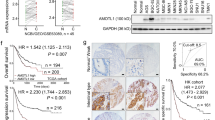
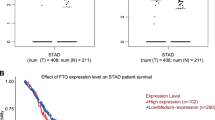
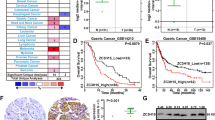
Abstract
Activation of Akt signaling pathway has been suggested involving in chemoresistance, metastasis and tumorigenesis of gastric cancer. However, the mechanism of Akt regulation in gastric cancer is not fully understood. RUNX3, which was first identified as a transcription factor, suppresses gastric tumorigenesis through regulating expression of target genes. Here, we found that restoration of RUNX3 significantly downregulates the protein and mRNA expression of Akt1 in gastric cancer cell lines, AGS and SNU-1. Knockdown of RUNX3 upregulates protein and mRNA expression of Akt1 in normal gastric epithelial cell line, GES-1. The negative correlation of RUNX3 and Akt expression and downstream β-catenin/cyclin D1 effectors was further confirmed in AGS and GES-1 cell lines, as well as clinical specimens of gastric cancer. We identified two RUNX3-binding sites in Akt1 promoter and the binding of RUNX3 on Akt1 promoter significantly inhibits Akt1 expression. The RUNX3-mediated inhibition of Akt1 caused β-catenin protein degradation and then cyclin D1 downregulation. Restoration of cyclin D1 reverses cell growth inhibition and G1 phase arrest induced by RUNX3 in gastric cancer cells. Our results show that loss of RUNX3 expression can enhance the Akt1-mediated signaling pathway and promote the tumorigenesis process in human gastric cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A, Kemler R . (1997). beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J 16: 3797–3804.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al. (1999). Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868.
Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO, Druey KM, Gutkind JS . (2005). Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer cell growth through a Gs-axin-beta-catenin signaling axis. Science 310: 1504–1510.
Chang TL, Ito K, Ko TK, Liu Q, Salto-Tellez M, Yeoh KG et al. (2010). Claudin-1 has tumor suppressive activity and is a direct target of RUNX3 in gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 138: 255–265 e1-3.
Chi XZ, Yang JO, Lee KY, Ito K, Sakakura C, Li QL et al. (2005). RUNX3 suppresses gastric epithelial cell growth by inducing p21(WAF1/Cip1) expression in cooperation with transforming growth factor {beta}-activated SMAD. Mol Cell Biol 25: 8097–8107.
Chuang LS, Ito Y . (2010). RUNX3 is multifunctional in carcinogenesis of multiple solid tumors. Oncogene 29: 2605–2615.
Chyou PH, Nomura AM, Hankin JH, Stemmermann GN . (1990). A case-cohort study of diet and stomach cancer. Cancer Res 50: 7501–7504.
Clements WM, Wang J, Sarnaik A, Kim OJ, MacDonald J, Fenoglio-Preiser C et al. (2002). beta-Catenin mutation is a frequent cause of Wnt pathway activation in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 62: 3503–3506.
Clevers H . (2006). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127: 469–480.
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA . (1995). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378: 785–789.
Daga A, Karlovich CA, Dumstrei K, Banerjee U . (1996). Patterning of cells in the Drosophila eye by Lozenge, which shares homologous domains with AML1. Genes Dev 10: 1194–1205.
Dihlmann S, Kloor M, Fallsehr C, von Knebel Doeberitz M . (2005). Regulation of AKT1 expression by beta-catenin/Tcf/Lef signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 26: 1503–1512.
Durst KL, Hiebert SW . (2004). Role of RUNX family members in transcriptional repression and gene silencing. Oncogene 23: 4220–4224.
Ebert MP, Fei G, Kahmann S, Muller O, Yu J, Sung JJ et al. (2002). Increased beta-catenin mRNA levels and mutational alterations of the APC and beta-catenin gene are present in intestinal-type gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 23: 87–91.
Etoh T, Kanai Y, Ushijima S, Nakagawa T, Nakanishi Y, Sasako M et al. (2004). Increased DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) protein expression correlates significantly with poorer tumor differentiation and frequent DNA hypermethylation of multiple CpG islands in gastric cancers. Am J Pathol 164: 689–699.
Fang DC, Wang RQ, Yang SM, Yang JM, Liu HF, Peng GY et al. (2003). Mutation and methylation of hMLH1 in gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability. World J Gastroenterol 9: 655–659.
Fukamachi H . (2006). Runx3 controls growth and differentiation of gastric epithelial cells in mammals. Dev Growth Differ 48: 1–13.
Fukamachi H, Ito K . (2004). Growth regulation of gastric epithelial cells by Runx3. Oncogene 23: 4330–4335.
