Abstract
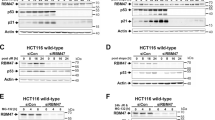
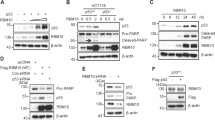
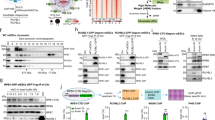
PPM1D phosphatase, also called wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1, promotes tumor development by inactivating the p53 tumor suppressor pathway. RBM38 RNA-binding protein, also called RNPC1 and a target of p53, inhibits p53 messenger RNA (mRNA) translation, which can be reversed by GSK3 protein kinase via phosphorylation of RBM38 at serine 195. Here we showed that ectopic expression of RBM38 increases, whereas knockdown of RBM38 inhibits, PPM1D mRNA translation. Consistent with this, we found that RBM38 directly binds to PPM1D 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) and promotes expression of a heterologous reporter gene that carries PPM1D 3′-UTR in a dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, we showed that PPM1D directly interacts with and dephosphorylates RBM38 at serine 195. Furthermore, we showed that PPM1D modulates p53 mRNA translation and p53-dependent growth suppression through dephosphorylation of RBM38. These findings provide evidence that the crosstalk between PPM1D and RBM38, both of which are targets and modulators of p53, has a critical role in p53 expression and activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shu L, Yan W, Chen X . RNPC1 an RNA-binding protein and a target of the p53 family, is required for maintaining the stability of the basal and stress-induced p21 transcript. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 2961–2972.
Feldstein O, Ben-Hamo R, Bashari D, Efroni S, Ginsberg D . RBM38 is a direct transcriptional target of E2F1 that limits E2F1-induced proliferation. Mol Cancer Res 2012; 10: 1169–1177.
Xu E, Zhang J, Chen X . MDM2 expression is repressed by the RNA-binding protein RNPC1 via mRNA stability. Oncogene 2012; 32: 2169–2178.
Yan W, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Jung YS, Chen X . p73 expression is regulated by RNPC1, a target of the p53 Family, via mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol 2012; 32: 2336–2348.
Zhang J, Cho SJ, Shu L, Yan W, Guerrero T, Kent M et al. Translational repression of p53 by RNPC1, a p53 target overexpressed in lymphomas. Genes Dev 2011; 25: 1528–1543.
Yin T, Cho SJ, Chen X . RNPC1 an RNA-binding protein and a p53 target, regulates macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) expression through mRNA stability. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 23680–23686.
Cho SJ, Jung YS, Zhang J, Chen X . The RNA-binding protein RNPC1 stabilizes the mRNA encoding the RNA-binding protein HuR and cooperates with HuR to suppress cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 14535–14544.
Leveille N, Elkon R, Davalos V, Manoharan V, Hollingworth D, Oude Vrielink J et al. Selective inhibition of microRNA accessibility by RBM38 is required for p53 activity. Nat Commun 2011; 2: 513.
Heinicke LA, Nabet B, Shen S, Jiang P, van Zalen S, Cieply B et al. The RNA binding protein RBM38 (RNPC1) regulates splicing during late erythroid differentiation. PLoS One 2013; 8: e78031.
Warzecha CC, Sato TK, Nabet B, Hogenesch JB, Carstens RP . ESRP1 and ESRP2 are epithelial cell-type-specific regulators of FGFR2 splicing. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 591–601.
Zhang M, Zhang J, Chen XL, Cho SJ, Chen XB . Glycogen synthase kinase 3 promotes p53 mRNA translation via phosphorylation of RNPC1. Genes Dev 2013; 27: 2246–2258.
Fiscella M, Zhang HL, Fan SJ, Sakaguchi K, Shen SF, Mercer WE et al. Wip1, a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 6048–6053.
Lu X, Ma O, Nguyen TA, Jones SN, Oren M, Donehower LA . The Wip1 Phosphatase acts as a gatekeeper in the p53-Mdm2 autoregulatory loop. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 342–354.
Lu X, Nannenga B, Donehower LA . PPM1D dephosphorylates Chk1 and p53 and abrogates cell cycle checkpoints. Genes Dev 2005; 19: 1162–1174.
Natrajan R, Lambros MB, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Moreno-Bueno G, Tan DS, Marchio C et al. Tiling path genomic profiling of grade 3 invasive ductal breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 2711–2722.
Li J, Yang Y, Peng Y, Austin RJ, van Eyndhoven WG, Nguyen KC et al. Oncogenic properties of PPM1D located within a breast cancer amplification epicenter at 17q23. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 133–134.
Nannenga B, Lu X, Dumble M, Van Maanen M, Nguyen TA, Sutton R et al. Augmented cancer resistance and DNA damage response phenotypes in PPM1D null mice. Mol Carcinog 2006; 45: 594–604.
Tan DS, Lambros MB, Rayter S, Natrajan R, Vatcheva R, Gao Q et al. PPM1D is a potential therapeutic target in ovarian clear cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 2269–2280.
