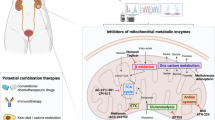
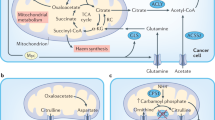
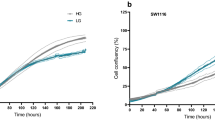
Abstract
Understanding the complexity of cancer and of the underlying regulatory networks provides a new paradigm that tackles cancer development and treatment through a system biology approach, contemporarily acting on various intersecting pathways. Cancer cell metabolism is an old pathogenetic issue that has recently gained new interest as target for therapeutic approaches. More than 70 years ago, Warburg discovered that malignant cells generally have altered metabolism with high rates of glucose uptake and increased glycolysis, even under aerobic condition. Observational studies have provided evidence that impaired metabolism, obesity, hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia may have a role in cancer development, progression and prognosis, and actually diabetic and obese patients have increased cancer risk. On the other hand, caloric restriction has been shown to prolong life span and reduce cancer incidence in several animal models, having an impact on different metabolic pathways. Metformin, an antidiabetic drug widely used for over 40 years, mimics caloric restriction acting on cell metabolism at multiple levels, reducing all energy-consuming processes in the cells, including cell proliferation. By overviewing molecular mechanisms of action, epidemiological evidences, experimental data in tumor models and early clinical study results, this review provides information supporting the promising use of metformin in cancer prevention and treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warburg O . On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956; 123: 309–314.
Fontana L, Partridge L, Longo VD . Extending healthy life span-from yeast to humans. Science 2010; 328: 321–326.
Hursting SD, Lashinger LM, Colbert LH, Rogers CJ, Wheatley KW, Nunez NP et al. Energy balance and carcinogenesis: underlying pathways and targets for intervention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2007; 7: 484–491.
Fontana L, Klein S . Aging, adiposity, and calorie restriction. JAMA 2007; 297: 986–994.
Colman RJ, Anderson RM, Johnson SC, Kastman EK, Kosmatka KJ, Beasley TM et al. Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Science 2009; 325: 201–204.
Campbell IW, Ritz P . Understanding the glucose-lowering actions of metformin. In: Bailey CJ, Campbell IW, Chan JCN, Davidson JA, Howlett HCS, Ritz P (eds) Metformin the Gold Standard. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK, 2007, pp 77–88.
Detaille D, Guigas B, Leverve X, Wiernsperger N, Devos P . Obligatory role of membrane events in the regulatory effect of metformin on the respiratory chain function. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 63: 1259–1272.
Giannarelli R, Aragona M, Coppelli A, Del Prato S . Reducing insulin resistance with metformin: the evidence today. Diabetes Metab 2003; 29: 6S28–6S35.
Matthaei S, Reibold JP, Hamann A, Benecke H, Häring HU, Greten H et al. In vivo metformin treatment ameliorates insulin resistance: evidence for potentiation of insulin-induced translocation and increased functional activity of glucose transporters in obese (fa/fa) Zucker rat adipocytes. Endocrinology 1993; 133: 304–311.
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 1674–1685.
Vigneri P, Frasca F, Sciacca L, Pandini G, Vigneri R . Diabetes and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009; 16: 1103–1123.
Barone BB, Yeh HC, Snyder CF, Peairs KS, Stein KB, Derr RL et al. Long-term all-cause mortality in cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2008; 300: 2754–2764.
Basen-Engquist K, Chang M . Obesity and cancer risk: recent review and evidence. Curr Oncol Rep 2011; 13: 71–76.
Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M . Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008; 371: 569–578.
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD . Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005; 330: 1304–1305.
Bowker SL, Yasui Y, Veugelers P, Johnson JA . Glucose-lowering agents and cancer mortality rates in type 2 diabetes: assessing effects of time-varying exposure. Diabetologia 2010; 53: 1631–1637.
Home PD, Kahn SE, Jones NP, Noronha D, Beck-Nielsen H, Viberti G . Experience of malignancies with oral glucose-lowering drugs in the randomised controlled ADOPT (A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial) and RECORD (Rosiglitazone Evaluated for Cardiovascular Outcomes and Regulation of Glycaemia in Diabetes) clinical trials. Diabetologia 2010; 53: 1838–1845.
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA . The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 1766–1777.
Monami M, Colombi C, Balzi D, Dicembrini I, Giannini S, Melani C et al. Metformin and cancer occurrence in insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 129–131.
