Abstract
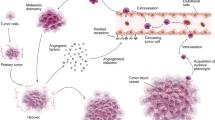
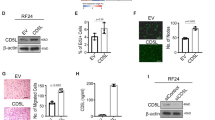
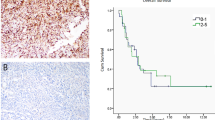
Dysregulation of Axl and its ligand growth arrest-specific 6 is implicated in the pathogenesis of several human cancers. In this study, we have used RNAi and monoclonal antibodies to assess further the oncogenic potential of Axl. Here we show that Axl knockdown reduces growth of lung and breast cancer xenograft tumors. Inhibition of Axl expression attenuates breast cancer cell migration and inhibits metastasis to the lung in an orthotopic model, providing the first in vivo evidence that links Axl directly to cancer metastasis. Axl knockdown in endothelial cells impaired tube formation and this effect was additive with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Further analysis demonstrated that Axl regulates endothelial cell functions by modulation of signaling through angiopoietin/Tie2 and Dickkopf (DKK3) pathways. We have developed and characterized Axl monoclonal antibodies that attenuate non-small cell lung carcinoma xenograft growth by downregulation of receptor expression, reducing tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Our data demonstrate that Axl plays multiple roles in tumorigenesis and that therapeutic antibodies against Axl may block Axl functions not only in malignant tumor cells but also in the tumor stroma. The additive effect of Axl inhibition with anti-VEGF suggests that blocking Axl function could be an effective approach for enhancing antiangiogenic therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelillo-Scherrer A, Burnier L, Lambrechts D, Fish RJ, Tjwa M, Plaisance S et al. (2008). Role of Gas6 in erythropoiesis and anemia in mice. J Clin Invest 118: 583–596.
Angelillo-Scherrer A, de Frutos P, Aparicio C, Melis E, Savi P, Lupu F et al. (2001). Deficiency or inhibition of Gas6 causes platelet dysfunction and protects mice against thrombosis. Nat Med 7: 215–221.
Berclaz G, Altermatt HJ, Rohrbach V, Kieffer I, Dreher E, Andres AC . (2001). Estrogen dependent expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in normal and malignant human breast. Ann Oncol 12: 819–824.
Budagian V, Bulanova E, Orinska Z, Duitman E, Brandt K, Ludwig A et al. (2005a). Soluble Axl is generated by ADAM10-dependent cleavage and associates with Gas6 in mouse serum. Mol Cell Biol 25: 9324–9339.
Budagian V, Bulanova E, Orinska Z, Thon L, Mamat U, Bellosta P et al. (2005b). A promiscuous liaison between IL-15 receptor and Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in cell death control. EMBO J 24: 4260–4270.
Cao WM, Murao K, Imachi H, Sato M, Nakano T, Kodama T et al. (2001). Phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase-Akt/protein kinase B pathway mediates Gas6 induction of scavenger receptor a in immortalized human vascular smooth muscle cell line. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21: 1592–1597.
Caraux A, Lu Q, Fernandez N, Riou S, Di Santo JP, Raulet DH et al. (2006). Natural killer cell differentiation driven by Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinases. Nat Immunol 7: 747–754.
Christofori G . (2006). New signals from the invasive front. Nature 441: 444–450.
Chung BI, Malkowicz SB, Nguyen TB, Libertino JA, McGarvey TW . (2003). Expression of the proto-oncogene Axl in renal cell carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol 22: 533–540.
Craven RJ, Xu LH, Weiner TM, Fridell YW, Dent GA, Srivastava S et al. (1995). Receptor tyrosine kinases expressed in metastatic colon cancer. Int J Cancer 60: 791–797.
D'Arcangelo D, Ambrosino V, Giannuzzo M, Gaetano C, Capogrossi MC . (2006). Axl receptor activation mediates laminar shear stress anti-apoptotic effects in human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 71: 754–763.
Dumont DJ, Gradwohl G, Fong GH, Puri MC, Gertsenstein M, Auerbach A et al. (1994). Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev 8: 1897–1909.
Gould WR, Baxi SM, Schroeder R, Peng YW, Leadley RJ, Peterson JT et al. (2005). Gas6 receptors Axl, Sky and Mer enhance platelet activation and regulate thrombotic responses. J Thromb Haemost 3: 733–741.
