Abstract
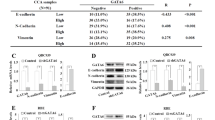
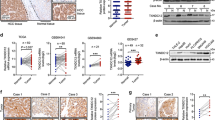
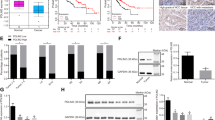
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is implicated in hepatocarcinogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis. HAb18G/CD147, which belongs to the CD147 family, is an HCC-associated antigen that has a crucial role in tumor invasion and metastasis. The goal of this study was to investigate the role of HAb18G/CD147 during EMT in hepatocarcinogenesis. Human normal hepatic cell lines QZG and L02, primary mouse hepatocytes and nude mouse models were used to determine the role of HAb18G/CD147 in EMT, and the involvement of the TGF-β-driven pathway. A dual-luciferase reporter assay and ChIP were used to investigate the transcriptional regulation of the CD147 gene. Samples from patients with liver disease were assessed to determine the relationship between HAb18G/CD147 and typical markers for EMT. Our results show that upregulation of HAb18G/CD147 is induced by TGF-β coupled with downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of N-cadherin and vimentin. The expression of HAb18G/CD147 is controlled by the cell survival PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway, and is directly regulated by the transcription factor Slug. Transfection of CD147 also induces an elevated expression of TGF-β. CD147-transfected hepatocytes have mesenchymal phenotypes that accelerate tumor formation and tumor metastasis in vivo. Immunohistochemistry analysis shows a negative correlation between HAb18G/CD147 and E-cadherin expression (rs=−0.3622, P=0.0105), and a positive correlation between HAb18G/CD147 and Slug expression (rs=0.3064, P=0.0323) in human HCC tissues. Our study uncovers a novel role of HAb18G/CD147 in mediating EMT in the process of HCC progression and showed that CD147 is a Slug target gene in the signaling cascade TGF-β→PI3K/Akt→GSK3β→Snail→Slug→CD147. Our results suggest that CD147 may be a potential target for the treatment and prevention of HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses HL, Arteaga CL . (2000). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem 275: 36803–36810.
Battaglia S, Benzoubir N, Nobilet S, Charneau P, Samuel D, Zignego AL et al. (2009). Liver cancer-derived hepatitis C virus core proteins shift TGF-beta responses from tumor suppression to epithelial–mesenchymal transition. PLoS One 4: e4355.
Bedossa P, Peltier E, Terris B, Franco D, Poynard T . (1995). Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and TGF-beta 1 receptors in normal, cirrhotic, and neoplastic human livers. Hepatology 21: 760–766.
Belton Jr RJ, Chen L, Mesquita FS, Nowak RA . (2008). Basigin-2 is a cell surface receptor for soluble basigin ligand. J Biol Chem 283: 17805–17814.
Chen ZN, Mi L, Xu J, Song F, Zhang Q, Zhang Z et al. (2006). Targeting radioimmunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma with iodine ((131)I) metuximab injection: clinical phase I/II trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65: 435–444.
Elsharkawy AM, Mann DA . (2007). Nuclear factor-kappaB and the hepatic inflammation–fibrosis–cancer axis. Hepatology 46: 590–597.
Fransvea E, Angelotti U, Antonaci S, Giannelli G . (2008). Blocking transforming growth factor-beta upregulates E-cadherin and reduces migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 47: 1557–1566.
Gabison EE, Mourah S, Steinfels E, Yan L, Hoang-Xuan T, Watsky MA et al. (2005). Differential expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) in normal and ulcerated corneas: role in epithelio-stromal interactions and matrix metalloproteinase induction. Am J Pathol 166: 209–219.
Giannelli G, Bergamini C, Fransvea E, Sgarra C, Antonaci S . (2005). Laminin-5 with transforming growth factor-beta1 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 129: 1375–1383.
Gou X, Ru Q, Zhang H, Chen Y, Li L, Yang H et al. (2009). HAb18G/CD147 inhibits starvation-induced autophagy in human hepatoma cell SMMC7721 with an involvement of Beclin 1 downregulation. Cancer Sci 100: 837–843.
Huet E, Vallée B, Szul D, Verrecchia F, Mourah S, Jester JV et al. (2008). Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer/CD147 promotes myofibroblast differentiation by inducing alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and collagen gel contraction: implications in tissue remodeling. FASEB J 22: 1144–1154.
Iacono KT, Brown AL, Greene MI, Saouaf SJ . (2007). CD147 immunoglobulin superfamily receptor function and role in pathology. Exp Mol Pathol 83: 283–295.
Jiang JL, Zhou Q, Yu MK, Ho LS, Chen ZN, Chan HC . (2001). The involvement of HAb18G/CD147 in regulation of store-operated calcium entry and metastasis of human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 276: 46870–46877.
Labbé E, Lock L, Letamendia A, Gorska AE, Gryfe R, Gallinger S et al. (2007). Transcriptional cooperation between the transforming growth factor-beta and Wnt pathways in mammary and intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 67: 75–84.
Matsuzaki K . (2009). Modulation of TGF-beta signaling during progression of chronic liver diseases. Front Biosci 14: 2923–2934.
Murata M, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, Sekimoto G, Tahashi Y, Mori S et al. (2009). Hepatitis B virus X protein shifts human hepatic transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling from tumor suppression to oncogenesis in early chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 49: 1203–1217.
Li Y, Xu J, Chen L, Zhong WD, Zhang Z, Mi L et al. (2009). HAb18G (CD147), a cancer-associated biomarker and its role in cancer detection. Histopathology 54: 677–687.
