Abstract
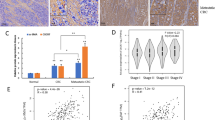
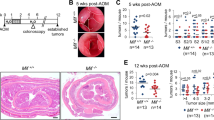
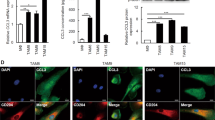
Chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1), one of the mammalian members of the chitinase family, is expressed in several types of human cancer, and elevated serum level of CHI3L1 is suggested to be a biomarker of poor prognosis in advanced cancer patients. However, the overall biological function of CHI3L1 in human cancers still remains unknown. Studies were performed to characterize the role of CHI3L1 in cancer pathophysiology utilizing human colorectal cancer samples and human cell lines. Plasma protein and tissue mRNA expression levels of CHI3L1 in colorectal cancer were strongly upregulated. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that CHI3L1 was expressed in cancer cells, and CHI3L1 expression had a significant association with the number of infiltrated macrophages and microvessel density (MVD). By utilizing transwell migration and tube-formation assays, overexpression of CHI3L1 in SW480 cells (human colon cancer cells) enhanced the migration of THP-1 cells (human macrophage cells) and HUVECs (human endothelial cells), and the tube formation of HUVECs. The knockdown of CHI3L1 by RNA interference or the neutralization of CHI3L1 by anti-CHI3L1 antibody displayed strong suppression of CHI3L1-induced migration and tube formation. Cell proliferation assay showed that CHI3L1 overexpression significantly enhanced the proliferation of SW480 cells. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis showed that CHI3L1 increased the secretion of inflammatory chemokines, IL-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), from SW480 cells through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Both neutralization of IL-8 or MCP-1 and inhibition or knockdown of MAPK in SW480 cells significantly inhibited CHI3L1-induced migration and tube formation. In a xenograft mouse model, overexpression of CHI3L1 in HCT116 cells (human colon cancer cells) enhanced the tumor growth as well as macrophage infiltration and MVD. In conclusion, CHI3L1 expressed in colon cancer cells promotes cancer cell proliferation, macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis. Thus, the inhibition of CHI3L1 activity may be a novel therapeutic strategy for human colorectal cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Arenberg DA, Addison CL, Ehlert JE, Burdick MD et al. (2000). CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol 68: 1–8.
Ben-Baruch A . (2006). The multifaceted roles of chemokines in malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25: 357–371.
Chen CC, Pekow J, Llado V, Kanneganti M, Lau CW, Mizoguchi A et al. (2011). Chitinase 3-like-1 expression in colonic epithelial cells as a potentially novel marker for colitis-associated neoplasia. Am J Pathol 179: 1494–1503.
Chupp GL, Lee CG, Jarjour N, Shim YM, Holm CT, He S et al. (2007). A chitinase-like protein in the lung and circulation of patients with severe asthma. N Engl J Med 357: 2016–2027.
Cintin C, Johansen JS, Christensen IJ, Price PA, Sorensen S, Nielsen HJ . (1999). Serum YKL-40 and colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 79: 1494–1499.
Eurich K, Segawa M, Toei-Shimizu S, Mizoguchi E . (2009). Potential role of chitinase 3-like-1 in inflammation-associated carcinogenic changes of epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 42: 5249–5259.
Guo X, Oshima H, Kitamura T, Taketo MM, Oshima M . (2008). Stromal fibroblasts activated by tumor cells promote angiogenesis in mouse gastric cancer. J Biol Chem 283: 19864–19871.
Hakala BE, White C, Recklies AD . (1993). Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem 268: 25803–25810.
Hanahan D, Folkman J . (1996). Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86: 353–364.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
Henrissat B, Bairoch A . (1993). New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 293: 781–788.
Henrissat B, Davies G . (1997). Structural and sequence-based classification of glycoside hydrolases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 7: 637–644.
Herrera-Estrella A, Chet I . (1999). Chitinases in biological control. EXS 87: 171–184.
Johansen JS. (2006). Studies on serum YKL-40 as a biomarker in diseases with inflammation, tissue remodeling fibroses and cancer. Dan Med Bull 53: 172–209.
Johansen JS, Jensen BV, Roslind A, Nielsen D, Price PA. (2006). Serum YKL-40, a new prognostic biomarker in cancer patients? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15: 194–202.
