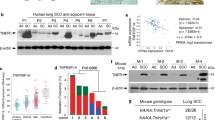
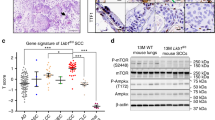
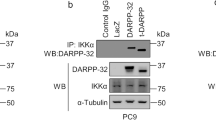
Abstract
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is generally believed to be pro-tumorigenic. Here we report a tumor-suppressive function for NF-κB1, the prototypical member of NF-κB. While NF-κB1 downregulation is associated with high lung cancer risk in humans and poor patient survival, NF-κB1-deficient mice are more vulnerable to lung tumorigenesis induced by the smoke carcinogen, urethane. Notably, the tumor-suppressive function of NF-κB1 is independent of its classical role as an NF-κB factor, but instead through stabilization of the Tpl2 kinase. NF-κB1-deficient tumors exhibit ‘normal’ NF-κB activity, but a decreased protein level of Tpl2. Reconstitution of Tpl2 or the NF-κB1 p105, but not p50 (the processed product of p105), inhibits the tumorigenicity of NF-κB1-deficient lung tumor cells. Remarkably, Tpl2-knockout mice resemble NF-κB1 knockouts in urethane-induced lung tumorigenesis. Mechanistic studies indicate that p105/Tpl2 signaling is required for suppressing urethane-induced lung damage and inflammation, and activating mutations of the K-Ras oncogene. These studies reveal an unexpected, NF-κB-independent but Tpl2-depenednt role of NF-κB1 in lung tumor suppression. These studies also reveal a previously unexplored role of p105/Tpl2 signaling in lung homeostasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu J, Xiao G . NF-κB and cancer: a paradigm of yin-yang. Am J Cancer Res 2011; 1: 192–221.
Gilmore TD . The Rel/NF-κB/IκB signal transduction pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Res 2003; 115: 241–265.
Karin M, Greten FR . NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 749–759.
Xiao G, Rabson AB, Young W, Qing G, Qu Z . Alternative pathways of NF-κB activation: a double-edged sword in health and disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2006; 17: 281–293.
Rayet B, Gélinas C . Aberrant rel/nfκb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 1999; 18: 6938–6947.
Wong KK, Jacks T, Dranoff G . NF-κB fans the flames of lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2010; 3: 403–405.
Cai Z, Tchou-Wong KM, Rom WN . NF-κB in lung tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel) 2011; 3: 4258–4268.
Chen W, Li Z, Bai L, Lin Y . NF-κB in lung cancer, a carcinogenesis mediator and a prevention and therapy target. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2011; 16: 1172–1185.
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 2014; 64: 9–29.
Wen J, Fu JH, Zhang W, Guo M . Lung carcinoma signaling pathways activated by smoking. Chin J Cancer 2011; 30: 551–558.
Hecht SS . Cigarette smoking and lung cancer: chemical mechanisms and approaches to prevention. Lancet Oncol 2002; 3: 461–469.
Zhang D, Jin X, Wang F, Wang S, Deng C, Gao Z et al. Combined prognostic value of both RelA and IκB-α expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2007; 14: 3581–3592.
Bassères DS, Ebbs A, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS . IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-Induced lung cancer with disrupted p53 activity. Genes Cancer 2014; 5: 41–55.
Meylan E, Dooley AL, Feldser DM, Shen L, Turk E, Ouyang C et al. Requirement for NF-κB signaling in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2009; 462: 104–107.
Stathopoulos GT, Sherrill TP, Cheng DS, Scoggins RM, Han W, Polosukhin VV et al. Epithelial NF-κB activation promotes urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 18514–18519.
Bassères DS, Ebbs A, Levantini E, Baldwin AS . Requirement of the NF-κB subunit p65/RelA for K-Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3537–3546.
Jones DR, Broad RM, Madrid LV, Baldwin AS Jr, Mayo MW . Inhibition of NF-κB sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Ann Thorac Surg 2000; 70: 930–936.
Chariot A . The NF-κB-independent functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol 2009; 19: 404–413.
Mulero MC, Ferres-Marco D, Islam A, Margalef P, Pecoraro M, Toll A et al. Chromatin-bound IκBα regulates a subset of polycomb target genes in differentiation and cancer. Cancer Cell 2013; 24: 151–166.
Belich MP, Salmerón A, Johnston LH, Ley SC . TPL-2 kinase regulates the proteolysis of the NF-κB-inhibitory protein NF-κB1 p105. Nature 1999; 397: 363–368.
Waterfield MR, Zhang M, Norman LP, Sun SC . NF-κB1/p105 regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated MAP kinase signaling by governing the stability and function of the Tpl2 kinase. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 685–694.
Tuveson DA, Jacks T . Modeling human lung cancer in mice: similarities and shortcomings. Oncogene 1999; 18: 5318–5324.
Sha WC, Liou HC, Tuomanen EI, Baltimore D . Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-κB leads to multifocal defects in immune responses. Cell 1995; 80: 321–330.
Dougan M, Li D, Neuberg D, Mihm M, Googe P, Wong KK et al. A dual role for the immune response in a mouse model of inflammation-associated lung cancer. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 2436–2446.
