management of HCCs. Thus, IL6/STAT3, a major signaling pathway in HCC stem cell renewal and proliferation, can provide a novel approach to the treatment of specific HCCs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSC:
-
cancer stem cell
- β2SP:
-
embryonic liver fodrin
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- STAT3:
-
signal transduction and activator of transcription
- TGFBR1:
-
transforming growth factor-β receptor I
- TGFBR2:
-
transforming growth factor-β receptor II
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor-beta
References
Aaronson DS, Horvath CM . (2002). A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science 296: 1653–1655.
Alison MR . (2005). Liver stem cells: implications for hepatocarcinogenesis. Stem Cell Rev 1: 253–260.
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al. (2006). Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444: 756–760.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. (1999). Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98: 295–303.
Cabibbo A, Consalez GG, Sardella M, Sitia R, Rubartelli A . (1998). Changes in gene expression during the growth arrest of HepG2 hepatoma cells induced by reducing agents or TGFbeta1. Oncogene 16: 2935–2943.
Chung J, Uchida E, Grammer TC, Blenis J . (1997). STAT3 serine phosphorylation by ERK-dependent and -independent pathways negatively modulates its tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6508–6516.
Dando JS, Tavian M, Catelain C, Poirault S, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Sainteny F et al. (2005). Notch/Delta4 interaction in human embryonic liver CD34+ CD38− cells: positive influence on BFU-E production and LTC-IC potential maintenance. Stem Cells 23: 550–560.
Frank NY, Margaryan A, Huang Y, Schatton T, Waaga-Gasser AM, Gasser M et al. (2005). ABCB5-mediated doxorubicin transport and chemoresistance in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 65: 4320–4333.
Hambardzumyan D, Squatrito M, Holland EC . (2006). Radiation resistance and stem-like cells in brain tumors. Cancer Cell 10: 454–456.
Im YH, Kim HT, Kim IY, Factor VM, Hahm KB, Anzano M et al. (2001). Heterozygous mice for the transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor gene have increased susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 61: 6665–6668.
Investigators TCotLIPC (1998). A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology 28: 751–755.
Kanzler S, Meyer E, Lohse AW, Schirmacher P, Henninger J, Galle PR et al. (2001). Hepatocellular expression of a dominant-negative mutant TGF-beta type II receptor accelerates chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene 20: 5015–5024.
Kew MC, Dos Santos HA, Sherlock S . (1971). Diagnosis of primary cancer of the liver. Br Med J 4: 408–411.
Kitisin K, Ganesan N, Tang Y, Jogunoori W, Volpe EA, Kim SS et al. (2007). Disruption of transforming growth factor-beta signaling through beta-spectrin ELF leads to hepatocellular cancer through cyclin D1 activation. Oncogene 26: 7103–7110.
Kojima H, Sasaki T, Ishitani T, Iemura S, Zhao H, Kaneko S et al. (2005). STAT3 regulates Nemo-like kinase by mediating its interaction with IL-6-stimulated TGFbeta-activated kinase 1 for STAT3 Ser-727 phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 4524–4529.
Kopf M, Baumann H, Freer G, Freudenberg M, Lamers M, Kishimoto T et al. (1994). Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature 368: 339–342.
LaBarge MA, Bissell MJ . (2008). Is CD133 a marker of metastatic colon cancer stem cells? J Clin Invest 118: 2111–2120.
Lim CP, Cao X . (1999). Serine phosphorylation and negative regulation of Stat3 by JNK. J Biol Chem 274: 31055–31061.
Lim CP, Cao X . (2001). Regulation of Stat3 activation by MEK kinase 1. J Biol Chem 276: 21004–21011.
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H, Abdulkadir IR et al. (2006). Analysis of gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer 5: 67.
Ma S, Chan KW, Hu L, Lee TK, Wo JY, Ng IO et al. (2007). Identification and characterization of tumorigenic liver cancer stem/progenitor cells. Gastroenterology 132: 2542–2556.
Ma S, Lee TK, Zheng BJ, Chan KW, Guan XY . (2008). CD133+ HCC cancer stem cells confer chemoresistance by preferential expression of the Akt/PKB survival pathway. Oncogene 27: 1749–1758.
Massague J, Blain SW, Lo RS . (2000). TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell 103: 295–309.
Nguyen LN, Furuya MH, Wolfraim LA, Nguyen AP, Holdren MS, Campbell JS et al. (2007). Transforming growth factor-beta differentially regulates oval cell and hepatocyte proliferation. Hepatology 45: 31–41.
Ohkawara B, Shirakabe K, Hyodo-Miura J, Matsuo R, Ueno N, Matsumoto K et al. (2004). Role of the TAK1-NLK-STAT3 pathway in TGF-beta-mediated mesoderm induction. Genes Dev 18: 381–386.
Roskams T . (2006). Liver stem cells and their implication in hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma. Oncogene 25: 3818–3822.
Shmelkov SV, Butler JM, Hooper AT, Hormigo A, Kushner J, Milde T et al. (2008). CD133 expression is not restricted to stem cells, and both CD133+ and CD133− metastatic colon cancer cells initiate tumors. J Clin Invest 118: 2111–2120.