Kawada K, Upadhyay G, Ferandon S, Janarthanan S, Hall M, Vilardaga JP et al. (2009). Cell migration is regulated by platelet-derived growth factor receptor endocytosis. Mol Cell Biol 16: 4508–4518.
Kawada M, Chen CC, Arihiro A, Nagatani K, Watanabe T, Mizoguchi E. (2008). Chitinase 3-like-1 enhances bacterial adhesion to colonic epithelial cells through the interaction with bacterial chitin-binding protein. Lab Invest 88: 883–895.
Kawada M, Hachiya Y, Arihiro A, Mizoguchi E. (2007). Role of mammalian chitinases in inflammatory conditions. Keio J Med 56: 21–27.
Lazennec G, Richmond A. (2010). Chemokines and chemokine receptors: new insights into cancer-related inflammation. Trends Mol Med 16: 133–144.
Ling H, Recklies AD. (2004). The chitinase 3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 inhibits cellular responses to the inflammatory cytokines inrerleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem J 380: 651–659.
Malinda KM, Ponce L, Kleinman HK, Shackelton LM, Millis AJ. (1999). Gp38k, a protein synthesized by vascular smooth muscle cells, stimulates directional migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 250: 168–173.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. (2008). Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454: 436–444.
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A. (2002). Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol 23: 549–555.
Mizoguchi E. (2006). Chitinase 3-like-1 exacerbates intestinal inflammation by enhancing bacterial adhesion and invasion in colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 130: 398–411.
Ono M. (2008). Molecular links between tumor angiogenesis and inflammation: inflammatory stimuli of macrophages and cancer cells as targets for therapeutic strategy. Cancer Sci 99: 1501–1506.
Pollard JW. (2004). Tumor-educated macrophages promote tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 71–78.
Recklies AD, White C, Ling H. (2002). The chitinase 3-like protein human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC-gp39) stimulates proliferation of human connective-tissue cells and activates both extracellular signal-regulated kinase- and protein kinase B-meditated signaling pathways. Biochem J 365: 119–126.
Rejman JJ, Hurley WL. (1988). Isolation and characterization of a novel 39 kilodalton whey protein from bovine mammary secretions collected during the nonlactating period. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 150: 329–334.
Salcedo R, Ponce ML, Young HA, Wasserman K, Ward JM, Kleinman HK et al. (2000). Human endothelial cells express CCR2 and respond to MCP-1: direct role of MCP-1 in angiogenesis and tumor progression. Blood 96: 34–40.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, Herrera R. (2004). Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 937–947.
Shackelton LM, Mann DM, Millis AJ. (1995). Identification of a 38-kDa heparin-binding glycoprotein (gp38k) in differentiating vascular smooth muscle cells as a member of a group of proteins associated with tissue remodeling. J Biol Chem 270: 13076–13083.
Shao R, Hamel K, Petersen L, Cao QJ, Arenas RB, Bigelow C et al. (2009). YKL-40, a secreted glycoprotein, promotes tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 28: 4456–4468.
Singh S, Sadanandam A, Singh RK. (2007). Chemokines in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26: 453–467.
Strieter RM . (2001). Chemokines: not just leukocyte chemoattractants in the promotion of cancer. Nat Immunol 2: 285–286.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (20790493, 21-40033, 23590937, 21229009), and Health and Labor Science Research Grants for Research on Intractable Diseases, and Research on Hepatitis from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan, and Research Foundation of Translational Research Center, Kyoto University and by a research grant (R01DK80070) from the National Institutes of Health in USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawada, M., Seno, H., Kanda, K. et al. Chitinase 3-like 1 promotes macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 31, 3111–3123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.498
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.498
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IL13Rα2 as a crucial receptor for Chi3l1 in osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption through the MAPK/AKT pathway
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Truncated O-glycosylation in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer reveals a gene expression signature associated with extracellular matrix and proteolysis
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Significance of chitinase-3-like protein 1 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases and cancer
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2024)
-
Macrophage’s role in solid tumors: two edges of a sword
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Myeloid-specific deletion of chitinase-3-like 1 protein ameliorates murine diet-induced steatohepatitis progression
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)