Abstract
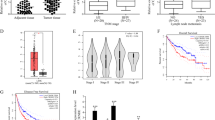
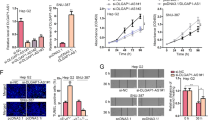
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Despite progress in diagnostics and treatment of HCC, its prognosis remains poor. Emerging studies showed that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have crucial regulatory roles in cancer biology. In the current study, differentially expressed lncRNAs between HCC and paired non-tumor tissues were identified using microarrays. The effects of a specific differentially expressed lncRNA (termed ZEB1-AS1) on tumor progression were investigated in vitro and in vivo. We found that ZEB1-AS1 is frequently upregulated in HCC samples, especially in metastatic tumor tissues. DNA methylation analysis shows a tumor-specific ZEB1-AS1 promoter hypomethylation. Aberrant methylation is tightly correlated with overexpression of ZEB1-AS1 in HCC. Patients with ZEB1-AS1 hypomethylation or with high ZEB1-AS1 expression have poor recurrence-free survival. Functionally, ZEB1-AS1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis, acts as an oncogene in HCC. The ZEB1-AS1 gene is located in physical contiguity with ZEB1 and positively regulates the ZEB1 expression. ZEB1 inhibition partially abrogates ZEB1-AS1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer metastasis. Our results provide novel insights into the function of lncRNA-driven hepatocarcinogenesis, highlight the important role of ZEB1-AS1 and ZEB1 in HCC progression, and indicate that ZEB1-AS1 may be served as a valuable prognostic biomarker for HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 September 2022
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02480-x
References
Malkowski P, Pacholczyk M, Lagiewska B, Adadynski L, Wasiak D, Kwiatkowski A et al. [Hepatocellular carcinoma–epidemiology and treatment]. Przegl Epidemiol 2006; 60: 731–740.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL . Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 2557–2576.
Yang JD, Roberts LR . Hepatocellular carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010; 7: 448–458.
Befeler AS, Di Bisceglie AM . Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 2002; 122: 1609–1619.
Xia L, Huang W, Tian D, Zhu H, Qi X, Chen Z et al. Overexpression of forkhead box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013; 57: 610–624.
Hammerle M, Gutschner T, Uckelmann H, Ozgur S, Fiskin E, Gross M et al. Posttranscriptional destabilization of the liver-specific long noncoding RNA HULC by the IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1). Hepatology 2013; 58: 1703–1712.
Tsai MC, Spitale RC, Chang HY . Long intergenic noncoding RNAs: new links in cancer progression. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3–7.
Huang JL, Zheng L, Hu YW, Wang Q . Characteristics of long non-coding RNA and its relation to hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2014; 35: 507–514.
Fatica A, Bozzoni I . Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet 2014; 15: 7–21.
He Y, Meng XM, Huang C, Wu BM, Zhang L, Lv XW et al. Long noncoding RNAs: Novel insights into hepatocelluar carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2014; 344: 20–27.
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM, Wong DJ et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010; 464: 1071–1076.
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY, Zhang F et al. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol 2011; 18: 1243–1250.
Gutschner T, Hammerle M, Eissmann M, Hsu J, Kim Y, Hung G et al. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 1180–1189.
Fan Y, Shen B, Tan M, Mu X, Qin Y, Zhang F et al. TGF-beta-induced upregulation of malat1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by associating with suz12. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 1531–1541.
Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MM, Guelly C, Moustafa T, Stradner M, Strohmaier HM et al. Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 330–342.
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, Huang N, Nuovo G, Costinean S et al. microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4750–4756.
De Craene B, Berx G . Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: 97–110.
Shah PP, Lockwood WW, Saurabh K, Kurlawala Z, Shannon SP, Waigel S et al. Ubiquilin1 represses migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2014; 340: 1709–1717.
Xu J, Lamouille S, Derynck R . TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res 2009; 19: 156–172.
Soini Y, Tuhkanen H, Sironen R, Virtanen I, Kataja V, Auvinen P et al. Transcription factors zeb1, twist and snai1 in breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2011; 11: 73.
Guo F, Parker Kerrigan BC, Yang D, Hu L, Shmulevich I, Sood AK et al. Post-transcriptional regulatory network of epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions. J. Hematol Oncol 2014; 7: 19.
Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K . The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J 2012; 31: 2714–2736.
Sanchez-Tillo E, de Barrios O, Siles L, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A, Postigo A . beta-catenin/TCF4 complex induces the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-activator ZEB1 to regulate tumor invasiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 19204–19209.
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 1487–1495.