Monami M, Lamanna C, Balzi D, Marchionni N, Mannucci E . Sulphonylureas and cancer: a case-control study. Acta Diabetol. 2009; 46: 279–284.
Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi DR, Morris AD, Evans JM . New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009; 32: 1620–1625.
Landman GW, Kleefstra N, van Hateren K, Groenier K, Gans RO, Bilo HJ . Metformin associated with lower cancer mortality in type 2 diabetes: ZODIAC-16. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 322–326.
Lee MS, Hsu CC, Wahlqvist ML, Tsai HN, Chang YH, Huang YC . Type 2 diabetes increases and metformin reduces total, colorectal, liver and pancreatic cancer incidences in Taiwanese: a representative population prospective cohort study of 800,000 individuals. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 20.
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krahenbuhl S, Jick SS, Meier CR . Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 1304–1308.
Bosco JL, Antonsen S, Sorensen HT, Pedersen L, Lash TL . Metformin and incident breast cancer among diabetic women: a population-based case-control study in Denmark. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2011; 20: 101–111.
Oliveria SA, Koro CE, Yood MU, Sowell M . Cancer incidence among patients treated with antidiabetic pharmacotherapy. Diabetes Metabol Syndr 2008; 2: 47–57.
Bodmer M, Becker C, Meier C, Jick SS, Meier CR . Use of metformin is not associated with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer: a case-control analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2012; 21: 280–286.
Li D, Yeung SC, Hassan MM, Konopleva M, Abbruzzese JL . Antidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2009; 137: 482–488.
Bodmer M, Becker C, Meier C, Jick SS, Meier CR . Use of antidiabetic agents and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a case-control analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2012; 107: 620–626.
Donadon V, Balbi M, Ghersetti M, Grazioli S, Perciaccante A, Della Valentina G et al. Antidiabetic therapy and increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15: 2506–2511.
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM et al. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3297–3302.
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Jenkins-Jones S, Gale EA, Johnson JA, Morgan CL . Mortality after incident cancer in people with and without type 2 diabetes: impact of metformin on survival. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 299–304.
Garrett CR, Hassabo HM, Bhadkamkar NA, Wen S, Baladandayuthapani V, Kee BK et al. Survival advantage observed with the use of metformin in patients with type II diabetes and colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2012; 106: 1374–1378.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Cufi S, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA . Metformin and energy metabolism in breast cancer: from insulin physiology to tumour-initiating stem cells. Curr Mol Med 2010; 10: 674–691.
Hardie DG . AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 774–785.
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M . Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 10269–10273.
Goodwin PJ, Pritchard KI, Ennis M, Clemons M, Graham M, Fantus IG . Insulin-lowering effects of metformin in women with early breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 2008; 8: 501–505.
Goodwin PJ, Stambolic V, Lemieux J, Chen BE, Parulekar WR, Gelmon KA et al. Evaluation of metformin in early breast cancer: a modification of the traditional paradigm for clinical testing of anti-cancer agents. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011; 126: 215–220.
Pollak M . Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 915–928.
Hosono K, Endo H, Takahashi H, Sugiyama M, Sakai E, Uchiyama T et al. Metformin suppresses colorectal aberrant crypt foci in a short-term clinical trial. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2010; 3: 1077–1083.
Muti P, Berrino F, Krogh V, Villarini A, Barba M, Strano S et al. Metformin, diet and breast cancer: an avenue for chemoprevention. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 2661.
Martin-Castillo B, Dorca J, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Lopez-Bonet E, Garcia M et al. Incorporating the antidiabetic drug metformin in HER2-positive breast cancer treated with neo-adjuvant chemotherapy and trastuzumab: an ongoing clinical-translational research experience at the Catalan Institute of Oncology. Ann Oncol 2010; 21: 187–189.
Martin-Castillo B, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Menendez JA . Metformin and cancer: Doses, mechanisms and the dandelion and hormetic phenomena. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1057–1064.
Algire C, Zakikhani M, Blouin MJ, Shuai JH, Pollak M . Metformin attenuates the stimulatory effect of a high-energy diet on in vivo LLC1 carcinoma growth. Endocr Relat Cancer 2008; 15: 833–839.
Kalender A, Selvaraj A, Kim SY, Gulati P, Brûlé S, Viollet B et al. Metformin, independent of AMPK, inhibits mTORC1 in a rag GTPase-dependent manner. Cell Metab 2010; 11: 390–401.
Sancak Y, Peterson TR, Shaul YD, Lindquist RA, Thoreen CC, Bar-Peled L et al. The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science 2008; 320: 1496–1501.