Liu F, Cui L, Zhang Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Fan Y et al. (2010). Expression of HAb18G is associated with tumor progression and prognosis of breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124: 677–688.
Nitta T, Kim JS, Mohuczy D, Behrns KE . (2008). Murine cirrhosis induces hepatocyte epithelial mesenchymal transition and alterations in survival signaling pathways. Hepatology 48: 909–919.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A . (2007). Snail1, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7: 415–428.
Sidhu SS, Nawroth R, Retz M, Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Dasari V, Basbaum C . (2010). EMMPRIN regulates the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, a potential role in accelerating lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 29: 4145–4156.
Song BC, Chung YH, Kim JA, Choi WB, Suh DD, Pyo SI et al. (2002). Transforming growth factor-beta1 as a useful serologic marker of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 94: 175–180.
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu LJ et al. (2009). The polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 119: 3626–3636.
Tang J, Wu YM, Zhao P, Yang XM, Jiang JL, Chen ZN . (2008). Overexpression of HAb18G/CD147 promotes invasion and metastasis via alpha3beta1 integrin mediated FAK-paxillin and FAK–PI3K–Ca2+ pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci 65: 2933–2942.
Taura K, Miura K, Iwaisako K, Osterreicher CH, Kodama Y, Penz-Österreicher M et al. (2009). Hepatocytes do not undergo epithelial–mesenchymal transition in liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 51: 1027–1036.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . (2009). Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139: 871–890.
Thuault S, Tan EJ, Peinado H, Cano A, Heldin CH, Moustakas A . (2008). HMGA2 and Smads co-regulate SNAIL1 expression during induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 283: 33437–33446.
Tsai JF, Jeng JE, Chuang LY, Yang ML, Ho MS, Chang WY et al. (1997). Elevated urinary transforming growth factor-beta1 level as a tumour marker and predictor of poor survival in cirrhotic hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 76: 244–250.
Valdés F, Alvarez AM, Locascio A, Vega S, Herrera B, Fernández M et al. (2002). The epithelial mesenchymal transition confers resistance to the apoptotic effects of transforming growth factor beta in fetal rat hepatocytes. Mol Cancer Res 1: 68–78.
Valdés F, Murillo MM, Valverde AM, Herrera B, Sánchez A, Benito M et al. (2004). Transforming growth factor-beta activates both proapoptotic and survival signals in fetal rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res 292: 209–218.
Vigneswaran N, Beckers S, Waigel S, Mensah J, Wu J, Mo J et al. (2006). Increased EMMPRIN (CD147) expression during oral carcinogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol 80: 147–159.
Vincent T, Neve EP, Johnson JR, Kukalev A, Rojo F, Albanell J et al. (2009). A SNAIL1–SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes TGF-beta mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 11: 943–950.
Xu J, Lamouille S, Derynck R . (2009). TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res 19: 156–172.
Xu J, Shen ZY, Chen XG, Zhang Q, Bian HJ, Zhu P et al. (2007a). A randomized controlled trial of Licartin for preventing hepatoma recurrence after liver transplantation. Hepatology 45: 269–276.
Xu J, Xu HY, Zhang Q, Song F, Jiang JL, Yang XM et al. (2007b). HAb18G/CD147 functions in invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res 5: 605–614.
Yan L, Han Y, Wang J, Liu J, Hong L, Fan D . (2007). Peripheral blood monocytes from patients with HBV related decompensated liver cirrhosis can differentiate into functional hepatocytes. Am J Hematol 82: 949–954.
Yang JD, Roberts LR . (2010). Hepatocellular carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7: 448–458.
Yang YA, Zhang GM, Feigenbaum L, Zhang YE . (2006). Smad3 reduces susceptibility to hepatocarcinoma by sensitizing hepatocytes to apoptosis through downregulation of Bcl-2. Cancer Cell 9: 445–457.
Yi JY, Shin I, Arteaga CL . (2005). Type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binds to and activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 280: 10870–10876.
Yoshino J, Monkawa T, Tsuji M, Inukai M, Itoh H, Hayashi M . (2007). Snail1 is involved in the renal epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 362: 63–68.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Xiao-Long Ji (Department of Pathology, General Hospital of the Chinese People's Armed Police Forces, Beijing, China), Professor Wei Zhang (Department of Pathology, Tangdu Hospital of Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, China) and Professor Qiao-Nan Guo (Department of Pathology, Southwest Hospital of Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China) for their pathology analyses. We thank Professor Mien-Chie Hung (Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA) for providing pEGFP-Snail1, and Dr Ling-Min Kong and Xia Ke in our lab for providing pGL3-CD147 (−1761/+37), pGL3-CD147 (−644/+37) and pGL3-CD147 (−338/+37). Financial support: This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30870944 and 30671196), and the Hi-tech Research and Development Programme of China (No. 2009CB521706). Writing assistance was provided by American Journal Experts, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Ru, NY., Zhang, Y. et al. HAb18G/CD147 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition through TGF-β signaling and is transcriptionally regulated by Slug. Oncogene 30, 4410–4427 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.149
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.149
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CD147 contributes to SARS-CoV-2-induced pulmonary fibrosis
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
TMPRSS4 promotes cancer stem–like properties in prostate cancer cells through upregulation of SOX2 by SLUG and TWIST1
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
CD147 deficiency in T cells prevents thymic involution by inhibiting the EMT process in TECs in the presence of TGFβ
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2021)
-
Silencing of CD147 inhibits hepatic stellate cells activation related to suppressing aerobic glycolysis via hedgehog signaling
Cytotechnology (2021)
-
CD147 promotes collective invasion through cathepsin B in hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2020)