Abstract
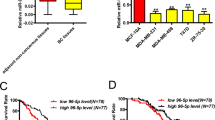
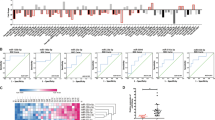
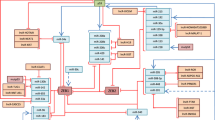
The WASF3 gene promotes invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells, which have undergone epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition (EMT). Overexpression of WASF3 in cells that do not show EMT increases their invasion potential as a result of increased ZEB1/2 levels, which specifically suppress the anti-invasion chromosome 1 miR-200a/200b/429 cluster. ZEB1/2 upregulation by WASF3 results from downregulation of KISS1, leading to the release of inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)κB by IκBα. We further show that ZEB1 expression is regulated by the NFκB transcription factor. Knockdown of WASF3 in breast cancer cells leads to reduced ZEB1 levels and increased miR-200 and E-cadherin levels, resulting in loss of invasion potential. The central regulation of this interactive pathway by WASF3 accounts for the increased invasion associated with increased WASF3 expression seen in aggressive breast cancer cells. WASF3, therefore, is a potential target to suppress invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Jechlinger M, Sommer A, Moriggl R, Seither P, Kraut N, Capodiecci P et al. Autocrine PDGFR signaling promotes mammary cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 1561–1570.
Johnson E, Seachrist DD, DeLeon-Rodriguez CM, Lozada KL, Miedler J, Abdul-Karim FW et al. HER2/ErbB2-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion require p120 catenin activation of Rac1 and Cdc42. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 29491–29501.
Chuang TC, Hsu SC, Cheng YT, Shao WS, Wu K, Fang GS et al. Magnolol down-regulates HER2 gene expression, leading to inhibition of HER2-mediated metastatic potential in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett 2011; 311: 11–19.
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z . Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010; 141: 52–67.
Steeg PS, Ouatas T, Halverson D, Palmieri D, Salerno M . Metastasis suppressor genes: basic biology and potential clinical use. Clin Breast Cancer 2003; 4: 51–62.
Teng Y, Liu M, Cowell JK . Functional interrelationship between the WASF3 and KISS1 metastasis-associated genes in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2011; 129: 2825–2835.
Pollock CB, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, Kolch W, Dhillon AS . Oncogenic K-RAS is required to maintain changes in cytoskeletal organization, adhesion, and motility in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 1244–1250.
Adorno M, Cordenonsi M, Montagner M, Dupont S, Wong C, Hann B et al. A Mutant-p53/Smad complex opposes p63 to empower TGFbeta-induced metastasis. Cell 2009; 137: 87–98.
Sossey-Alaoui K, Li X, Ranalli TA, Cowell JK . WAVE3-mediated cell migration and lamellipodia formation are regulated downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 21748–21755.
Sossey-Alaoui K, Ranalli TA, Li X, Bakin AV, Cowell JK . WAVE3 promotes cell motility and invasion through the regulation of MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9 expression. Exp Cell Res 2005; 308: 135–145.
Sossey-Alaoui K, Safina A, Li X, Vaughan MM, Hicks DG, Bakin AV et al. Down-regulation of WAVE3, a metastasis promoter gene, inhibits invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Am J Pathol 2007a; 170: 2112–2121.
Teng Y, Ren MQ, Cheney R, Sharma S, Cowell JK . Inactivation of the WASF3 gene in prostate cancer cells leads to suppression of tumorigenicity and metastases. Br J Cancer 2010; 103: 1066–1075.
Sossey-Alaoui K, Su G, Malaj E, Roe B, Cowell JK . WAVE3 an actin-polymerization gene, is truncated and inactivated as a result of a constitutional t (1;13)(q21;q12) chromosome translocation in a patient with ganglioneuroblastoma. Oncogene 2002; 21: 5967–5974.
Takenawa T, Miki H . WASP and WAVE family proteins: key molecules for rapid rearrangement of cortical actin filaments and cell movement. J Cell Sci 2001; 114: 1801–1809.
Takenawa T, Suetsugu S . The WASP-WAVE protein network: connecting the membrane to the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 37–48.
Sossey-Alaoui K, Li X, Cowell JK . c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation of WAVE3 is required for lamellipodia formation and cell migration. J Biol Chem 2007b; 282: 26257–26265.
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Welch DR . Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7495–7498.
Ma L, Weinberg RA . MicroRNAs in malignant progression. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 570–572.
Tavazoie SF, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, Padua D, Wang Q, Bos PD et al. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2008; 451: 147–152.