Gargano G, Calcara D, Corsale S, Agnese V, Intrivici C, Fulfaro F et al. (2007). Aberrant methylation within RUNX3 CpG island associated with the nuclear and mitochondrial microsatellite instability in sporadic gastric cancers. Results of a GOIM (Gruppo Oncologico dell’Italia Meridionale) prospective study. Ann Oncol 18 (Suppl 6): vi103–vi109.
Guo C, Ding J, Yao L, Sun L, Lin T, Song Y et al. (2005). Tumor suppressor gene Runx3 sensitizes gastric cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs by downregulating Bcl-2, MDR-1 and MRP-1. Int J Cancer 116: 155–160.
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC, van de Velde CJ . (2009). Gastric cancer. Lancet 374: 477–490.
Hsu PI, Hsieh HL, Lee J, Lin LF, Chen HC, Lu PJ et al. (2009). Loss of RUNX3 expression correlates with differentiation, nodal metastasis, and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 16: 1686–1694.
Ito K, Lim AC, Salto-Tellez M, Motoda L, Osato M, Chuang LS et al. (2008). RUNX3 attenuates beta-catenin/T cell factors in intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 14: 226–237.
Ito K, Liu Q, Salto-Tellez M, Yano T, Tada K, Ida H et al. (2005). RUNX3, a novel tumor suppressor, is frequently inactivated in gastric cancer by protein mislocalization. Cancer Res 65: 7743–7750.
Ito Y . (1999). Molecular basis of tissue-specific gene expression mediated by the runt domain transcription factor PEBP2/CBF. Genes Cells 4: 685–696.
Ito Y . (2004). Oncogenic potential of the RUNX gene family: ‘overview’. Oncogene 23: 4198–4208.
Ito Y . (2008). RUNX genes in development and cancer: regulation of viral gene expression and the discovery of RUNX family genes. Adv Cancer Res 99: 33–76.
Jin YH, Jeon EJ, Li QL, Lee YH, Choi JK, Kim WJ et al. (2004). Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates p300-dependent RUNX3 acetylation, which inhibits ubiquitination-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem 279: 29409–29417.
Kania MA, Bonner AS, Duffy JB, Gergen JP . (1990). The Drosophila segmentation gene runt encodes a novel nuclear regulatory protein that is also expressed in the developing nervous system. Genes Dev 4: 1701–1713.
Ke Y, Ning T, Wang B . (1994). [Establishment and characterization of a SV40 transformed human fetal gastric epithelial cell line-GES-1]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 16: 7–10.
Kim JH, Choi JK, Cinghu S, Jang JW, Lee YS, Li YH et al. (2009). Jab1/CSN5 induces the cytoplasmic localization and degradation of RUNX3. J Cell Biochem 107: 557–565.
Kim JH, Takahashi T, Chiba I, Park JG, Birrer MJ, Roh JK et al. (1991). Occurrence of p53 gene abnormalities in gastric carcinoma tumors and cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 83: 938–943.
Levanon D, Negreanu V, Bernstein Y, Bar-Am I, Avivi L, Groner Y . (1994). AML1, AML2, and AML3, the human members of the runt domain gene-family: cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal localization. Genomics 23: 425–432.
Li QL, Ito K, Sakakura C, Fukamachi H, Inoue K, Chi XZ et al. (2002). Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell 109: 113–124.
Li VS, Wong CW, Chan TL, Chan AS, Zhao W, Chu KM et al. (2005). Mutations of PIK3CA in gastric adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 5: 29.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X . (2009). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17: 9–26.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M . (2009). Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9: 153–166.
Misra UK, Pizzo SV . (2007). Upregulation of AKT1 protein expression in forskolin-stimulated macrophage: evidence from ChIP analysis that CREB binds to and activates the AKT1 promoter. J Cell Biochem 100: 1022–1033.
Nomura A, Grove JS, Stemmermann GN, Severson RK . (1990). A prospective study of stomach cancer and its relation to diet, cigarettes, and alcohol consumption. Cancer Res 50: 627–631.
Ogawa S, Satake M, Ikuta K . (2008). Physical and functional interactions between STAT5 and Runx transcription factors. J Biochem 143: 695–709.
Oki E, Baba H, Tokunaga E, Nakamura T, Ueda N, Futatsugi M et al. (2005). Akt phosphorylation associates with LOH of PTEN and leads to chemoresistance for gastric cancer. Int J Cancer 117: 376–380.
Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H . (2004). PI3K-Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis 9: 667–676.
Otto F, Lubbert M, Stock M . (2003). Upstream and downstream targets of RUNX proteins. J Cell Biochem 89: 9–18.
Park S, Kim D, Kaneko S, Szewczyk KM, Nicosia SV, Yu H et al. (2005). Molecular cloning and characterization of the human AKT1 promoter uncovers its up-regulation by the Src/Stat3 pathway. J Biol Chem 280: 38932–38941.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P . (2005). Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55: 74–108.
