Abstract
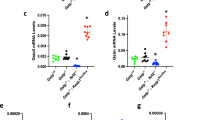
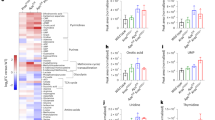
Accumulating evidence indicates that cyclooxygenase (COX)-2-derived prostaglandin (PG) E2 is involved in the development of various tumors, including colorectal cancer. However, the precise contribution of microsomal PGE synthase (mPGES)-1, a terminal enzyme that acts downstream of COX-2 in the PGE2-biosynthetic pathway, to multiple processes of tumor development is not yet fully understood. Here, we show the pro-tumorigenic role of mPGES-1 in chemical carcinogen-induced colon carcinogenesis and intrasplenic tumor transplantation models. Genetic deletion of mPGES-1 significantly reduced both the total number and size of colorectal polyps at 18 weeks after azoxymethane administration with reduced nuclear translocation of β-catenin, altered expression profiles of chemokines/cytokines and increased production of antitumorigenic PGs, prostaglandin D2 and prostacyclin in tumor tissues. At an early stage (6 weeks), mPGES-1 deficiency significantly reduced the number of aberrant crypt foci, while its transgenic overexpression increased the number. Furthermore, the growth of intrasplenically transplanted tumor cells was suppressed in mPGES-1 knockout (KO) mice. Co-culture of tumor cells with bone marrow-derived macrophages (BM-MΦs) isolated from wild-type (WT) mice resulted in the induction of mPGES-1 in BM-MΦs and increased the growth of tumor cells in vitro, whereas mPGES-1-null BM-MΦs failed to facilitate tumor growth. The adoptive transfer of WT BM-MΦs into mPGES-1 KO mice restored the growth of transplanted tumor cells, indicating that mPGES-1 in MΦs is important for the growth of adjacent tumor cells. Taken together, our findings suggest that the inhibition of mPGES-1 is an alternative therapeutic target for colorectal and possibly other cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ban JO, Kwak DH, Oh JH, Park EJ, Cho MC, Song HS et al. (2010). Suppression of NF-κB and GSK-3β is involved in colon cancer cell growth inhibition by the PPAR agonist troglitazone. Chem Biol Interact 188: 75–85.
Bombardier C, Laine L, Reicin A, Shapiro D, Burgos-Vargas R, Davis B et al. (2000). Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med 343: 1520–1528.
Boulet L, Ouellet M, Bateman KP, Ethier D, Percival MD, Riendeau D, Mancini JA et al. (2004). Deletion of microsomal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthase-1 reduces inducible and basal PGE2 production and alters the gastric prostanoid profile. J Biol Chem 279: 23229–23237.
Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, Bolognese JA, Oxenius B, Horgan K et al. (2005). Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med 352: 1092–1102.
Casós K, Siguero L, Fernández-Figueras MT, León X, Sardá MP, Vila L et al. (2011). Tumor cells induce COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression in microvascular endothelial cells mainly by means of IL-1 receptor activation. Microvasc Res 81: 261–268.
Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO, Druey KM, Gutkind JS . (2005). Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer cell growth through a Gs–axin–β-catenin signaling axis. Science 310: 1504–1510.
Cathcart MC, Reynolds JV, O'Byrne KJ, Pidgeon GP . (2010). The role of prostacyclin synthase and thromboxane synthase signaling in the development and progression of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805: 153–166.
Garg A, Aggarwal BB . (2002). Nuclear transcription factor-κB as a target for cancer drug development. Leukemia 16: 1053–1068.
Golijanin D, Tan JY, Kazior A, Cohen EG, Russo P, Dalbagni G et al. (2004). Cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 are overexpressed in squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. Clin Cancer Res 10: 1024–1031.
Guda K, Upender MB, Belinsky G, Flynn C, Nakanishi M, Marino JN et al. (2004). Carcinogen-induced colon tumors in mice are chromosomally stable and are characterized by low-level microsatellite instability. Oncogene 23: 3813–3821.
Hanaka H, Pawelzik S-C, Johnsen JI, Rakonjac M, Terawaki K, Rasmuson A et al. (2009). Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase 1 determines tumor growth in vivo of prostate and lung cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 44: 18757–18762.