Levy C, Khaled M, Iliopoulos D, Janas MM, Schubert S, Pinner S et al. Intronic miR-211 assumes the tumor suppressive function of its host gene in melanoma. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 841–849.
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH, Gregory PA, Goodall GJ et al. Contextual extracellular cues promote tumor cell EMT and metastasis by regulating miR-200 family expression. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 2140–2151.
Schliekelman MJ, Gibbons DL, Faca VM, Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH, Zhang Q et al. Targets of the tumor suppressor miR-200 in regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 7670–7682.
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF et al. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 7846–7854.
Elmén J, Lindow M, Schütz S, Lawrence M, Petri A, Obad S et al. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008; 452: 896–899.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 593–601.
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y . The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 14910–14914.
Ahmad A, Aboukameel A, Kong D, Wang Z, Sethi S, Chen W et al. Phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulated by miR-200 in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3400–3409.
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S et al. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep 2008; 9: 582–589.
Brabletz S, Bajdak K, Meidhof S, Burk U, Niedermann G, Firat E et al. The ZEB1/miR-200 feedback loop controls Notch signalling in cancer cells. EMBO J 2011; 30: 770–782.
Mazda M, Nishi K, Naito Y, Ui-Tei K . E-cadherin is transcriptionally activated via suppression of ZEB1 transcriptional repressor by small RNA-mediated gene silencing. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e28688.
Hurteau GJ, Carlson JA, Spivack SD, Brock GJ . Overexpression of the microRNA hsa-miR-200c leads to reduced expression of transcription factor 8 and increased expression of E-cadherin. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 7972–7976.
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Wahlbuhl M, Dimmler A, Bauer K, Sultan A et al. The transcriptional repressor ZEB1 promotes metastasis and loss of cell polarity in cancer. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 537–544.
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE, Morimiya A, Badve S, Nakshatri H . NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells: potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2. Oncogene 2007; 26: 711–724.
Edwards LA, Woolard K, Son MJ, Li A, Lee J, Ene C et al. Effect of brain- and tumor-derived connective tissue growth factor on glioma invasion. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011; 103: 1162–1178.
Almeida MI, Reis RM, Calin GA . MYC-microRNA-9-metastasis connection in breast cancer. Cell Res 2010; 20: 603–604.
Png KJ, Halberg N, Yoshida M, Tavazoie SF . A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and metastasis by cancer cells. Nature 2011; 481: 190–194.
Teng Y, Ngoka L, Mei Y, Lesoon L, Cowell JK . HSP90 and HSP70 proteins are essential for stabilization and activation of WASF3 metastasis-promoting protein. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 10051–10059.
Ghoshal P, Teng Y, Lesoon L, Cowell JK . Hypoxia—induced upregulation of the WASF3 metastasis associated gene leads to enhanced invasion in breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2012; 131: E905–E915.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A . Snail Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 415–428.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009; 139: 871–890.
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Fournier KF, Wang H, Marquis L, Abbruzzese JL et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 5820–5828.
Kurisu S, Takenawa T . WASP and WAVE family proteins: friends or foes in cancer invasion? Cancer Sci 2010; 101: 2093–2104.
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C, Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2010; 12: R68.
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T et al. A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 515–527.
Cabanillas AM, Darling DS . Alternative splicing gives rise to two isoforms of Zfhep, a zinc finger/homeodomain protein that binds T3-response elements. DNA Cell Biol 1996; 15: 643–651.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Leslie Ann Lesoon for the technical assistance and helpful comments during the writing of this manuscript. We also thank the staff of Cancer Center Shared Resources at GHSU for assistance during microarray data collection. Dr Cowell is supported by the Georgia Cancer Coalition as a distinguished cancer scholar and funded by the NIH. This study was supported, in part, by the National Institutes of Health Grant CA120510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, Y., Mei, Y., Hawthorn, L. et al. WASF3 regulates miR-200 inactivation by ZEB1 through suppression of KISS1 leading to increased invasiveness in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 33, 203–211 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.565
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.565
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The WAVE3/β-catenin oncogenic signaling regulates chemoresistance in triple negative breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research (2023)
-
The Ephrin tyrosine kinase a3 (EphA3) is a novel mediator of RAGE-prompted motility of breast cancer cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
SHOX2 cooperates with STAT3 to promote breast cancer metastasis through the transcriptional activation of WASF3
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
Phosphorylation of the proline-rich domain of WAVE3 drives its oncogenic activity in breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
WAVE3 phosphorylation regulates the interplay between PI3K, TGF-β, and EGF signaling pathways in breast cancer
Oncogenesis (2020)