Abstract
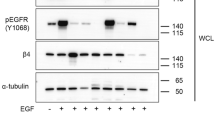
Cancer progression, response to therapy and metastasis depend on tumor microenvironment. Integrins are cell-adhesion receptors that mediate interactions of cells with extracellular matrix. The αv-β-family of integrins contributes to tumorigenesis, response to therapy and cancer stem cell biology. Thus, understanding the function of specific integrins in cancer is critical for the development of therapeutic approaches targeting integrins. The study investigated the role of integrin β5 in breast carcinomas by depleting integrin β5 using RNA interference and reexpression of integrin β5. Depletion of integrin β5 in triple-negative breast carcinoma cells markedly reduced tumor take, growth and tumor angiogenesis, whereas reexpression of integrin β5 rescued this phenotype. Reduction in tumor angiogenesis is associated with lower expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-A in integrin β5-depleted tumors. Tumor cells deficient in integrin β5 have lower migration and proliferative capacities. Biochemical assays revealed that integrin β5 mediates the Src-focal adhesion kinase and MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling events that operate independently, and inhibition of these pathways phenocopies integrin β5 deficiency. Breast carcinoma cells express high levels of integrin β5, whereas expression of integrin β3 is limited to stromal compartments and integrin β6 is lost in metastatic cells. Together, these findings show a critical role for integrin β5 in the tumorigenic potential of breast carcinoma cells and therapeutic targeting of integrin β5 is especially attractive for triple-negative breast carcinomas, which are refractory to most of the current therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ . Cancer Statistics 2007 CA Cancer J Clin 2007; 57: 43–66.
Colombo P-E, Milanezi F, Weigelt B, Reis-Filho J . Microarrays in the 2010s: the contribution of microarray-based gene expression profiling to breast cancer classification, prognostication and prediction. Breast Cancer Research 2011; 13: 212.
Alvarez R . Present and future evolution of advanced breast cancer therapy. Breast Cancer Res 2010; 12 (Suppl 2): S1.
Turner N, Lambros MB, Horlings HM, Pearson A, Sharpe R, Natrajan R et al. Integrative molecular profiling of triple negative breast cancers identifies amplicon drivers and potential therapeutic targets. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2013–2023.
Ding L, Ellis MJ, Li S, Larson DE, Chen K, Wallis JW et al. Genome remodelling in a basal-like breast cancer metastasis and xenograft. Nature 2010; 464: 999–1005.
Takada Y, Ye X, Simon S . The integrins. Genome Biol 2007; 8: 215.
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA . Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 9–22.
Bianchi A, Gervasi M, Bakin A . Role of beta5-integrin in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in response to TGF-beta. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1647–1659.
Hood JD, Frausto R, Kiosses WB, Schwartz MA, Cheresh DA . Differential alphav integrin-mediated Ras-ERK signaling during two pathways of angiogenesis. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 933–943.
Maubant S, Cruet-Hennequart S, Poulain L, Carreiras F, Sichel F, Luis J et al. Altered adhesion properties and alphav integrin expression in a cisplatin-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cell line. Int J Cancer 2002; 97: 186–194.
Monferran S, Skuli N, Delmas C, Favre G, Bonnet J, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E et al. Alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 integrins control glioma cell response to ionising radiation through ILK and RhoB. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 357–364.
Luo M, Guan J-L . Focal adhesion kinase: a prominent determinant in breast cancer initiation, progression and metastasis. Cancer Lett 2010; 289: 127–139.
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, Evans J, Brunton VG, Frame MC . The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer - a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 505–515.
Eliceiri BP, Puente XS, Hood JD, Stupack DG, Schlaepfer DD, Huang XZ et al. Src-mediated coupling of focal adhesion kinase to integrin alpha(v)beta5 in vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. J Cell Biol 2002; 157: 149–160.
Lim Y, Han I, Jeon J, Park H, Bahk YY, Oh ES . Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at tyrosine 861 is crucial for Ras transformation of fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 29060–29065.
Lin TH, Aplin AE, Shen Y, Chen Q, Schaller M, Romer L et al. Integrin-mediated activation of MAP kinase is independent of FAK: evidence for dual integrin signaling pathways in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 1997; 136: 1385–1395.
Schlaepfer DD, Jones KC, Hunter T . Multiple Grb2-mediated integrin-stimulated signaling pathways to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase: summation of both c-Src- and focal adhesion kinase-initiated tyrosine phosphorylation events. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 2571–2585.
Schlaepfer DD, Hanks SK, Hunter T, van der Geer P . Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 1994; 372: 786–791.
Yom C, Noh D-Y, Kim W, Kim H . Clinical significance of high focal adhesion kinase gene copy number and overexpression in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011; 128: 647–655.
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, Lu X, Brown M, Miron A et al. X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 121–132.
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S, Souleimanova M, Zhao H et al. Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat Med 2008; 14: 518–527.
Bakin AV, Safina A, Rinehart C, Daroqui C, Darbary H, Helfman DM . A critical role of tropomyosins in TGF-{beta} regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell motility in epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 2004; 15: 4682–4694.
Frisch SM, Screaton RA . Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001; 13: 555–562.
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W . Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 2010; 79: 351–379.
Meyer T, Marshall JF, Hart IR . Expression of alphav integrins and vitronectin receptor identity in breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 1998; 77: 530–536.
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C . Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 2315–2319.
Turner CE . Paxillin and focal adhesion signalling. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: E231–E236.
Frey RS, Mulder KM . Involvement of ERK 2 and stress-activated protein kinase/JNK activation by TGF-beta in the negative growth control of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 628–633.