Sanchez-Tillo E, Siles L, de Barrios O, Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A et al. Expanding roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Am J Cancer Res 2011; 1: 897–912.
Hasuwa H, Ueda J, Ikawa M, Okabe M . miR-200b and miR-429 function in mouse ovulation and are essential for female fertility. Science 2013; 341: 71–73.
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Deng G, Chang I, Greene K et al. MicroRNA-23b functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating Zeb1 in bladder cancer. PLoS One 2013; 8: e67686.
Wei W, Pelechano V, Jarvelin AI, Steinmetz LM . Functional consequences of bidirectional promoters. Trends Genet 2011; 27: 267–276.
Wang W, Meng M, Zhang Y, Wei C, Xie Y, Jiang L et al. Global transcriptome-wide analysis of CIK cells identify distinct roles of IL-2 and IL-15 in acquisition of cytotoxic capacity against tumor. BMC Med Genomics 2014; 7: 49.
Kozak M . Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell 1986; 44: 283–292.
Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Balbin OA, Dhanasekaran SM, Cao Q, Brenner JC et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat Biotechnol 2011; 29: 742–749.
Du Z, Fei T, Verhaak RG, Su Z, Zhang Y, Brown M et al. Integrative genomic analyses reveal clinically relevant long noncoding RNAs in human cancer. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2013; 20: 908–913.
Sun L, Luo H, Bu D, Zhao G, Yu K, Zhang C et al. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: e166.
Wu W, Bhagat TD, Yang X, Song JH, Cheng Y, Agarwal R et al. Hypomethylation of noncoding DNA regions and overexpression of the long noncoding RNA, AFAP1-AS1, in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013; 144: e954.
Lepoivre C, Belhocine M, Bergon A, Griffon A, Yammine M, Vanhille L et al. Divergent transcription is associated with promoters of transcriptional regulators. BMC Genomics 2013; 14: 914.
Kurihara M, Shiraishi A, Satake H, Kimura AP . A conserved noncoding sequence can function as a spermatocyte-specific enhancer and a bidirectional promoter for a ubiquitously expressed gene and a testis-specific long noncoding RNA. J Mol Biol 2014; 426: 3069–3093.
Gong C, Maquat LE . lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3' UTRs via Alu elements. Nature 2011; 470: 284–288.
Khaitan D, Dinger ME, Mazar J, Crawford J, Smith MA, Mattick JS et al. The melanoma-upregulated long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 modulates apoptosis and invasion. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3852–3862.
Babajko S, Petit S, Fernandes I, Meary F, LeBihan J, Pibouin L et al. Msx1 expression regulation by its own antisense RNA: consequence on tooth development and bone regeneration. Cells Tissues Organs 2009; 189: 115–121.
Quagliata L, Matter MS, Piscuoglio S, Arabi L, Ruiz C, Procino A et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP/HOXA13 expression is associated with disease progression and predicts outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Hepatology 2014; 59: 911–923.
Wang KC, Yang YW, Liu B, Sanyal A, Corces-Zimmerman R, Chen Y et al. A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature 2011; 472: 120–124.
Yang WT, Zheng PS . Promoter hypermethylation of KLF4 inactivates its tumor suppressor function in cervical carcinogenesis. PLoS One 2014; 9: e88827.
Valastyan S, Chang A, Benaich N, Reinhardt F, Weinberg RA . Concurrent suppression of integrin alpha5, radixin, and RhoA phenocopies the effects of miR-31 on metastasis. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 5147–5154.
Abdulghani J, Gu L, Dagvadorj A, Lutz J, Leiby B, Bonuccelli G et al. Stat3 promotes metastatic progression of prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 2008; 172: 1717–1728.
Ho MY, Liang SM, Hung SW, Liang CM . MIG-7 controls COX-2/PGE2-mediated lung cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 439–449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Xie, J., Shen, C. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Upregulation of long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes tumor metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 35, 1575–1584 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.223
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.223
This article is cited by
-
LncRNA LINC01123 promotes malignancy of ovarian cancer by targeting hsa-miR-516b-5p/VEGFA
Genes & Genomics (2024)
-
The study of long noncoding RNA TUG 1 and ZEB2-AS1 expression in newly diagnosed Egyptian adult acute myeloid leukemia patients
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2023)
-
Long non-coding RNAs involved in different steps of cancer metastasis
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2022)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: FAM83H-AS1/miR-485-5p/MEF2D axis facilitates proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
Expression profiles and functional prediction of long non-coding RNAs LINC01133, ZEB1-AS1 and ABHD11-AS1 in the luminal subtype of breast cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2021)