Sicklick JK, Li YX, Jayaraman A, Kannangai R, Qi Y, Vivekanandan P et al. (2006a). Dysregulation of the Hedgehog pathway in human hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 27: 748–757.
Sicklick JK, Li YX, Melhem A, Schmelzer E, Zdanowicz M, Huang J et al. (2006b). Hedgehog signaling maintains resident hepatic progenitors throughout life. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290: G859–G870.
Siddiquee K, Zhang S, Guida WC, Blaskovich MA, Greedy B, Lawrence HR et al. (2007). Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 7391–7396.
Suetsugu A, Nagaki M, Aoki H, Motohashi T, Kunisada T, Moriwaki H . (2006). Characterization of CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells as cancer stem/progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351: 820–824.
Tang B, Bottinger EP, Jakowlew SB, Bagnall KM, Mariano J, Anver MR et al. (1998). Transforming growth factor-beta1 is a new form of tumor suppressor with true haploid insufficiency. Nat Med 4: 802–807.
Tang Y, Katuri V, Dillner A, Mishra B, Deng CX, Mishra L . (2003). Disruption of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in ELF beta-spectrin-deficient mice. Science 299: 574–577.
Tang Y, Kitisin K, Jogunoori W, Li C, Deng CX, Mueller SC et al. (2008). Progenitor/stem cells give rise to liver cancer due to aberrant TGF-beta and IL-6 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 2445–2450.
Turkson J, Ryan D, Kim JS, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Haura E et al. (2001). Phosphotyrosyl peptides block Stat3-mediated DNA binding activity, gene regulation, and cell transformation. J Biol Chem 276: 45443–45455.
Vistica DT, Skehan P, Scudiero D, Monks A, Pittman A, Boyd MR . (1991). Tetrazolium-based assays for cellular viability: a critical examination of selected parameters affecting formazan production. Cancer Res 51: 2515–2520.
Wallner L, Dai J, Escara-Wilke J, Zhang J, Yao Z, Lu Y et al. (2006). Inhibition of interleukin-6 with CNTO328, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, inhibits conversion of androgen-dependent prostate cancer to an androgen-independent phenotype in orchiectomized mice. Cancer Res 66: 3087–3095.
Weinstein M, Yang X, Deng C . (2000). Functions of mammalian Smad genes as revealed by targeted gene disruption in mice. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 11: 49–58.
Wen Z, Zhong Z, Darnell Jr JE . (1995). Maximal activation of transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 requires both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation. Cell 82: 241–250.
Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, Zhang W, Roayaie S, Schwartz M et al. (2007). Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 45: 938–947.
Yang SF, Wang SN, Wu CF, Yeh YT, Chai CY, Chunag SC et al. (2007). Altered p-STAT3 (tyr705) expression is associated with histological grading and intratumour microvessel density in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 60: 642–648.
Yeoh GC, Ernst M, Rose-John S, Akhurst B, Payne C, Long S et al. (2007). Opposing roles of gp130-mediated STAT-3 and ERK-1/2 signaling in liver progenitor cell migration and proliferation. Hepatology 45: 486–494.
Yin S, Li J, Hu C, Chen X, Yao M, Yan M et al. (2007). CD133 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells possess high capacity for tumorigenicity. Int J Cancer 120: 1444–1450.
Zender L, Spector MS, Xue W, Flemming P, Cordon-Cardo C, Silke J et al. (2006). Identification and validation of oncogenes in liver cancer using an integrative oncogenomic approach. Cell 125: 1253–1267.
Zhou J, Wulfkuhle J, Zhang H, Gu P, Yang Y, Deng J et al. (2007). Activation of the PTEN/mTOR/STAT3 pathway in breast cancer stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 16158–16163.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr Said M Sebti for helpful discussions on the use of NSC 74859; Dr Joseph Cory for critical review and helpful suggestions with the manuscript; Tiffany Blake, Ed Flores, E Volpe and Sandra Acheampong for excellent technical expertise and manuscript preparation; Mr Carlos Benitez for xenograft production and injection of drugs; and Dr Richard Amdur for statistical analysis. Grant support was provided by NIH R01 CA106614A (LM), NIH R01 DK56111 (LM), NIH R01 CA4285718A (LM), VA Merit Award (LM) (Bao et al.), R Robert and Sally D Funderburg Research Scholar (LM), B Orr Foundation (LM), and NIH P30 CA51008-13 (transgenic shared resource; Cancer Center Support Grant).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Amin, R., Gallicano, G. et al. The STAT3 inhibitor NSC 74859 is effective in hepatocellular cancers with disrupted TGF-β signaling. Oncogene 28, 961–972 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.448
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.448
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serine 727 phosphorylation is necessary to induce the STAT3-mediated transcription of LINC00184 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2022)
-
Liver regeneration and inflammation: from fundamental science to clinical applications
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2021)
-
miR-486 is involved in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia by regulating JAK-STAT signaling
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2021)
-
A positive feedback loop between Periostin and TGFβ1 induces and maintains the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via AP-2α activation
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Down-regulated lncRNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits tumorigenesis through STAT3 signaling pathway by suppressing CADM1 promoter methylation in liver cancer stem cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)