Hara S, Kamei D, Sasaki Y, Tanemoto A, Nakatani Y, Murakami M . (2010). Prostaglandin E synthases: understanding their pathophysiologial roles through mouse genetic models. Biochimie 92: 651–659.
Hembruff SL, Cheng N . (2009). Chemokine signaling in cancer: implications on the tumor microenvironment and therapeutic targeting. Cancer Ther 7: 254–267.
Jakobsson PJ, Thoren S, Morgenstern R, Samuelsson B . (1999). Identification of human prostaglandin E synthase: a microsomal, glutathione-dependent, inducible enzyme, constituting a potential novel drug target. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 7220–7225.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E . (2010). Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60: 277–300.
Kamata H, Hosono K, Suzuki T, Ogawa Y, Kubo H, Katoh H et al. (2010). mPGES-1-expressing bone marrow-derived cells enhance tumor growth and angiogenesis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 64: 409–416.
Kamei D, Murakami M, Nakatani Y, Ishikawa Y, Ishii T, Kudo I . (2003). Potential role of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 in tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 278: 19396–19405.
Kamei D, Murakami M, Sasaki Y, Nakatani Y, Majima M, Ishikawa Y et al. (2010). Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 in both cancer cells and hosts contributes to tumour growth, invasion and metastasis. Biochem J 425: 361–371.
Kamei D, Yamakawa K, Takegoshi Y, Mikami-Nakanishi M, Nakatani Y, Oh-Ishi S et al. (2004). Reduced pain hypersensitivity and inflammation in mice lacking microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1. J Biol Chem 279: 33684–33695.
Kanegae Y, Takamori K, Sato Y, Lee G, Nakai M, Saito I . (1996). Efficient gene activation system on mammalian cell chromosomes using recombinant adenovirus producing Cre recombinase. Gene 181: 207–2012.
Keith RL, Miller YE, Hudish TM, Girod CE, Sotto-Santiago S, Franklin WA et al. (2004). Pulmonary prostacyclin synthase overexpression chemoprevents tobacco smoke lung carcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Res 64: 5897–5904.
Lavergne E, Combadière C, Iga M, Boissonnas A, Bonduelle O, Maho M et al. (2004). Intratumoral CC chemokine ligand 5 overexpression delays tumor growth and increases tumor cell infiltration. J Immunol 173: 3755–3762.
Mancini JA, Blood K, Guay J, Gordon R, Claveau D, Chan CC et al. (2001). Cloning, expression, and up-regulation of inducible rat prostaglandin e synthase during lipopolysaccharide-induced pyresis and adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Biol Chem 276: 4469–4475.
Mansure JJ, Nassim R, Kassouf W . (2009). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in bladder cancer: a promising therapeutic target. Cancer Biol Ther 8: 1–9.
Murakami M, Kudo I . (2004). Recent advances in molecular biology and physiology of the prostaglandin E2-biosynthetic pathway. Prog Lipid Res 43: 3–35.
Murakami M, Naraba H, Tanioka T, Semmyo N, Nakatani Y, Kojima F et al. (2000). Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 275: 32783–32792.
Nakanishi M, Menoret A, Tanaka T, Miyamoto S, Montrose DC, Vella AT et al. (2011). Selective PGE2 suppression impairs colon carcinogenesis and modifies local mucosal immunity. Cancer Prevent Res 4: 1198–1208.
Nakanishi M, Montrose DC, Clark P, Nambiar PR, Belinsky GS, Claffey KP et al. (2008). Genetic deletion of mPGES-1 suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 68: 3251–3259.
Nakatani Y . (2007). Regulation of cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase. J Health Sci 53: 251–256.
Nambiar PR, Girnun G, Lillo NA, Guda K, Whiteley HE, Rosenberg DW . (2003). Preliminary analysis of azoxymethane induced colon tumors in inbred mice commonly used as transgenic/knockout progenitors. Int J Oncol 22: 145–150.
Osawa E, Nakajima A, Wada K, Ishimine S, Fujisawa N, Kawamori T et al. (2003). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ ligands suppress colon carcinogenesis induced by azoxymethane in mice. Gastroenterology 124: 361–367.
