Abstract
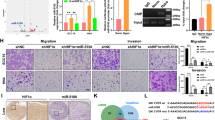
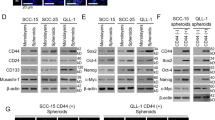
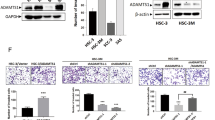
MicroRNAs are often associated with the pathogenesis of many cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). In particular, microRNA-21 (miR-21) appears to have a critical role in tumor cell survival, chemoresistance and HNSCC progression. In this study, we investigated matrix hyaluronan (HA)-induced CD44 (a primary HA receptor) interaction with the stem cell markers, Nanog and Stat-3, in HNSCC cells (HSC-3 cells). Our results indicate that HA binding to CD44 promotes Nanog–Stat-3 (also tyrosine phosphorylated Stat-3) complex formation, nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation. Further analyses reveal that miR-21 is controlled by an upstream promoter containing Stat-3 binding site(s), while chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrate that stimulation of miR-21 expression by HA/CD44 signaling is Nanog/Stat-3-dependent in HNSCC cells. This process results in a decrease of a tumor suppressor protein (PDCD4), and an upregulation of i nhibitors of the apoptosis family of proteins (IAPs) as well as chemoresistance in HSC-3 cells. Treatment of HSC-3 cells with Nanog- and/or Stat-3-specific small interfering RNAs effectively blocks HA-mediated Nanog–Stat-3 signaling events, abrogates miR-21 production and increases PDCD4 expression. Subsequently, this Nanog–Stat-3 signaling inhibition causes downregulation of survival protein (IAP) expression and enhancement of chemosensitivity. To further evaluate the role of miR-21 in tumor cell-specific functions, HSC-3 cells were also transfected with a specific anti-miR-21 inhibitor in order to silence miR-21 expression and block its target functions. Our results demonstrate that anti-miR-21 inhibitor not only upregulates PDCD4 expression but also decreases IAP expression and enhances chemosensitivity in HA-treated HNSCC cells. Together, these findings indicate that the HA-induced CD44 interaction with Nanog and Stat-3 has a pivotal role in miR-21 production leading to PDCD4 reduction, IAP upregulation and chemoresistance in HNSCC cells. This novel Nanog/Stat-3 signaling pathway-specific mechanism involved in miR-21 production is significant for the formation of future intervention strategies in the treatment of HA/CD44-activated HNSCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asangani IA, Rasheed SAK, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S et al. (2008). Allgayer H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27: 2128–2136.
Bourguignon LY . (2008). Hyaluronan-mediated CD44 activation of RhoGTPase signaling and cytoskeleton function promotes tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol 18: 251–259.
Bourguignon LY, Peyrollier K, Xia W, Gilad E . (2008). Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction activates stem cell marker Nanog, Stat-3-mediated MDR1 gene expression, and ankyrin-regulated multidrug efflux in breast and ovarian tumor cells. J Biol Chem 283: 17635–17651.
Bourguignon LY, Spevak CC, Wong G, Xia W, Gilad E . (2009a). Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with PKCɛ promotes oncogenic signaling by the stem cell marker, Nanog and the production of microRNA-21 leading to downregulation of the tumor suppressor protein, PDCD4, anti-apoptosis and chemotherapy resistance in breast tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284: 26533–26546.
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C, Krueger K, Spevak CC . (2010). Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes c-Src-mediated Twist signaling, microRNA-10b expression and RhoA/RhoC upregulation leading to Rho-Kinase-associated cytoskeleton activation and breast tumor cell invasion. J Biol Chem 285: 36721–36735.
Bourguignon LY, Xia W, Wong G . (2009b). Hyaluronan-mediated CD44 interaction with p300 and SIRT1 regulates beta-catenin signaling and NFkappaB-specific transcription activity leading to MDR1 and Bcl-xL gene expression and chemoresistance in breast tumor cells. J Biol Chem 284: 2657–2671.
Chang SS, Jiang WW, Smith I, Poeta LM, Begum S, Glazer C et al. (2008). MicroRNA alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 123: 2791–2797.
Chiou SH, Yu CC, Huang CY, Lin SC, Liu CJ, Tsai TH . (2008). Positive correlations of Oct-4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high-grade oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 14: 4085–4095.
