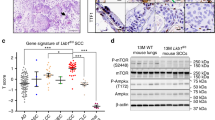
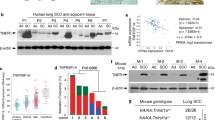
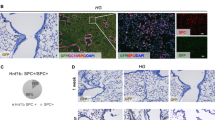
Abstract
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is linked to multiple cancers, including pulmonary adenocarcinoma. However, the role of STAT3 in lung cancer pathogenesis has not been determined. Using lung epithelial-specific inducible knockout strategies, we demonstrate that STAT3 has contrasting roles in the initiation and growth of both chemically and genetically induced lung cancers. Selective deletion of lung epithelial STAT3 in mice before cancer induction by the smoke carcinogen, urethane, resulted in increased lung tissue damage and inflammation, K-Ras oncogenic mutations and tumorigenesis. Deletion of lung epithelial STAT3 after establishment of lung cancer inhibited cancer cell proliferation. Simultaneous deletion of STAT3 and expression of oncogenic K-Ras in mouse lung elevated pulmonary injury, inflammation and tumorigenesis, but reduced tumor growth. These studies indicate that STAT3 prevents lung cancer initiation by maintaining pulmonary homeostasis under oncogenic stress, whereas it facilitates lung cancer progression by promoting cancer cell growth. These studies also provide a mechanistic basis for targeting STAT3 to lung cancer therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30.
Hecht SS . Cigarette smoking and lung cancer: chemical mechanisms and approaches to prevention. Lancet Oncol 2002; 3: 461–469.
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM . Lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1367–1380.
Riely GJ, Marks J, Pao W . KRAS mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2009; 6: 201–205.
Smith CJ, Perfetti TA, King JA . Perspectives on pulmonary inflammation and lung cancer risk in cigarette smokers. Inhal Toxicol 2006; 18: 667–677.
Hussain SP, Hofseth LJ, Harris CC . Radical causes of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 276–285.
Tuveson DA, Jacks T . Modeling human lung cancer in mice: similarities and shortcomings. Oncogene 1999; 18: 5318–5324.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R . STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 798–809.
Li N, Grivennikov SI, Karin M . The unholy trinity: inflammation, cytokines, and STAT3 shape the cancer microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 429–431.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999; 98: 295–303.
Azare J, Leslie K, Al-Ahmadie H, Gerald W, Weinreb PH, Violette SM et al. Constitutively activated Stat3 induces tumorigenesis and enhances cell motility of prostate epithelial cells through integrin beta 6. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 4444–4453.
Li Y, Du H, Qin Y, Roberts J, Cummings OW, Yan C . Activation of the signal transducers and activators of the transcription 3 pathway in alveolar epithelial cells induces inflammation and adenocarcinomas in mouse lung. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 8494–8503.
Mostertz W, Stevenson M, Acharya C, Chan I, Walters K, Lamlertthon W et al. Age- and sex-specific genomic profiles in non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA 2010; 303: 535–543.
Jiang R, Jin Z, Liu Z, Sun L, Wang L, Li K . Correlation of activated STAT3 expression with clinicopathologic features in lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Diagn Ther 2011; 15: 347–352.
Ai T, Wang Z, Zhang M, Zhang L, Wang N, Li W et al. Expression and prognostic relevance of STAT3 and cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biol Markers 2012; 27: e132–e138.
Dolled-Filhart M, Camp RL, Kowalski DP, Smith BL, Rimm DL . Tissue microarray analysis of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (Stat3) and phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) in node-negative breast cancer shows nuclear localization is associated with a better prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 594–600.
Pectasides E, Egloff AM, Sasaki C, Kountourakis P, Burtness B, Fountzilas G et al. Nuclear localization of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is associated with a better prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 2427–2434.
Couto JP, Daly L, Almeida A, Knauf JA, Fagin JA, Sobrinho-Simões M et al. STAT3 negatively regulates thyroid tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: E2361–E2370.
de la Iglesia N, Konopka G, Puram SV, Chan JA, Bachoo RM, You MJ et al. Identification of a PTEN-regulated STAT3 brain tumor suppressor pathway. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 449–462.
Musteanu M, Blaas L, Mair M, Schlederer M, Bilban M, Tauber S et al. Stat3 is a negative regulator of intestinal tumor progression in Apc(Min) mice. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 1003–1011.
Chan KS, Sano S, Kiguchi K, Anders J, Komazawa N, Takeda J et al. Disruption of Stat3 reveals a critical role in both the initiation and the promotion stages of epithelial carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 720–728.
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 103–113.
Ihara S, Kida H, Arase H, Tripathi LP, Chen YA, Kimura T et al. Inhibitory roles of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in antitumor immunity during carcinogen-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2012; 72: 2990–2999.
Peyser ND, Grandis JR . Critical analysis of the potential for targeting STAT3 in human malignancy. Onco Targets Ther 2013; 6: 999–1010.
Xu X, Rock JR, Lu Y, Futtner C, Schwab B, Guinney J et al. Evidence for type II cells as cells of origin of K-Ras-induced distal lung adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 4910–4915.
Hokuto I, Ikegami M, Yoshida M, Takeda K, Akira S, Perl AK et al. Stat-3 is required for pulmonary homeostasis during hyperoxia. J Clin Invest 2004; 113: 28–37.