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N et al. (1991). Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med 325: 1127–1131.
Peng Z, Wei D, Wang L, Tang H, Zhang J, Le X et al. (2006). RUNX3 inhibits the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and reduces the angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis of human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12: 6386–6394.
Polk DB, Peek Jr RM . (2010). Helicobacter pylori: gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 403–414.
Remy I, Montmarquette A, Michnick SW . (2004). PKB/Akt modulates TGF-beta signalling through a direct interaction with Smad3. Nat Cell Biol 6: 358–365.
Sano T, Tsujino T, Yoshida K, Nakayama H, Haruma K, Ito H et al. (1991). Frequent loss of heterozygosity on chromosomes 1q, 5q, and 17p in human gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res 51: 2926–2931.
Sato F, Meltzer SJ . (2006). CpG island hypermethylation in progression of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer 106: 483–493.
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I, Albanese C, D'Amico M, Pestell R et al. (1999). The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 5522–5527.
Soung YH, Lee JW, Nam SW, Lee JY, Yoo NJ, Lee SH . (2006). Mutational analysis of AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3 genes in common human carcinomas. Oncology 70: 285–289.
Stock M, Otto F . (2005). Gene deregulation in gastric cancer. Gene 360: 1–19.
Suzuki H, Iwasaki E, Hibi T . (2009). Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 12: 79–87.
Tsugane S, Sasazuki S . (2007). Diet and the risk of gastric cancer: review of epidemiological evidence. Gastric Cancer 10: 75–83.
Ushijima T, Sasako M . (2004). Focus on gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 5: 121–125.
Wei D, Gong W, Oh SC, Li Q, Kim WD, Wang L et al. (2005). Loss of RUNX3 expression significantly affects the clinical outcome of gastric cancer patients and its restoration causes drastic suppression of tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res 65: 4809–4816.
Wu MS, Shun CT, Wang HP, Sheu JC, Lee WJ, Wang TH et al. (1997). Genetic alterations in gastric cancer: relation to histological subtypes, tumor stage, and Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterology 112: 1457–1465.
Xing X, Wang J, Xing LX, Li YH, Yan X, Zhang XH . (2011). Involvement of MAPK and PI3 K signaling pathway in sterigmatocystin-induced G2 phase arrest in human gastric epithelium cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 55: 749–760.
Yanada M, Yaoi T, Shimada J, Sakakura C, Nishimura M, Ito K et al. (2005). Frequent hemizygous deletion at 1p36 and hypermethylation downregulate RUNX3 expression in human lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 14: 817–822.
Yano T, Ito K, Fukamachi H, Chi XZ, Wee HJ, Inoue K et al. (2006). The RUNX3 tumor suppressor upregulates Bim in gastric epithelial cells undergoing transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 26: 4474–4488.
Zheng L, Wang L, Ajani J, Xie K . (2004). Molecular basis of gastric cancer development and progression. Gastric Cancer 7: 61–77.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by grants from the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC 97-2311-B-006-003-MY3 and NSC 99-2627-B-006-021), National Cheng Kung University Hospital of Taiwan (NCKUH-9803004 and NCKUH-9903051) and Chi Mei Medical Center of Taiwan (CMNCKU9901). We acknowledge Dr Xiang Hong Zhang from Hebei Medical University in China for kindly providing GES-1 cell line, and Dr Ching-Shih Chen from Ohio State University for kindly providing Akt, myr-Akt and DN-Akt constructs.
Author contributions: F-CL, Y-PL, MH and P-JL designed the research. C-HLai carried out part of the experiments. F-CL and Y-PL analyzed the data. C-HLai and C-HW helped to design cloning strategies. H-CC, C-HLai and C-HW carried out the immunohistochemistry. JQC provided Akt promoter construct. F-CL, Y-PL, C-HLee, Y-CL, H-YW and P-JL contributed to extra technical assistance. P-IH and Y-SS provided clinical specimens. MH helped immunohistochemistry scoring for specimens. F-CL, Y-PL and P-JL organized the figures and wrote the paper. All authors participated in the interpretation of the data and production of the final paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, FC., Liu, YP., Lai, CH. et al. RUNX3-mediated transcriptional inhibition of Akt suppresses tumorigenesis of human gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 31, 4302–4316 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.596
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.596
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Explore the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of JianPi QingRe HuaYu Methods in the treatment of gastric inflammation-cancer transformation by network pharmacology and experimental validation
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2023)
-
CircTENM3 inhibites tumor progression via the miR-558/RUNX3 axis in prostate cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential of HDAC9 in intervertebral disc degeneration
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2023)
-
RUNX3 inhibits glioma survival and invasion via suppression of the β-catenin/TCF-4 signaling pathway
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2018)
-
Transcriptional Regulatory Network Analysis for Gastric Cancer Based on mRNA Microarray
Pathology & Oncology Research (2017)