Abstract
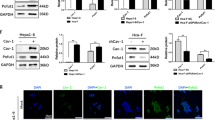
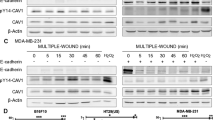
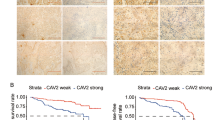
Caveolin-1 exhibits a stage-dependent, functional fluctuation during pancreatic cancer development, but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we report that cavin-1, a structural protein of caveolae, modulates the oncogenic function of caveolin-1 and cooperates with caveolin-1 to enhance pancreatic cancer aggressiveness. Cavin-1 expression is associated with caveolin-1 in pancreatic cancer tissue samples and cell lines, and predicts the metastatic potential of pancreatic cancer. Interactome analyses further revealed the physical interaction of cavin-1 and caveolin-1 and their colocalization in pancreatic cancer cells. Cavin-1 stabilizes caveolin-1 expression or activity by inhibiting its internalization and subsequent lysosomal degradation. More in-depth functional experiments showed that caveolin-1-enhanced aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer cells is dependent on the presence of cavin-1. In contrast, cavin-1 depletion inhibited the invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells, which could not be restored by caveolin-1-rescue construct. Tissue microarray analyses in two independent clinic cohorts also supported the augment of cavin-1 on the prognostic potency of caveolin-1, and showed that combination of cavin-1 with caveolin-1 predicted worse survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Of note, the phenotypes because of cavin-1 could not be achieved by other cavins such as cavin-2, and the tumor-promoting role of cavin-1 in pancreatic cancer was found to be largely dependent on caveolin-1 expression, which highlights the critical role of cavin-1/caveoin-1 in pancreatic cancer progression, and suggests that the interruption of cavin-1/caveolin-1 interaction is a promising therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMT:
-
epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- IP:
-
immunoprecipitation
- RT–PCR:
-
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- qRT–PCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- GST:
-
glutathione S-transferase
- PI3K:
-
phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- TMA:
-
tissue microarray
References
Goetz JG, Lajoie P, Wiseman SM, Nabi IR . Caveolin-1 in tumor progression: the good, the bad and the ugly. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2008; 27: 715–735.
Hansen CG, Nichols BJ . Exploring the caves: cavins, caveolins and caveolae. Trends Cell Biol 2010; 20: 177–186.
Wiechen K, Diatchenko L, Agoulnik A, Scharff KM, Schober H, Arlt K et al. Caveolin-1 is down-regulated in human ovarian carcinoma and acts as a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Am J Pathol 2001; 159: 1635–1643.
Bender FC, Reymond MA, Bron C, Quest AF . Caveolin-1 levels are down-regulated in human colon tumors, and ectopic expression of caveolin-1 in colon carcinoma cell lines reduces cell tumorigenicity. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 5870–5878.
Chiu WT, Lee HT, Huang FJ, Aldape KD, Yao J, Steeg PS et al. Caveolin-1 upregulation mediates suppression of primary breast tumor growth and brain metastases by stat3 inhibition. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 4932–4943.
Wiechen K, Sers C, Agoulnik A, Arlt K, Dietel M, Schlag PM et al. Down-regulation of caveolin-1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene, in sarcomas. Am J Pathol 2001; 158: 833–839.
Fong A, Garcia E, Gwynn L, Lisanti MP, Fazzari MJ, Li M . Expression of caveolin-1 and caveolin-2 in urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder correlates with tumor grade and squamous differentiation. Am J Clin Pathol 2003; 120: 93–100.
Kato K, Hida Y, Miyamoto M, Hashida H, Shinohara T, Itoh T et al. Overexpression of caveolin-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with lymph node metastasis and pathologic stage. Cancer 2002; 94: 929–933.
Li L, Yang G, Ebara S, Satoh T, Nasu Y, Timme TL et al. Caveolin-1 mediates testosterone-stimulated survival/clonal growth and promotes metastatic activities in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4386–4392.
Ito Y, Yoshida H, Nakano K, Kobayashi K, Yokozawa T, Hirai K et al. Caveolin-1 overexpression is an early event in the progression of papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Br J Cancer 2002; 86: 912–916.
Murakami S, Miyamoto M, Hida Y, Cho Y, Fukunaga A, Oshikiri T et al. Caveolin-1 overexpression is a favorable prognostic factor for patients with extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. Br J Cancer 2003; 88: 1234–1238.
Karam JA, Lotan Y, Roehrborn CG, Ashfaq R, Karakiewicz PI, Shariat SF . Caveolin-1 overexpression is associated with aggressive prostate cancer recurrence. Prostate 2007; 67: 614–622.
Ho CC, Kuo SH, Huang PH, Huang HY, Yang CH, Yang PC . Caveolin-1 expression is significantly associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2008; 59: 105–110.
Burgermeister E, Xing X, Rocken C, Juhasz M, Chen J, Hiber M et al. Differential expression and function of caveolin-1 in human gastric cancer progression. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 8519–8526.
Terris B, Blaveri E, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, Jones M, Missiaglia E, Ruszniewski P et al. Characterization of gene expression profiles in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Am J Pathol 2002; 160: 1745–1754.
Chen ST, Lin SY, Yeh KT, Kuo SJ, Chan WL, Chu YP et al. Mutational, epigenetic and expressional analyses of caveolin-1 gene in breast cancers. Int J Mol Med 2004; 14: 577–582.
Lin M, DiVito MM, Merajver SD, Boyanapalli M, van GKL . Regulation of pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by RhoC GTPase and caveolin-1. Mol Cancer 2005; 4: 21.