Matsuzaki Y, Xu Y, Ikegami M, Besnard V, Park KS, Hull WM et al. Stat3 is required for cytoprotection of the respiratory epithelium during adenoviral infection. J Immunol 2006; 177: 527–537.
Dougan M, Li D, Neuberg D, Mihm M, Googe P, Wong KK et al. A dual role for the immune response in a mouse model of inflammation-associated lung cancer. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 2436–2446.
Ichikawa T, Yano Y, Uchida M, Otani S, Hagiwara K, Yano T . The activation of K-ras gene at an early stage of lung tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Lett 1996; 107: 165–170.
Wang X, Witschi H . Mutations of the Ki-ras protooncogene in 3-methylcholanthrene and urethan-induced and butylated hydroxytoluene-promoted lung tumors of strain A/J and SWR mice. Cancer Lett 1995; 91: 33–39.
Jackson EL, Willis N, Mercer K, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Montoya R et al. Analysis of lung tumor initiation and progression using conditional expression of oncogenic K-ras. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 3243–3248.
Yu CL, Meyer DJ, Campbell GS, Larner AC, Carter-Su C, Schwartz J et al. Enhanced DNA-binding activity of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src oncoprotein. Science 1995; 269: 81–83.
Chang Q, Bournazou E, Sansone P, Berishaj M, Gao SP, Daly L et al. The IL-6/JAK/Stat3 feed-forward loop drives tumorigenesis and metastasis. Neoplasia 2013; 15: 848–862.
Qu Z, Fu J, Ma H, Zhou J, Jin M, Mapara MY et al. PDLIM2 restricts Th1 and Th17 differentiation and prevents autoimmune disease. Cell Biosci 2012; 2: 23.
Yan P, Fu J, Qu Z, Li S, Tanaka T, Grusby MJ, Xiao G . PDLIM2 suppresses HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis by targeting Tax into the nuclear matrix for proteasomal degradation. Blood 2009; 113: 4370–4380.
Qu Z, Fu J, Yan P, Hu J, Cheng SY, Xiao G . Epigenetic repression of PDLIM2: implications for the biology and treatment of breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 11786–11792.
Qu Z, Yan P, Fu J, Jiang J, Grusby MJ, Smithgall TE et al. DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDLIM2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 1766–1772.
Yan P, Qu Z, Ishikawa C, Mori N, Xiao G . Human T-cell leukemia virus type I-mediated repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 involves DNA methylation but independent of the viral oncoprotein tax. Neoplasia 2009; 11: 1036–1041.
Fu J, Yan P, Li S, Qu Z, Xiao G . Molecular determinants of PDLIM2 in suppressing HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Onocogene 2010; 29: 6499–6507.
Zhang X, Guo A, Yu J, Possemato A, Chen Y, Zheng W et al. Identification of STAT3 as a substrate of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase T. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 4060–4064.
Brantley EC, Nabors LB, Gillespie GY, Choi YH, Palmer CA, Harrison K et al. Loss of protein inhibitors of activated STAT-3 expression in glioblastoma multiforme tumors: implications for STAT-3 activation and gene expression. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 4694–4704.
Sen M, Thomas SM, Kim S, Yeh JI, Ferris RL, Johnson JT et al. First-in-human trial of a STAT3 decoy oligonucleotide in head and neck tumors: implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 694–705.
Pan Y, Zhou F, Zhang R, Claret FX . Stat3 inhibitor Stattic exhibits potent antitumor activity and induces chemo- and radio-sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One 2013; 8: e54565.
Qu Z, Sun D, Young W . Lithium promotes neural precursor cell proliferation: evidence for the involvement of the non-canonical GSK-3β-NF-AT signaling. Cell Biosci 2011; 1: 18.
Rice WR, Conkright JJ, Na CL, Ikegami M, Shannon JM, Weaver TE . Maintenance of the mouse type II cell phenotype in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002; 283: L256–L264.
Corti M, Brody AR, Harrison JH . Isolation and primary culture of murine alveolar type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1996; 14: 309–315.
Qing G, Qu Z, Xiao G . Endoproteolytic processing of C-terminally truncated NF-κB2 precursors at κB-containing promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5324–5329.
Qing G, Qu Z, Xiao G . Stabilization of basally translated NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) protein functions as a molecular switch of processing of NF-κB2 p100. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 40578–40582.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the National Institute of Health (NIH)/National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants R01 CA172090, R21 CA175252, P30 CA047904, as well as the American Lung Association (ALA) Lung Cancer Discovery Award and American Cancer Society (ACS) Fellowship RSG-06-066-01-MGO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Qu, Z., Yan, S. et al. Differential roles of STAT3 in the initiation and growth of lung cancer. Oncogene 34, 3804–3814 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.318
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.318
This article is cited by
-
Oncogenic dependency on STAT3 serine phosphorylation in KRAS mutant lung cancer
Oncogene (2022)
-
The deubiquitinase USP16 functions as an oncogenic factor in K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis
Oncogene (2021)
-
Causative role of PDLIM2 epigenetic repression in lung cancer and therapeutic resistance
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Sex specific function of epithelial STAT3 signaling in pathogenesis of K-ras mutant lung cancer
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Hdac7 promotes lung tumorigenesis by inhibiting Stat3 activation
Molecular Cancer (2017)