Darnell Jr JE . (1997). STATs and gene regulation. Science 277: 1630–1635.
Ezeh UI, Turek PJ, Reijo RA, Clark AT . (2005). Human embryonic stem cell genes OCT4, NANOG, STELLAR, and GDF3 are expressed in both seminoma and breast carcinoma. Cancer 104: 2255–2265.
Gyrd-Hansen M, Meier P . (2010). IAPs: from caspase inhibitors to modulators of NF-kappaB, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 561–574.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Muller-Newen G, Schaper F . (2003). Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J 374: 1–20.
Huang S . (2007). Regulation of metastases by signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway: clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1362–1366.
Hunter AM . (2007). The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) as cancer targets. Apoptosis 12: 1543–1568.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T et al. (2008). Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58: 71–96.
Kashyap V, Rezende NC, Scotland KB, Shaffer SM, Persson JL, Gudas LJ et al. (2009). Regulation of stem cell pluripotency and differentiation involves a mutual regulatory circuit of the NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 pluripotency transcription factors with polycomb repressive complexes and stem cell microRNAs. Stem Cells Dev 18: 1093–1108.
Löffler D, Brocke-Heidrich K, Pfeifer G, Stocsits C, Hackermüller J, Kretzschmar AK et al. (2007). Interleukin-6 dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood 110: 1330–1333.
Lu J, Bai L, Sun H, Nikolovska-Coleska Z, McEachern D, Qiu S et al. (2008). SM-164: a novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. Cancer Res 68: 9384–9393.
Mitsui K, Tokuzawa Y, Itoh H, Segawa K, Murakami M, Takahashi K et al. (2003). The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell 113: 631–642.
Nakamura M, Nakatani K, Uzawa K, Ono K, Uesugi H, Ogawara K . (2005). Establishment and characterization of a cisplatin-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line, H-1R. Oncol Rep 14: 1281–1286.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P . (2005). Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55: 74–108.
Song JI, Grandis JR . (2000). STAT signaling in head and neck cancer. Oncogene 19: 2489–2495.
Toole BP, Hascall VC . (2002). Hyaluronan and tumor growth. Am J Pathol 161: 745–747.
Toole BP, Wight TN, Tammi MJ . (2002). Hyaluronan-cell interactions in cancer and vascular disease. J Biol Chem 277: 4593–4596.
Torre C, Wang SJ, Xia W, Bourguignon LY . (2010). Reduction of hyaluronan-CD44-mediated growth, migration, and cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer due to inhibition of Rho kinase and PI-3 kinase signaling. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136: 493–501.
Turley EA, Noble PW, Bourguignon LY . (2002). Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem 277: 4589–4592.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F et al. (2006). A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2257–2261.
Wang S, Bourguignon LY . (2011). Role of hyaluronan-mediated CD44 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression and chemoresistance. Am J Pathol 178: 956–963.
Wang SJ, Wong G, de Heer AM, Xia W, Bourguignon LY . (2009). CD44 variant isoforms in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Laryngoscope 119: 1518–1530.
Wen Z, Zhong Z, Darnell Jr JE . (1995). Maximal activation of transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 requires both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation. Cell 82: 241–250.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Drs Gerard J Bourguignon and Walter M Holleran in the preparation and review of this manuscript. We are grateful for Ms Christina Camacho for her assistance in preparing graphs and illustrations. We would also like to thank for Dr Shaomeng Wang from the University of Michigan for providing us an IAP inhibitor, SM164. This work was supported by Veterans Affairs (VA) Merit Review grant and United States Public Health grants (R01 CA66163, R01 CA78633 and P01 AR39448). LYWB is a VA Senior Research Career Scientist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bourguignon, L., Earle, C., Wong, G. et al. Stem cell marker (Nanog) and Stat-3 signaling promote MicroRNA-21 expression and chemoresistance in hyaluronan/CD44-activated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncogene 31, 149–160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.222
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.222
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Niche stiffness sustains cancer stemness via TAZ and NANOG phase separation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Markers of pancreatic cancer stem cells and their clinical and therapeutic implications
Molecular Biology Reports (2019)
-
Differential expression of hsa-miR-221, hsa-miR-21, hsa-miR-135b, and hsa-miR-29c suggests a field effect in oral cancer
BMC Cancer (2018)
-
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas
Molecular Cancer (2018)