Hafizi S, Dahlbäck B . (2006). Signaling and functional diversity within the Axl subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 295–304.
Hasanbasic I, Rajotte I, Blostein M . (2005). The role of gamma-carboxylation in the anti-apoptotic function of gas6. J Thromb Haemost 3: 2790–2797.
Holland SJ, Powell MJ, Franci C, Chan EW, Friera AM, Atchison RE et al. (2005). Multiple roles for the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in tumor formation. Cancer Res 65: 9294–9303.
Hong CC, Lay JD, Huang JS, Cheng AL, Tang JL, Lin MT et al. (2008). Receptor tyrosine kinase AXL is induced by chemotherapy drugs and overexpression of AXL confers drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Lett 268: 314–324.
Hutterer M, Knyazev P, Abate A, Reschke M, Maier H, Stefanova N et al. (2008). Axl and growth arrest-specific gene 6 are frequently overexpressed in human gliomas and predict poor prognosis in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 14: 130–138.
Ito T, Ito M, Naito S, Ohtsuru A, Nagayama Y, Kanematsu T et al. (1999). Expression of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in human thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 9: 563–567.
Janssen JW, Schulz AS, Steenvoorden AC, Schmidberger M, Strehl S, Ambros PF et al. (1991). A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor with oncogenic potential. Oncogene 6: 2113–2120.
Katagiri M, Hakeda Y, Chikazu D, Ogasawara T, Takato T, Kumegawa M et al. (2001). Mechanism of stimulation of osteoclastic bone resorption through Gas6/Tyro 3, a receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, in mouse osteoclasts. J Biol Chem 276: 7376–7382.
Keating AK, Salzberg DB, Sather S, Liang X, Nickoloff S, Anwar A et al. (2006). Lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma in mice overexpressing the Mer (MerTK) receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 25: 6092–6100.
Korshunov VA, Daul M, Massett MP, Berk BC . (2007). Axl mediates vascular remodeling induced by deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertension. Hypertension 50: 1057–1062.
Korshunov VA, Mohan AM, Georger MA, Berk BC . (2006). Axl, a receptor tyrosine kinase, mediates flow-induced vascular remodeling. Circ Res 98: 1446–1452.
Krupnik VE, Sharp JD, Jiang C, Robison K, Chickering TW, Amaravadi L et al. (1999). Functional and structural diversity of the human Dickkopf gene family. Gene 238: 301–313.
Lai C, Lemke G . (1991). An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron 6: 691–704.
Lemke G, Rothlin CV . (2008). Immunobiology of the TAM receptors. Nat Rev Immunol 8: 327–336.
Lu Q, Gore M, Zhang Q, Camenisch T, Boast S, Casagranda F et al. (1999). Tyro-3 family receptors are essential regulators of mammalian spermatogenesis. Nature 398: 723–728.
Mahadevan D, Cooke L, Riley C, Swart R, Simons B, Della Croce K et al. (2007). A novel tyrosine kinase switch is a mechanism of imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene 26: 3909–3919.
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C et al. (1997). Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277: 55–60.
Melaragno MG, Fridell YW, Berk BC . (1999). The Gas6/Axl system: a novel regulator of vascular cell function. Trends Cardiovasc Med 9: 250–253.
Meric F, Lee WP, Sahin A, Zhang H, Kung HJ, Hung MC . (2002). Expression profile of tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8: 361–367.
Monaghan AP, Kioschis P, Wu W, Zuniga A, Bock D, Poustka A et al. (1999). Dickkopf genes are co-ordinately expressed in mesodermal lineages. Mech Dev 87: 45–56.
O'Bryan JP, Frye RA, Cogswell PC, Neubauer A, Kitch B, Prokop C et al. (1991). axl, a transforming gene isolated from primary human myeloid leukemia cells, encodes a novel receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 11: 5016–5031.
Peters KG, Kontos CD, Lin PC, Wong AL, Rao P, Huang L et al. (2004). Functional significance of Tie2 signaling in the adult vasculature. Recent Prog Horm Res 59: 51–71.