Sancak Y, Bar-Peled L, Zoncu R, Markhard AL, Nada S, Sabatini DM . Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 2010; 141: 290–303.
Ben Sahra I, Regazzetti C, Robert G, Laurent K, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Auberger P et al. Metformin, independent of AMPK, induces mTOR inhibition and cell cycle arrest through REDD1. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 4366–4372.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Cufí S, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA . Metformin activates an Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM)/Chk2-regulated DNA damage-like response. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 1499–1501.
GoDARTS and UKPDS Diabetes Pharmacogenetics Study Group; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Zhou K, Bellenguez C, Spencer CC, Bennett AJ, Coleman RL, Tavendale R et al. Common variants near ATM are associated with glycemic response to metformin in type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 117–120.
Cheung PC, Salt IP, Davies SP, Hardie DG, Carling D . Characterization of AMP-activated protein kinase subunit isoforms and their role in AMP binding. J Biochem 2000; 346: 659–669.
Xiao B, Sanders MJ, Underwood E, Heath R, Mayer FV, Carmena D et al. Structure of mammalian AMPK and its regulation by ADP. Nature 2011; 472: 230–233.
Oakhill JS, Steel R, Chen ZP, Scott JW, Ling N, Tam S et al. AMPK is a direct adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Science 2011; 332: 1433–1435.
Carling D, Mayer FV, Sanders MJ, Gamblin SJ . AMP-activated protein kinase: nature's energy sensor. Nat Chem Biol 2011; 7: 512–518.
Hawley SA, Boudeau J, Reid JL, Mustard KJ, Udd L, Mäkelä TP et al. Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol 2003; 2: 28.
Woods A, Johnstone SR, Dickerson K, Leiper FC, Fryer LG, Neumann D et al. LKB1 is the upstream kinase in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. Curr Biol 2003; 13: 2004–2008.
Woods A, Dickerson K, Heath R, Hong SP, Momcilovic M, Johnstone SR et al. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase in mammalian cells. Cell Metab 2005; 2: 21–33.
Momcilovic M, Hong SP, Carlson M . Mammalian TAK1 activates Snf1 protein kinase in yeast and phosphorylates AMP-activated protein kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 25336–25343.
Zeqiraj E, Filippi BM, Deak M, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM . Structure of the LKB1-STRAD-MO25 complex reveals an allosteric mechanism of kinase activation. Science 2009; 326: 1707–1711.
Zeqiraj E, Filippi BM, Goldie S, Navratilova I, Boudeau J, Deak M et al. ATP and MO25alpha regulate the conformational state of the STRADalpha pseudokinase and activation of the LKB1 tumour suppressor. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e1000126.
McCarthy A, Lord CJ, Savage K, Grigoriadis A, Smith DP, Weigelt B et al. Conditional deletion of the Lkb1 gene in the mouse mammary gland induces tumour formation. J Pathol 2009; 219: 306–316.
Jansen M, Ten Klooster JP, Offerhaus GJ, Clevers H . LKB1 and AMPK family signaling: the intimate link between cell polarity and energy metabolism. Physiol Rev 2009; 89: 777–798.
Hemminki A, Markie D, Tomlinson I, Avizienyte E, Roth S, Loukola A et al. A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature 1998; 391: 184–187.
Esteller M, Avizienyte E, Corn PG, Lothe RA, Baylin SB, Aaltonen LA et al. Epigenetic inactivation of LKB1 in primary tumors associated with the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Oncogene 2000; 19: 164–168.
Bungard D, Fuerth BJ, Zeng PY, Faubert B, Maas NL, Viollet B et al. Signaling kinase AMPK activates stress-promoted transcription via histone H2B phosphorylation. Science 2010; 329: 1201–1205.
Kim J, Guan KL . Amino acid signaling in TOR activation. Annu Rev Biochem 2011; 80: 1001–1032.
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F et al. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6745–6752.
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Giuliano S, Larbret F, Ponzio G, Gounon P et al. Targeting cancer cell metabolism: the combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2465–2475.
Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan KL . TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell 2003; 115: 577–590.
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF, Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS et al. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell 2008; 30: 214–226.
Zakikhani M, Blouin MJ, Piura E, Pollak MN . Metformin and rapamycin have distinct effects on the AKT pathway and proliferation in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010; 123: 271–279.
Hsu PP, Kang SA, Rameseder J, Zhang Y, Ottina KA, Lim D et al. The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science 2011; 332: 1317–1322.