Rao X, Evans J, Chae H, Pilrose J, Kim S, Yan P et al. CpG island shore methylation regulates caveolin-1 expression in breast cancer. Oncogene 2013; 32: 4519–4528.
Huang C, Qiu Z, Wang L, Peng Z, Jia Z, Logsdon CD et al. A novel FoxM1-caveolin signaling pathway promotes pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 655–665.
Nabi IR . Cavin fever: regulating caveolae. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 789–791.
Hill MM, Bastiani M, Luetterforst R, Kirkham M, Kirkham A, Nixon SJ et al. PTRF-Cavin, a conserved cytoplasmic protein required for caveolae formation and function. Cell 2008; 132: 113–124.
Hansen CG, Bright NA, Howard G, Nichols BJ . SDPR induces membrane curvature and functions in the formation of caveolae. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 807–814.
McMahon KA, Zajicek H, Li WP, Peyton MJ, Minna JD, Hernandez VJ et al. SRBC/cavin-3 is a caveolin adapter protein that regulates caveolae function. EMBO J 2009; 28: 1001–1015.
Bastiani M, Liu L, Hill MM, Jedrychowski MP, Nixon SJ, Lo HP et al. MURC/Cavin-4 and cavin family members form tissue-specific caveolar complexes. J Cell Biol 2009; 185: 1259–1273.
Quest AF, Gutierrez-Pajares JL, Torres VA . Caveolin-1: an ambiguous partner in cell signalling and cancer. J Cell Mol Med 2008; 12: 1130–1150.
Aung CS, Hill MM, Bastiani M, Parton RG, Parat MO . PTRF-cavin-1 expression decreases the migration of PC3 prostate cancer cells: role of matrix metalloprotease 9. Eur J Cell Biol 2011; 90: 136–142.
Gamez-Pozo A, Sanchez-Navarro I, Calvo E, Agulló-Ortuño MT, López-Vacas R, Díaz E et al. PTRF/cavin-1 and MIF proteins are identified as non-small cell lung cancer biomarkers by label-free proteomics. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e33752.
Harris J, Werling D, Koss M, Monaghan P, Taylor G, Howard CJ . Expression of caveolin by bovine lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells. Immunology 2002; 105: 190–195.
Thomas S, Preda-Pais A, Casares S, Brumeanu TD . Analysis of lipid rafts in T cells. Mol Immunol 2004; 41: 399–409.
Joshi B, Strugnell SS, Goetz JG, Kojic LD, Cox ME, Griffith OL et al. Phosphorylated caveolin-1 regulates Rho/ROCK-dependent focal adhesion dynamics and tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 8210–8220.
Jansa P, Mason SW, Hoffmann-Rohrer U, Grummt I . Cloning and functional characterization of PTRF, a novel protein which induces dissociation of paused ternary transcription complexes. EMBO J 1998; 17: 2855–2864.
Hasegawa T, Takeuchi A, Miyaishi O, Xiao H, Mao J, Isobe K . PTRF (polymerase I and transcript-release factor) is tissue-specific and interacts with the BFCOL1 (binding factor of a type-I collagen promoter) zinc-finger transcription factor which binds to the two mouse type-I collagen gene promoters. Biochem J 2000; 347 (Pt 1): 55–59.
Shi WD, Meng ZQ, Chen Z, Lin JH, Zhou ZH, Liu LM . Identification of liver metastasis-related genes in a novel human pancreatic carcinoma cell model by microarray analysis. Cancer Lett 2009; 283: 84–91.
Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Kuniyasu H, Eue I, Fidler IJ . In vivo selection and characterization of metastatic variants from human pancreatic adenocarcinoma by using orthotopic implantation in nude mice. Neoplasia 1999; 1: 50–62.
Liu L, Pilch PF . A critical role of cavin (polymerase I and transcript release factor) in caveolae formation and organization. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 4314–4322.
Liu L, Zhu XD, Wang WQ, Shen Y, Qin Y, Ren ZG et al. Activation of beta-catenin by hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to enhanced metastatic potential and poor prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 2740–2750.
Liu L, Ren ZG, Shen Y, Zhu XD, Zhang W, Xiong W et al. Influence of hepatic artery occlusion on tumor growth and metastatic potential in a human orthotopic hepatoma nude mouse model: relevance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Sci 2010; 101: 120–128.
Acknowledgements
We thank Zhi-Qiang Meng for providing the pancreatic cancer cells SW1990HM and Huan-Yu Xia for assistance in collecting the patient data. This research project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172005 and 81172276), the National Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (11ZR1407000) and PhD Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20110071120096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Xu, HX., Wang, WQ. et al. Cavin-1 is essential for the tumor-promoting effect of caveolin-1 and enhances its prognostic potency in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 33, 2728–2736 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.223
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.223
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of functional candidate genes for milk production traits in dairy sheep subjected to protein restriction in the prepubertal stage
BMC Genomics (2023)
-
Assessment of the diagnostic and prognostic relevance of ACAT1 and CE levels in plasma, peritoneal fluid and tumor tissue of epithelial ovarian cancer patients - a pilot study
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Caveolin-1 enhances brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer, potentially in association with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker SNAIL
Cancer Cell International (2019)
-
Identification of intracellular cavin target proteins reveals cavin-PP1alpha interactions regulate apoptosis
Nature Communications (2019)
-
LINC81507 act as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-199b-5p to facilitate NSCLC proliferation and metastasis via regulating the CAV1/STAT3 pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2019)