Abstract
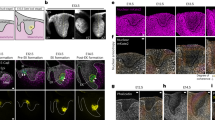
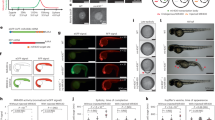
In mouse mammary epithelial cells, cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 1 (CPEB1) mediates the apical localization of ZO-1 mRNA, which encodes a critical tight junction component. In mice lacking CPEB1 and in cultured cells from which CPEB has been depleted, randomly distributed ZO-1 mRNA leads to the loss of cell polarity. We have investigated whether this diminution of polarity results in an epithelial-to-mesenchyme (EMT) transition and possible increased metastatic potential. Here, we show that CPEB1-depleted mammary epithelial cells alter their gene expression profile in a manner consistent with an EMT and also become motile, which are made particularly robust when cells are treated with transforming growth factor-β, an enhancer of EMT. CPEB1-depleted mammary cells become metastatic to the lung following injection into mouse fat pads while ectopically expressed CPEB1 prevents metastasis. Surprisingly, CPEB1 depletion causes some EMT/metastasis-related mRNAs to have shorter poly(A) tails while other mRNAs to have longer poly(A) tails. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) mRNA, which encodes a metastasis-promoting factor, undergoes poly(A) lengthening and enhanced translation upon CPEB reduction. Moreover, in human breast cancer cells that become progressively more metastatic, CPEB1 is reduced while MMP9 becomes more abundant. These data suggest that at least in part, CPEB1 regulation of MMP9 mRNA expression mediates metastasis of breast cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Groisman I, Jung MY, Sarkissian M, Cao Q, Richter JD . Translational control of the embryonic cell cycle. Cell 2002; 109: 473–483.
Burns DM, D'Ambrogio A, Nottrott S, Richter JD . CPEB and two poly(A) polymerases control miR-122 stability and p53 mRNA translation. Nature 2011; 473: 105–108.
D'Ambrogio A, Nagaoka K, Richter JD . Translational control of cell growth and malignancy by the CPEB1s. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: 283–290.
Ivshina M, Lasko P, Richter JD . Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding proteins in development, health, and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2014; 30: 393–415.
Tay J, Richter JD . Germ cell differentiation and synaptonemal complex formation are disrupted in CPEB1 knockout mice. Dev Cell 2001; 1: 201–213.
Alarcon JM, Hodgman R, Theis M, Huang YS, Kandel ER, Richter JD . Selective modulation of some forms of schaffer collateral-CA1 synaptic plasticity in mice with a disruption of the CPEB-1 gene. Learn Mem 2004; 11: 318–327.
Berger-Sweeney J, Zearfoss NR, Richter JD . Reduced extinction of hippocampal-dependent memories in CPEB1 knockout mice. Learn Mem 2006; 13: 4–7.
Groisman I, Ivshina M, Marin V, Kennedy NJ, Davis RJ, Richter JD . Control of cellular senescence by CPEB1. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 2701–2712.
Burns DM, Richter JD . CPEB1 regulation of human cellular senescence, energy metabolism, and p53 mRNA translation. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 3449–3460.
Alexandrov IM, Ivshina M, Jung DY, Friedline R, Ko HJ, Xu M et al. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein deficiency stimulates PTEN and Stat3 mRNA translation and induces hepatic insulin resistance. PLoS Genet 2012; 8: e1002457.
Udagawa T, Farny NG, Jakovcevski M, Kaphzan H, Alarcon JM, Anilkumar S et al. Genetic and acute CPEB1 depletion ameliorate fragile X pathophysiology. Nat Med 2013; 19: 1473–1477.
Groisman I, Huang YS, Mendez R, Cao Q, Theurkauf W, Richter JD . CPEB1, maskin, and cyclin B1 mRNA at the mitotic apparatus: implications for local translational control of cell division. Cell 2000; 103: 435–447.
Barnard DC, Ryan K, Manley JL, Richter JD . Symplekin and xGLD-2 are required for CPEB1-mediated cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Cell 2004; 119: 641–651.
Eliscovich C, Peset I, Vernos I, Méndez R . Spindle-localized CPE-mediated translation controls meiotic chromosome segregation. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 858–865.
Huang YS, Jung MY, Sarkissian M, Richter JD . N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor signaling results in Aurora kinase-catalyzed CPEB1 phosphorylation and alpha CaMKII mRNA polyadenylation at synapses. EMBO J 2002; 21: 2139–2148.
Huang YS, Carson JH, Barbarese E, Richter JD . Facilitation of dendritic mRNA transport by CPEB1. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 638–653.
Bestman JE, Cline HT . The RNA binding protein CPEB1 regulates dendrite morphogenesis and neuronal circuit assembly in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 20494–20499.