Yea SS, Fruman DA . Cell signaling. New mTOR targets Grb attention. Science 2011; 332: 1270–1271.
Yu Y, Yoon SO, Poulogiannis G, Yang Q, Ma XM, Villén J et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies Grb10 as an mTORC1 substrate that negatively regulates insulin signaling. Science 2011; 332: 1322–1326.
Ning J, Clemmons DR . AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits IGF-I signaling and protein synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells via stimulation of insulin receptor substrate 1 S794 and tuberous sclerosis 2 S1345 phosphorylation. Mol Endocrinol 2010; 24: 1218–1229.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA . If mammalian target of metformin indirectly is mammalian target of rapamycin, then the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor axis will audit the efficacy of metformin in cancer clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: e207–e209.
Rozengurt E, Sinnett-Smith J, Kisfalvi K . Crosstalk between insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and G protein-coupled receptor signaling systems: a novel target for the antidiabetic drug metformin in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 2505–2511.
Kisfalvi K, Eibl G, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E . Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein-coupled receptor and insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 6539–6545.
Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, Buzzai M, Mu J, Xu Y et al. AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell 2005; 18: 283–293.
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ, Jin S . The coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci US 2005; 102: 8204–8209.
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G . TP53 and MTOR crosstalk to regulate cellular senescence. Aging (Albany NY) 2010; 2: 535–537.
Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Malik SA, Kroemer G . Autophagy regulation by p53. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010; 22: 181–185.
Liang J, Shao SH, Xu ZX, Hennessy B, Ding Z, Larrea M et al. The energy sensing LKB1-AMPK pathway regulates p27(kip1) phosphorylation mediating the decision to enter autophagy or apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 218–224.
Budanov AV, Karin M . p53 target genes sestrin1 and sestrin2 connect genotoxic stress and mTOR signaling. Cell 2008; 134: 451–460.
Maiuri MC, Malik SA, Morselli E, Kepp O, Criollo A, Mouchel PL et al. Stimulation of autophagy by the p53 target gene Sestrin2. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 1571–1576.
Leontieva OV, Gudkov AV, Blagosklonny MV . Weak p53 permits senescence during cell cycle arrest. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 4323–4327.
Narita M, Young AR, Arakawa S, Samarajiwa SA, Nakashima T, Yoshida S et al. Spatial coupling of mTOR and autophagy augments secretory phenotypes. Science 2011; 332: 966–970.
Algire C, Amrein L, Bazile M, David S, Zakikhani M, Pollak M . Diet and tumor LKB1 expression interact to determine sensitivity to anti-neoplastic effects of metformin in vivo. Oncogene 2011; 30: 1174–1182.
Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T, Christophorou MA, Evan GI et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 326–336.
Segal ED, Yasmeena A, Beauchampa M-C, Rosenblatta J, Pollakb M, Gotlieba WH et al. Relevance of the OCT1 transporter to the antineoplastic effect of biguanides. Biochem. Biophys. Res Commun 2011; 414: 694–699.
Shu Y, Sheardown SA, Brown C, Owen RP, Zhang S, Castro RA et al. Effect of genetic variation in the organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) on metformin action. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 1422–1431.
Tzvetkov MV, Vormfelde SV, Balen D, Meineke I, Schmidt T, Sehrt D et al. The effects of genetic polymorphisms in the organic cation transporters OCT1, OCT2, and OCT3 on the renal clearance of metformin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2009; 86: 299–306.
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene 2008; 27: 3576–3586.
Cantrell LA, Zhou C, Mendivil A, Malloy KM, Gehrig PA, Bae-Jump VL . Metformin is a potent inhibitor of endometrial cancer cell proliferation-implications for a novel treatment strategy. Gynecol Oncol 2010; 116: 92–98.
Gotlieb WH, Saumet J, Beauchamp MC, Gu J, Lau S, Pollak MN et al. In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2008; 110: 246–250.
Green AS, Chapuis N, Maciel TT, Willems L, Lambert M, Arnoult C et al. The LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway has tumor suppressor activity in acute myeloid leukemia through the repression of mTOR-dependent oncogenic mRNA translation. Blood 2010; 116: 4262–4273.
Isakovic A, Harhaji L, Stevanovic D, Markovic Z, Sumarac-Dumanovic M, Starcevic V et al. Dual antiglioma action of metformin: cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2007; 64: 1290–1302.
Memmott RM, Mercado JR, Maier CR, Kawabata S, Fox SD, Dennis PA . Metformin prevents tobacco carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2010; 3: 1066–1076.
