Abstract
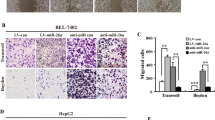
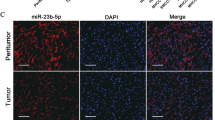
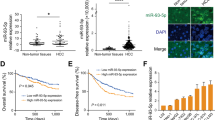
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent malignancies and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Tumour metastasis is one of the major causes of high mortality. microRNAshave been implicated in HCC metastasis. In this study, we found that miR-625 was frequently downregulated in HCC samples. A decrease in miR-625 was significantly correlated with lymph node anddistance metastasis (P=0.013), the presence of portal venous invasion (P=0.036), tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (P=0.027) and unfavourable overall survival (P=0.003). Compared with primary tumours, miR-625 expression was markedly reduced in portal venous metastatic tumours. Re-expression of miR-625 in HCC cells was remarkably effective in suppressing cell migration andinvasiveness in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, miR-625 was confirmed to downregulate IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1(IGF2BP1) directly, the expression of which was inversely correlated with the level of miR-625 in HCC cell lines and tissues. High expression of IGF2BP1 was frequently found in HCC samples, and associated with poor prognosis. Knockdown of endogenous IGF2BP1 by siRNA exhibited similar effects as the overexpression of miR-625, whereas overexpression of IGF2BP1 (without the 3′-UTR) abrogated miR-625-mediated metastasis inhibition. Interference of the PTEN/HSP27 pathway contributed to miR-625-mediated metastasis inhibition. Taken together, our data suggest that miR-625 might function as an antimetastatic miRNA to have an important role in HCC progression by modulating the IGF2BP1/PTEN pathway. The newly identified miR-625/IGF2BP1 axis represents a new potential therapeutic target for HCC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forner A, Hessheimer AJ, Isabel RM, Bruix J . Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006; 60: 89–98.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL . Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 2557–2576.
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN . Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008; 48: 2047–2063.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Negrini M, Nicoloso MS, Calin GA . MicroRNAs and cancer–new paradigms in molecular oncology. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009; 21: 470–479.
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . c-Myc-regulated microRNAsmodulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005; 435: 839–843.
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG et al. Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6092–6099.
Shimizu S, Takehara T, Hikita H, Kodama T, Miyagi T, Hosui A et al. The let-7 family of microRNAsinhibits Bcl-xL expression and potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2010; 52: 698–704.
Yao J, Liang L, Huang S, Ding J, Tan N, Zhao Y et al. MicroRNA-30d promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting Galphai2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010; 51: 846–856.
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, Au SL, Lee JM, Poon RT et al. The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology 2011; 140: 322–331.
Tan S, Li R, Ding K, Lobie PE, Zhu T . miR-198 inhibits migration andinvasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway. FEBS Lett 2011; 585: 2229–2234.
Yaniv K, Yisraeli JK . The involvement of a conserved family of RNA binding proteins in embryonic development and carcinogenesis. Gene 2002; 287: 49–54.
Yisraeli JK . VICKZ proteins: a multi-talented family of regulatory RNA-binding proteins. Biol Cell 2005; 97: 87–96.
Huttelmaier S, Zenklusen D, Lederer M, Dictenberg J, Lorenz M, Meng X et al. Spatial regulation of beta-actin translation by Src-dependent phosphorylation of ZBP1. Nature 2005; 438: 512–515.
Kobel M, Weidensdorfer D, Reinke C, Lederer M, Schmitt WD, Zeng K et al. Expression of the RNA-binding protein IMP1 correlates with poor prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Oncogene 2007; 26: 7584–7589.
Vainer G, Vainer-Mosse E, Pikarsky A, Shenoy SM, Oberman F, Yeffet A et al. A role for VICKZ proteins in the progression of colorectal carcinomas: regulating lamellipodia formation. J Pathol 2008; 215: 445–456.
Li LZ, Zhang CZ, Liu LL, Yi C, Lu SX, Zhou X et al. miR-720 inhibits tumor invasion and migration in breast cancer by targeting TWIST1. Carcinogenesis 2013; 35: 469–478.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007; 129: 1401–1414.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005; 435: 834–838.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Tang ZY . Hepatocellular carcinoma–cause, treatment and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7: 445–454.
Zhang X, Liu S, Hu T, He Y, Sun S . Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin expression. Hepatology 2009; 50: 490–499.
Tsai WC, Hsu PW, Lai TC, Chau GY, Lin CW, Chen CM et al. MicroRNA-122, a tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009; 49: 1571–1582.
Yan Y, Luo YC, Wan HY, Wang J, Zhang PP, Liu M et al. MicroRNA-10a is involved in the metastatic process by regulating Eph tyrosine kinase receptor A4-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transitionand adhesion in hepatoma cells. Hepatology 2013; 57: 667–677.
Oberman F, Rand K, Maizels Y, Rubinstein AM, Yisraeli JK . VICKZ proteins mediate cell migration via their RNA binding activity. RNA 2007; 13: 1558–1569.
Ross AF, Oleynikov Y, Kislauskis EH, Taneja KL, Singer RH . Characterization of a beta-actin mRNA zipcode-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 2158–2165.
Leung KM, van Horck FP, Lin AC, Allison R, Standart N, Holt CE . Asymmetrical beta-actin mRNA translation in growth cones mediates attractive turning to netrin-1. Nat Neurosci 2006; 9: 1247–1256.
Yao J, Sasaki Y, Wen Z, Bassell GJ, Zheng JQ . An essential role for beta-actin mRNA localization and translation in Ca2+-dependent growth cone guidance. Nat Neurosci 2006; 9: 1265–1273.
Lapidus K, Wyckoff J, Mouneimne G, Lorenz M, Soon L, Condeelis JS et al. ZBP1 enhances cell polarity and reduces chemotaxis. J Cell Sci 2007; 120: 3173–3178.
Vikesaa J, Hansen TV, Jonson L, Borup R, Wewer UM, Christiansen J et al. RNA-binding IMPs promote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation. EMBO J 2006; 25: 1456–1468.
Stohr N, Kohn M, Lederer M, Glass M, Reinke C, Singer RH et al. IGF2BP1 promotes cell migration by regulating MK5 and PTEN signaling. Genes Dev 2012; 26: 176–189.
Read DE, Gorman AM . Heat shock protein 27 in neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 382: 6–8.
Read DE, Gorman AM . Involvement of Akt in neurite outgrowth. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 2975–2984.
During RL, Gibson BG, Li W, Bishai EA, Sidhu GS, Landry J et al. Anthrax lethal toxin paralyzes actin-based motility by blocking Hsp27 phosphorylation. EMBO J 2007; 26: 2240–2250.
Ioannidis P, Mahaira LG, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD, Sotiropoulou PA, Kavalakis GJ et al. CRD-BP/IMP1 expression characterizes cord blood CD34+ stem cells and affects c-myc and IGF-II expression in MCF-7 cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 20086–20093.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81372572, 81201717), and the Project of State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Zhang, C., Lu, SX. et al. miR-625 suppresses tumour migration and invasion by targeting IGF2BP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 34, 965–977 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.35
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.35
This article is cited by
-
Vector engineering, strategies and targets in cancer gene therapy
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
The enhancer activity of long interspersed nuclear element derived microRNA 625 induced by NF-κB
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Long non-coding RNA ILF3-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by stabilizing ILF3 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner
Human Cell (2021)
-
LIN28B-AS1-IGF2BP1 binding promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell progression
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Hypoxia-associated circDENND2A promotes glioma aggressiveness by sponging miR-625-5p
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019)