Udagawa T, Swanger SA, Takeuchi K, Kim JH, Nalavadi V, Shin J et al. Bidirectional control of mRNA translation and synaptic plasticity by the cytoplasmic polyadenylation complex. Mol Cell 2012; 47: 253–266.
Shen W, Liu HH, Schiapparelli L, McClatchy D, He HY, Yates JR 3rd et al. Acute synthesis of CPEB is required for plasticity of visual avoidance behavior in Xenopus. Cell Rep 2014; 6: 737–747.
Nagaoka K, Udagawa T, Richter JD . CPEB1-mediated ZO-1 mRNA localization is required for epithelial tight-junction assembly and cell polarity. Nat Commun 2012; 3: 675.
Mailleux AA, Overholtzer M, Brugge JS . Lumen formation during mammary epithelial morphogenesis: insights from in vitro and in vivo models. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 57–62.
Knights AJ, Funnell AP, Crossley M, Pearson RC . Holding tight: cell junctions and cancer spread. Trends Cancer Res 2012; 8: 61–69.
Scheel C, Weinberg RA . Cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: concepts and molecular links. Semin Cancer Biol 2012; 22: 396–403.
Voulgari A, Pintzas A . Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1796: 75–90.
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA . A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011; 331: 1559–1564.
Zavadil J, Bitzer M, Liang D, Yang YC, Massimi A, Kneitz S et al. Genetic programs of epithelial cell plasticity directed by transforming growth factor-beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 6686–6691.
Lin CL, Evans V, Shen S, Xing Y, Richter JD . The nuclear experience of CPEB: implications for RNA processing and translational control. RNA 2010; 16: 338–348.
Du L, Richter JD . Activity-dependent polyadenylation in neurons. RNA 2005; 11: 1340–1347.
Racki WJ, Richter JD . CPEB controls oocyte growth and follicle development in the moue. Development 2006; 133: 4527–4537.
Hiratsuka S, Nakamura K, Iwai S, Murakami M, Itoh T, Kijima H et al. MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 289–300.
Groppo R, Richter JD . CPEB control of NF-kappaB nuclear localization and interleukin-6 production mediates cellular senescence. Mol Cell Biol 2011; 31: 2707–2714.
D'Ambrogio A, Gu W, Udagawa T, Mello CC, Richter JD . Specific miRNA stabilization by Gld2-catalyzed monoadenylation. Cell Rep 2012; 2: 1537–1545.
Nairismägi ML, Vislovukh A, Meng Q, Kratassiouk G, Beldiman C, Petretich M et al. Translational control of TWIST1 expression in MCF-10 A cell lines recapitulating breast cancer progression. Oncogene 2012; 31: 4960–4966.
Grudzien-Nogalska E, Reed BC, Rhoads RE . CPEB1 promotes differentiation and suppresses EMT in mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 2014; 127: 2326–2338.
Gonzalez DM, Medici D . Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci Signal 2014; 7: re8.
Zhang J, Tian XJ, Zhang H, Teng Y, Li R, Bai F et al. TGF-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise activation of multiple feedback loops. Sci Signal 2014; 7: ra91.
Kim JH, Richter JD . Opposing polymerase-deadenylase activities regulate cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Mol Cell 2006; 24: 173–183.
Janusz A, Milek J, Perycz M, Pacini L, Bagni C, Kaczmarek L et al. The Fragile X mental retardation protein regulates matrix metalloproteinase 9 mRNA at synapses. J Neurosci 2013; 33: 18234–18241.
Licatalosi DD, Mele A, Fak JJ, Ule J, Kayikci M, Chi SW et al. HITS-CLIP yields genome-wide insights into brain alternative RNA processing. Nature 2008; 456: 464–469.
Kochanek DM, Wells DG . CPEB1 regulates the expression of MTDH/AEG-1 and glioblastoma cell migration. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 11: 149–160.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant GM46779 (to JDR).
Author contributions
KN and JDR designed the research; KN, HZ, KF and GW performed research; MI made antibody; KN and JDR analyzed data; and KN and JDR wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaoka, K., Fujii, K., Zhang, H. et al. CPEB1 mediates epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition and breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene 35, 2893–2901 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.350
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.350
This article is cited by
-
CPEB2 inhibit cell proliferation through upregulating p21 mRNA stability in glioma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Mir-25-3p in extracellular vesicles from fibroblast-like synoviocytes alleviates pyroptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (2023)
-
RNA-binding proteins in ovarian cancer: a novel avenue of their roles in diagnosis and treatment
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
CPEB1 directs muscle stem cell activation by reprogramming the translational landscape
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Processing body (P-body) and its mediators in cancer
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2022)