Alimova IN, Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Dillon T, Lind SE et al. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 909–915.
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N . Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10804–10812.
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Deng XS, Alimova IN, Lind SE et al. Metformin induces unique biological and molecular responses in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 2031–2040.
Phoenix KN, Vumbaca F, Claffey KP . Therapeutic metformin/AMPK activation promotes the angiogenic phenotype in the ERalpha negative MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009; 113: 101–111.
Zhuang Y, Miskimins WK . Cell cycle arrest in Metformin treated breast cancer cells involves activation of AMPK, downregulation of cyclin D1, and requires p27Kip1 or p21Cip1. J Mol Signal 2008; 3: 18.
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K . Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7507–7511.
Saito S, Furuno A, Sakurai J, Sakamoto A, Park HR, Shin-Ya K et al. Chemical genomics identifies the unfolded protein response as a target for selective cancer cell killing during glucose deprivation. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 4225–4234.
Rattan R, Graham RP, Maguire JL, Giri S, Shridhar V . Metformin suppresses ovarian cancer growth and metastasis with enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity in vivo. Neoplasia 2011; 13: 483–491.
Zhuang Y, Miskimins WK . Metformin induces both caspase-dependent and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-dependent cell death in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 2011; 9: 603–615.
Anisimov VN, Berstein LM, Egormin PA, Piskunova TS, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA et al. Effect of metformin on life span and on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Exp Gerontol 2005; 40: 685–693.
Anisimov VN, Berstein LM, Egormin PA, Piskunova TS, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA et al. Metformin slows down aging and extends life span of female SHR mice. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 2769–2773.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Menendez JA . The antidiabetic drug metformin suppresses HER2 (erbB-2) oncoprotein overexpression via inhibition of the mTOR effector p70S6K1 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 88–96.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Cufi S, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B, Lopez-Bonet E et al. The anti-diabetic drug metformin suppresses the metastasis-associated protein CD24 in MDA-MB-468 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 2011; 25: 135–140.
Kakarala M, Wicha MS . Implications of the cancer stem-cell hypothesis for breast cancer prevention and therapy. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 2813–2820.
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C, Osborne CK, Wu MF et al. Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 672–679.
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K . Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3196–3201.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA . The anti-diabetic drug metformin suppresses self-renewal and proliferation of trastuzumab-resistant tumor-initiating breast cancer stem cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011; 126: 355–364.
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Cufi S, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B, Menendez JA . Metformin regulates breast cancer stem cell ontogeny by transcriptional regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) status. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 3807–3814.
Zakikhani M, Dowling RJ, Sonenberg N, Pollak MN . The effects of adiponectin and metformin on prostate and colon neoplasia involve activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2008; 1: 369–375.
Tomimoto A, Endo H, Sugiyama M, Fujisawa T, Hosono K, Takahashi H et al. Metformin suppresses intestinal polyp growth in ApcMin/+ mice. Cancer Sci 2008; 99: 2136–2141.
Hosono K, Endo H, Takahashi H, Sugiyama M, Uchiyama T, Suzuki K et al. Metformin suppresses azoxymethane-induced colorectal aberrant crypt foci by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol Carcing 2010; 49: 662–671.
Algire C, Amrein L, Zakikhani M, Panasci L, Pollak M . Metformin blocks the stimulative effect of a high-energy diet on colon carcinoma growth in vivo and is associated with reduced expression of fatty acid synthase. Endocr Relat Cancer 2010; 17: 351–360.
Kourelis TV, Siegel RD . Metformin and cancer: new applications for an old drug. Med Oncol 2012; 29: 1314–1327.
Campagnoli C, Pasanisi P, Abbà C, Ambroggio S, Biglia N, Brucato T et al. Effect of different doses of Metformin on serum testosterone and insulin in non-diabetic breast cancer patients: a randomized study. Clinical Breast Cancer 2012; 12: 175–182.
Cazzaniga M, Bonanni B, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Decensi A . Is it time to test metformin in breast cancer clinical trials? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009; 18: 701–705.
Mackenzie MJ, Ernst S, Johnson C, Winquist E . A phase I study of temsirolimus and metformin in advanced solid tumours. Invest New Drugs 2012; 30: 647–652.
Roberts DL, Dive C, Renehan AG . Biological mechanisms linking obesity and cancer risk: new perspectives. Annu Rev Med 2010; 61: 301–316.
Pavlides S, Whitaker-Menezes D, Castello-Cros R, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Frank PG et al. The reverse Warburg effect: aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor stroma. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 3984–4001.