Ruark E, Snape K, Humburg P, Loveday C, Bajrami I, Brough R et al. Mosaic PPM1D mutations are associated with predisposition to breast and ovarian cancer. Nature 2013; 493: 406–410.
Kleiblova P, Shaltiel IA, Benada J, Sevcik J, Pechackova S, Pohlreich P et al. Gain-of-function mutations of PPM1D/Wip1 impair the p53-dependent G1 checkpoint. J Cell Biol 2013; 201: 511–521.
Cho SJ, Zhang J, Chen X . RNPC1 modulates the RNA-binding activity of, and cooperate with, HuR to regulate p21 mRNA stability. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38: 2256–2267.
Fujimoto H, Onishi N, Kato N, Takekawa M, Xu XZ, Kosugi A et al. Regulation of the antioncogenic Chk2 kinase by the oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 1170–1180.
Takekawa M, Adachi M, Nakahata A, Nakayama I, Itoh F, Tsukuda H et al. p53-inducible wip1 phosphatase mediates a negative feedback regulation of p38 MAPK-p53 signaling in response to UV radiation. EMBO J 2000; 19: 6517–6526.
Shreeram S, Demidov ON, Hee WK, Yamaguchi H, Onishi N, Kek C et al. Wip1 phosphatase modulates ATM-dependent signaling pathways. Mol Cell 2006; 23: 757–764.
Rayter S, Elliott R, Travers J, Rowlands MG, Richardson TB, Boxall K et al. A chemical inhibitor of PPM1D that selectively kills cells overexpressing PPM1D. Oncogene 2008; 27: 1036–1044.
Zhang W, McClain C, Gau JP, Guo XY, Deisseroth AB . Hyperphosphorylation of p53 induced by okadaic acid attenuates its transcriptional activation function. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 4448–4453.
Lu XB, Ma O, Nguyen TA, Joness SN, Oren M, Donehower LA . The Wip1 phosphatase acts as a gatekeeper in the p53-Mdm2 autoregulatory loop. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 342–354.
Gilmartin AG, Faitg TH, Richter M, Groy A, Seefeld MA, Darcy MG et al. Allosteric Wip1 phosphatase inhibition through flap-subdomain interaction. Nat Chem Biol 2014; 10: 181–187.
Parssinen J, Alarmo EL, Karhu R, Kallioniemi A . PPM1D silencing by RNA interference inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines with wild-type p53. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2008; 182: 33–39.
Pandolfi S, Montagnani V, Penachioni JY, Vinci MC, Olivito B, Borgognoni L et al. WIP1 phosphatase modulates the Hedgehog signaling by enhancing GLI1 function. Oncogene 2013; 32: 4737–4747.
Wang W, Zhu H, Zhang H, Zhang L, Ding Q, Jiang H . Targeting PPM1D by lentivirus-mediated RNA interference inhibits the tumorigenicity of bladder cancer cells. Braz J Med Biol Res 2014; 47: 1044–1049.
Fiscella M, Zhang H, Fan S, Sakaguchi K, Shen S, Mercer WE et al. Wip1, a novel human protein phosphatase that is induced in response to ionizing radiation in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 6048–6053.
Oliva-Trastoy M, Berthonaud V, Chevalier A, Ducrot C, Marsolier-Kergoat MC, Mann C et al. The Wip1 phosphatase (PPM1D) antagonizes activation of the Chk2 tumour suppressor kinase. Oncogene 2007; 26: 1449–1458.
Yoda A, Xu XZ, Onishi N, Toyoshima K, Fujimoto H, Kato N et al. Intrinsic kinase activity and SQ/TQ domain of Chk2 kinase as well as N-terminal domain of Wip1 phosphatase are required for regulation of Chk2 by Wip1. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 24847–24862.
Ran FA, Hsu PD, Wright J, Agarwala V, Scott DA, Zhang F . Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Protoc 2013; 8: 2281–2308.
Zhang J, Chen X . DeltaNp73 modulates nerve growth factor-mediated neuronal differentiation through repression of TrkA. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 3868–3880.
Zhang J, Jun Cho S, Chen X . RNPC1 an RNA-binding protein and a target of the p53 family, regulates p63 expression through mRNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 9614–9619.
Bonifacino JS . Metabolic labeling with amino acids. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 2001; Chapter 3: Unit 3.7.
Peritz T, Zeng F, Kannanayakal TJ, Kilk K, Eiriksdottir E, Langel U et al. Immunoprecipitation of mRNA-protein complexes. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 577–580.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by NIH grants CA076069, CA081237 and CA121137.
Author Contributions
MZ and EX did the experiments; MZ, EX and JZ analyzed the data; XC supervised the project and analyzed the data; MZ and XC wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and commented on the draft version of the manuscript and approved the final version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Xu, E., Zhang, J. et al. PPM1D phosphatase, a target of p53 and RBM38 RNA-binding protein, inhibits p53 mRNA translation via dephosphorylation of RBM38. Oncogene 34, 5900–5911 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.31