Qu Z, Sun F, Zhou J, Li L, Shapiro SD, Xiao G . Interleukin-6 prevents the initiation but enhances the progression of lung cancer. Cancer Res 2015, ; e-pub ahead of print 29 June 2015.
Ichikawa T, Yano Y, Uchida M, Otani S, Hagiwara K, Yano T . The activation of K-ras gene at an early stage of lung tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Lett 1996; 107: 165–170.
Aoki M, Akiyama T, Miyoshi J, Toyoshima K . Identification and characterization of protein products of the cot oncogene with serine kinase activity. Oncogene 1991; 6: 1515–1519.
Patriotis C, Makris A, Bear SE, Tsichlis PN . Tumor progression locus 2 (Tpl-2) encodes a protein kinase involved in the progression of rodent T-cell lymphomas and in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 2251–2255.
Zhou J, Qu Z, Yan S, Sun F, Whitsett JA, Shapiro SD et al. Differential roles of STAT3 in the initiation and growth of lung cancer. Oncogene 2014; 34: 3804–3814.
Serebrennikova OB, Tsatsanis C, Mao C, Gounaris E, Ren W, Siracusa LD et al. Tpl2 ablation promotes intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis in Apcmin mice by inhibiting IL-10 secretion and regulatory T-cell generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: E1082–E1091.
Tsatsanis C, Vaporidi K, Zacharioudaki V, Androulidaki A, Sykulev Y, Margioris AN et al. Tpl2 and ERK transduce antiproliferative T cell receptor signals and inhibit transformation of chronically stimulated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 2987–2992.
Gilmore TD, Herscovitch M . Inhibitors of NF-κB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene 2006; 25: 6887–6899.
Gkirtzimanaki K, Gkouskou KK, Oleksiewicz U, Nikolaidis G, Vyrla D, Liontos M et al. TPL2 kinase is a suppressor of lung carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E1470–E1479.
Schramek D, Kotsinas A, Meixner A, Wada T, Elling U, Pospisilik JA et al. The stress kinase MKK7 couples oncogenic stress to p53 stability and tumor suppression. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 212–219.
Qing G, Qu Z, Xiao G . Endoproteolytic processing of C-terminally truncated NF-κB2 precursors at κB-containing promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 5324–5329.
Sun F, Xiao Y, Qu Z . Oncovirus KSHV represses tumor suppressor PDLIM2 to persistently activate NF-κB and STAT3 transcription factors for tumorigenesis and tumor maintenance. J Biol Chem 2015; 290: 7362–7368.
Qu Z, Sun D, Young W . Lithium promotes neural precursor cell proliferation: evidence for the involvement of the non-canonical GSK-3β-NF-AT signaling. Cell Biosci 2011; 1: 18.
Qu Z, Fu J, Ma H, Zhou J, Jin M, Mapara MY et al. PDLIM2 restricts Th1 and Th17 differentiation and prevents autoimmune disease. Cell Biosci 2012; 2: 23.
Yan P, Fu J, Qu Z, Li S, Tanaka T, Grusby MJ et al. PDLIM2 suppresses HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis by targeting Tax into the nuclear matrix for proteasomal degradation. Blood 2009; 113: 4370–4380.
Fu J, Qu Z, Yan P, Ishikawa C, Aqeilan RI, Rabson AB et al. The tumor suppressor gene WWOX links the canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways in HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Blood 2011; 117: 1652–1661.
Fu J, Yan P, Li S, Qu Z, Xiao G . Molecular determinants of PDLIM2 in suppressing HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Onocogene 2010; 29: 6499–6507.
Qu Z, Yan P, Fu J, Jiang J, Grusby MJ, Smithgall TE et al. DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDLIM2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 1766–1772.
Qing G, Qu Z, Xiao G . Stabilization of basally translated NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) protein functions as a molecular switch of processing of NF-κB2 p100. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 40578–40582.
Qu Z, Fu J, Yan P, Hu J, Cheng SY, Xiao G . Epigenetic repression of PDLIM2: implications for the biology and treatment of breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 11786–11792.
Stabile LP, Dacic S, Land SR, Lenzner DE, Dhir R, Acquafondata M et al. Combined analysis of estrogen receptor beta-1 and progesterone receptor expression identifies lung cancer patients with poor outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17: 154–164.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Philip N Tsichlis for providing us the Tpl2Δ/Δ mice. This study was supported in part by the National Institute of Health (NIH)/National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants R01 CA172090, R21 CA175252, R21 CA189703, P30 CA047904 and P50 CA090440-Lung Cancer Developmental Research Award, as well as the American Lung Association (ALA) Lung Cancer Discovery Award and American Cancer Society (ACS) Fellowship PF-12-081-01-TBG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Qu, Z., Xiao, Y. et al. NF-κB1 p105 suppresses lung tumorigenesis through the Tpl2 kinase but independently of its NF-κB function. Oncogene 35, 2299–2310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.299
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.299
This article is cited by
-
FBXW7 in breast cancer: mechanism of action and therapeutic potential
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Cell adhesion tunes inflammatory TPL2 kinase signal transduction
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Causative role of PDLIM2 epigenetic repression in lung cancer and therapeutic resistance
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Radiosensitization of clioquinol and zinc in human cancer cell lines
BMC Cancer (2018)