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pestell RG, Howell A, Tykocinski ML, Nagajyothi F, Machado FS et al. Energy transfer in “parasitic” cancer metabolism. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 4208–4216.
Whitaker-Menezes D, Flomenberg N, Birbe RC, Witkiewicz AK, Pavlides S, Tsirigos A et al. Hyperactivation of oxidative mitochondrial metabolism in epithelial cancer cells in situ: visualizing the therapeutic effects of metformin in tumor tissue. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 4047–4064.
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Prisco M, Ertel A, Tsirigos A, Lin Z, Pavlides S et al. Ketones and lactate increase cancer cell “stemness”, driving recurrence, metastasis and poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. Achieving personalized medicine via metabolo-genomics. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 1271–1286.
Vazquez-Martin A, López-Bonetc E, Cufí S, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B et al. Repositioning chloroquine and metformin to eliminate cancer stem cell traits in pre-malignant lesions. Drug Resist Updat 2011; 14: 212–223.
Ward PS, Thompson CB . Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 297–308.
Pollak M . Metformin and other biguanides in oncology: advancing the research agenda. Cancer Prev Res 2010; 9: 1060–1065.
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B et al. Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res 2010; 11: 1451–1461.
Pollak M . The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: an update. Nat Rev Can 2012; 13: 159–169.
Niraula S, Stambolic V, Dowling RJO, Ennis M, Chang MC, Done SJ et al. Clinical and biologic effects of metformin in early stage breast cancer. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 104s.
Hadad SM, Dewar JA, Elseedawy E, Jordan LB, Purdie C, Bray SE et al. Gene signature of metformin actions on primary breast cancer within a window of opportunity randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 560.
Hadad SM, Iwamoto T, Jordan L, Purdie C, Bray S, Baker L et al. Evidence for biological effects of metformin in operable breast cancer: a pre-operative, window-of-opportunity, randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011; 128: 783–794.
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Cufí S, Vazquez-Martin A, Torres-Garcia VZ, Del Barco S, Martin-Castillo B et al. Micro(mi)RNA expression profile of breast cancer epithelial cells treated with the anti-diabetic drug metformin: induction of the tumor suppressor miRNA let-7a and suppression of the TGF-induced oncomiR miRNA-181a. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 1144–1151.
Feng Z . p53 regulation of the IGF-1/AKT/mTOR pathways and the endosomal compartment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a001057.
Lee JW, Park S, Takahashi Y, Wang HG . The association of AMPK with ULK1 regulates autophagy. PLoS One 2010; 5: e15394.
Chiacchiera F, Simone C . The AMPK-FoxO3A axis as a target for cancer treatment. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1091–1096.
Frenzel A, Grespi F, Chmelewskij W, Villunger A . Bcl2 family proteins in carcinogenesis and the treatment of cancer. Apoptosis 2009; 14: 584–596.
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Mizrachy L, Idelchuk Y, Koren I, Eisenstein M et al. DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1 promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of autophagy. EMBO Rep 2009; 10: 285–292.
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Eisenstein M, Kimchi A . Phosphorylation of Beclin 1 by DAP-kinase promotes autophagy by weakening its interactions with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. Autophagy 2009; 5: 720–722.
Strappazzon F, Vietri-Rudan M, Campello S, Nazio F, Florenzano F, Fimia GM et al. Mitochondrial BCL-2 inhibits AMBRA1-induced autophagy. EMBO J. 2011; 30: 1195–1208.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministero dell′Università e della Ricerca with the MIUR 5 × 1000 grant no. DO11/002 and by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC grant no. R10/029). MAP would like to thank Dr Mathias Christian Zohoungbogbo who first introduced him to metformin. The authors wish to thank Dr Daniela Majerna for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierotti, M., Berrino, F., Gariboldi, M. et al. Targeting metabolism for cancer treatment and prevention: metformin, an old drug with multi-faceted effects. Oncogene 32, 1475–1487 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.181
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.181
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Metformin and cancer hallmarks: shedding new lights on therapeutic repurposing
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Diabetes and anti-diabetic interventions and the risk of gynaecological and obstetric morbidity: an umbrella review of the literature
BMC Medicine (2023)
-
Novel phloretin-based combinations targeting glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma through GLUT2/PEPCK axis of action: in silico molecular modelling and in vivo studies
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
The development and benefits of metformin in various diseases
Frontiers of Medicine (2023)
-
The promising therapeutic effects of metformin on metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts in solid tumors
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2022)