Oshima H, Oshima M, Inaba K, Taketo MM . (2004). Hyperplastic gastric tumors induced by activated macrophages in COX-2/mPGES-1 transgenic mice. EMBO J 23: 1669–1678.
Oshima M, Oshima H, Matsunaga A, Taketo MM . (2005). Hyperplastic gastric tumors with spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia caused by tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent inflammation in cyclooxygenase-2/microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 transgenic mice. Cancer Res 65: 9147–9151.
Ohtsuki M, Taketomi T, Arata S, Masuda S, Ishikawa T, Ishii T et al. (2006). Transgenic expression of group V, but not group X, secreted phospholipase A2 in mice leads to neonatal lethality because of lung dysfunction. J Biol Chem 281: 36420–36433.
Park JM, Kanaoka Y, Eguchi N, Aritake K, Grujic S, Materi AM et al. (2007). Hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase suppresses intestinal adenomas in ApcMin/+ mice. Cancer Res 67: 881–889.
Qian X, Zhang J, Liu J . (2011). Tumor-secreted PGE2 inhibits CCL5 production in activated macrophages through cAMP/PKA signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 286: 2111–2120.
Robinson SC, Scott KA, Wilson JL, Thompson RG, Proundfoot AE, Balkwill FR . (2003). A chemokine receptor antagonist inhibits experimental breast tumor growth. Cancer Res 63: 8360–8365.
Samuelsson B, Morgenstern R, Jakobsson PJ . (2007). Membrane prostaglandin E synthase-1: a novel therapeutic target. Pharmacol Rev 59: 207–224.
Scher JU, Pillinger MH . (2005). 15d-PGJ2: the anti-inflammatory prostaglandin? Clin Immunol 114: 100–109.
Segditsas S, Tomlinson I . (2006). Colorectal cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene 25: 7531–7537.
Singh B, Vincent L, Berry JA, Multani AS, Lucci A . (2007). Cyclooxygenase-2 expression induces genomic instability in MCF10A breast epithelial cells. J Surg Res 140: 220–226.
Stichtenoth DO, Thoren S, Bian H, Peters-Golden M, Jakobsson PJ, Crofford LJ . (2001). Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase is regulated by proinflammatory cytokines and glucocorticoids in primary rheumatoid synovial cells. J Immunol 167: 469–474.
Thompson EA . (2007). PPARγ physiology and pathology in gastrointestinal epithelial cells. Mol Cells 24: 167–176.
Tsujii M, DuBois RN . (1995). Alterations in cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell 83: 493–501.
Tsujii M, Kawano S, Tsuji S, Sawaoka H, Hori M, DuBois RN . (1998). Cyclooxygenase regulates angiogenesis induced by colon cancer cells. Cell 93: 705–716.
Wang D, DuBois RN . (2010a). The role of COX-2 in intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer. Oncogene 29: 781–788.
Wang D, DuBois RN . (2010b). Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 181–193.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research; by a Private University High Technology Research Center Project matching-fund subsidy from the Ministry of Education, Sports, Science, Culture and Technology of Japan; and by a Showa University Special Grant-in-Aid for Innovative Collaborative Research Projects. D Kamei was supported by Research Fellowships from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for Young Scientists. M Murakami was supported by PRESTO from the Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, Y., Kamei, D., Ishikawa, Y. et al. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 is involved in multiple steps of colon carcinogenesis. Oncogene 31, 2943–2952 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.472
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.472
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sirt3 restricts tumor initiation via promoting LONP1 deacetylation and K63 ubiquitination
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Anticancer Activities of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Targeting Apoptosis and Inflammatory Pathways in Colon Cancer Cells
Journal of Cluster Science (2022)
-
Genetic-deletion of Cyclooxygenase-2 Downstream Prostacyclin Synthase Suppresses Inflammatory Reactions but Facilitates Carcinogenesis, unlike Deletion of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
The role of selenoprotein W in inflammatory injury in chicken immune tissues and cultured splenic lymphocyte
BioMetals (2015)
-
Multifaceted roles of PGE2 in inflammation and cancer
Seminars in Immunopathology (2013)