Mucsi I, Skorecki KL, Goldberg HJ . ERK and the small GTP-binding protein, Rac, contribute to the effects of TGF-beta1 on gene expression. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 16567–16572.
Dumont N, Bakin AV, Arteaga CL . Autocrine transforming growth factor-beta signaling mediates smad-independent motility in human cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 3275–3285.
Ricono JM, Huang M, Barnes LA, Lau SK, Weis SM, Schlaepfer DD et al. Specific cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and integrin alphavbeta5 promotes carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1383–1391.
Moro L, Dolce L, Cabodi S, Bergatto E, Erba EB, Smeriglio M et al. Integrin-induced epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor activation requires c-Src and p130Cas and leads to phosphorylation of specific EGF receptor tyrosines. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 9405–9414.
Lombardo LJ, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Barrish JC, Behnia K et al. Discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methyl-phenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino)thiazole-5-carboxamide (BMS-354825), a dual Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical assays. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 6658–6661.
Slack-Davis JK, Martin KH, Tilghman RW, Iwanicki M, Ung EJ, Autry C et al. Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14845–14852.
Wary KK, Mariotti A, Zurzolo C, Giancotti FG . A requirement for caveolin-1 and associated kinase Fyn in integrin signaling and anchorage-dependent cell growth. Cell 1998; 94: 625–634.
Brunton VG, Avizienyte E, Fincham VJ, Serrels B, Metcalf CA, Sawyer TK et al. Identification of Src-specific phosphorylation site on focal adhesion kinase: dissection of the role of Src SH2 and catalytic functions and their consequences for tumor cell behavior. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 1335–1342.
Mitra SK, Mikolon D, Molina JE, Hsia DA, Hanson DA, Chi A et al. Intrinsic FAK activity and Y925 phosphorylation facilitate an angiogenic switch in tumors. Oncogene 2006; 25: 5969–5984.
Schneider BP, Sledge GW . Drug insight: VEGF as a therapeutic target for breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2007; 4: 181–189.
Lee TH, Seng S, Sekine M, Hinton C, Fu Y, Avraham HK et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates intracrine survival in human breast carcinoma cells through internally expressed VEGFR1/FLT1. PLoS Med 2007; 4: e186.
Abu-Ghazaleh R, Kabir J, Jia H, Lobo M, Zachary I . Src mediates stimulation by vascular endothelial growth factor of the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at tyrosine 861, and migration and anti-apoptosis in endothelial cells. Biochem J 2001; 360 (Pt 1): 255–264.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000; 100: 57–70.
Ogata H, Sato H, Takatsuka J, De Luca LM . Human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells fail to express the neurofibromin protein, lack its type I mRNA isoform and show accumulation of P-MAPK and activated Ras. Cancer Lett 2001; 172: 159–164.
Ricono JM, Huang M, Barnes LA, Lau SK, Weis SM, Schlaepfer DD et al. Specific cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and integrin alphavbeta5 promotes carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1383–1391.
Lim Y, Han I, Jeon J, Park H, Bahk Y-Y, Oh E-S . Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at tyrosine 861 is crucial for ras transformation of fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 29060–29065.
Ishigaki T, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Shimojo N, Matsushima S, Taki W, Yoshida T . Tenascin-C enhances crosstalk signaling of integrin αvÎ23/PDGFR-Î2 complex by SRC recruitment promoting PDGF-induced proliferation and migration in smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 2011; 226: 2617–2624.
Feig LA, Cooper GM . Relationship among guanine nucleotide exchange, GTP hydrolysis, and transforming potential of mutated ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol 1988; 8: 2472–2478.
Zhang H, Li Z, Viklund EK, Stromblad S . P21-activated kinase 4 interacts with integrin alpha v beta 5 and regulates alpha v beta 5-mediated cell migration. J Cell Biol 2002; 158: 1287–1297.
Berditchevski F . Complexes of tetraspanins with integrins: more than meets the eye. J Cell Sci 2001; 114 (Pt 23): 4143–4151.
Safina A, Vandette E, Bakin AV . ALK5 promotes tumor angiogenesis by upregulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 in tumor cells. Oncogene 2007; 26: 2407–2422.
Safina A, Ren M-Q, Vandette E, Bakin AV . TAK1 is required for TGF-[beta]1-mediated regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and metastasis. Oncogene 2008; 27: 1198–1207.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NYSDOH-HSRB Peter T Rowley Breast Cancer Project and in part by RPCI Cancer Center Support Grant CA 16056. We thank Dr Irwin Gelman for his helpful discussion of the manuscript, Drs Raymond Birge, Jianmin Zhang and Yahao Bu for providing reagents and Drs Kitty De Jong and Janice Hoffmann (RPCI flow cytometry facility) for their technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianchi-Smiraglia, A., Paesante, S. & Bakin, A. Integrin β5 contributes to the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells through the Src-FAK and MEK-ERK signaling pathways. Oncogene 32, 3049–3058 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.320
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.320
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TGF-β1 signalling in Alzheimer’s pathology and cytoskeletal reorganization: a specialized Tau perspective
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2023)
-
Extracellular matrix remodeling in tumor progression and immune escape: from mechanisms to treatments
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
SRC kinase-mediated signaling pathways and targeted therapies in breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research (2022)
-
Numb exon 9 inclusion regulates Integrinβ5 surface expression and promotes breast cancer metastasis
Oncogene (2022)
-
Osthole inhibits the migration and invasion of highly metastatic breast cancer cells by suppressing ITGα3/ITGβ5 signaling
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)