Prasad D, Rothlin CV, Burrola P, Burstyn-Cohen T, Lu Q, Garcia de Frutos P et al. (2006). TAM receptor function in the retinal pigment epithelium. Mol Cell Neurosci 33: 96–108.
Rothlin CV, Ghosh S, Zuniga EI, Oldstone MB, Lemke G . (2007). TAM receptors are pleiotropic inhibitors of the innate immune response. Cell 131: 1124–1136.
Sainaghi PP, Castello L, Bergamasco L, Galletti M, Bellosta P, Avanzi GC . (2005). Gas6 induces proliferation in prostate carcinoma cell lines expressing the Axl receptor. J Cell Physiol 204: 36–44.
Sasaki T, Knyazev PG, Clout NJ, Cheburkin Y, Göhring W, Ullrich A et al. (2006). Structural basis for Gas6-Axl signalling. EMBO J 25: 80–87.
Shankar SL, O'Guin K, Kim M, Varnum B, Lemke G, Brosnan CF et al. (2006). Gas6/Axl signaling activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt1 survival pathway to protect oligodendrocytes from tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. J Neurosci 26: 5638–5648.
Sharif MN, Sosic D, Rothlin CV, Kelly E, Lemke G, Olson EN et al. (2006). Twist mediates suppression of inflammation by type I IFNs and Axl. J Exp Med 203: 1891–1901.
Shieh YS, Lai CY, Kao YR, Shiah SG, Chu YW, Lee HS et al. (2005). Expression of axl in lung adenocarcinoma and correlation with tumor progression. Neoplasia 7: 1058–1064.
Stitt TN, Conn G, Gore M, Lai C, Bruno J, Radziejewski C et al. (1995). The anticoagulation factor protein S and its relative, Gas6, are ligands for the Tyro 3/Axl family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 80: 661–670.
Sun W, Fujimoto J, Tamaya T . (2004). Coexpression of Gas6/Axl in human ovarian cancers. Oncology 66: 450–457.
Suri C, McClain J, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Zhou H, Oldmixon EH et al. (1998). Increased vascularization in mice overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science 282: 468–471.
Tai KY, Shieh YS, Lee CS, Shiah SG, Wu CW . (2008). Axl promotes cell invasion by inducing MMP-9 activity through activation of NF-kappaB and Brg-1. Oncogene 27: 4044–4055.
Untergasser G, Steurer M, Zimmermann M, Hermann M, Kern J, Amberger A et al. (2008). The Dickkopf-homolog 3 is expressed in tumor endothelial cells and supports capillary formation. Int J Cancer 122: 1539–1547.
Vajkoczy P, Knyazev P, Kunkel A, Capelle HH, Behrndt S, von Tengg-Kobligk H et al. (2006). Dominant-negative inhibition of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses brain tumor cell growth and invasion and prolongs survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 5799–5804.
Varnum BC, Young C, Elliott G, Garcia A, Bartley TD, Fridell YW et al. (1995). Axl receptor tyrosine kinase stimulated by the vitamin K-dependent protein encoded by growth-arrest-specific gene 6. Nature 373: 623–626.
Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW, Lai CH, Huang CL, Lo SS et al. (2002). Clinical significance of AXL kinase family in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 22: 1071–1078.
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J . (2000). Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 407: 242–248.
Zhang YX, Knyazev PG, Cheburkin YV, Sharma K, Knyazev YP, Orfi L et al. (2008). AXL is a potential target for therapeutic intervention in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 68: 1905–1915.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Avi Ashkenazi and Dr Jing Qing for reading the article and providing helpful suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Ye, X., Tan, C. et al. Axl as a potential therapeutic target in cancer: role of Axl in tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis. Oncogene 28, 3442–3455 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.212
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.212
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
AXL is required for hypoxia-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha function in glioblastoma
Toxicological Research (2023)
-
AXL Inhibitors: Status of Clinical Development
Current Oncology Reports (2023)
-
AXL, along with PROS1, is overexpressed in papillary thyroid carcinoma and regulates its biological behaviour
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2022)
-
Epstein–Barr virus miR-BART4-3p regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and migration by targeting AXL in gastric carcinoma
Virus Genes (2022)
-
DNA repair pathways and their roles in drug resistance for lung adenocarcinoma
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)