Abstract
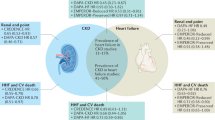
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major public health issue and an independent risk factor for cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. Diabetic kidney disease develops in 30–50% of diabetic patients and it is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease in the Western world. Strict blood pressure control and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blocker use are the cornerstones of CKD treatment; however, their application in everyday clinical practice is not always ideal and in many patients CKD progression still occurs. Accumulated evidence in the past few years clearly suggests that sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors present potent nephroprotective properties. In clinical trials in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, these agents were shown to reduce albuminuria and proteinuria by 30–50% and the incidence of composite hard renal outcomes by 40–50%. Furthermore, their mechanism of action appears rather solid, as they interfere with the major mechanism of proteinuric CKD progression, i.e., glomerular hypertension and hyperfiltration. The present review summarizes the current evidence from human trials on the effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on nephroprotection and discusses their position in everyday clinical practice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drey N, Roderick P, Mullee M, Rogerson M. A population-based study of the incidence and outcomes of diagnosed chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:677–84.
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–305.
Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL. Microalbuminuria and chronic kidney disease as risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:2366–74.
Tonelli M, Muntner P, Lloyd A, Manns BJ, Klarenbach S, Pannu N, et al. Risk of coronary events in people with chronic kidney disease compared with those with diabetes: a population-level cohort study. Lancet 2012;380:807–14.
Couser WG, Riella MC, Abraham G, Beerkens P, Feehally J, Garcia Garcia G, et al. World Kidney Day 2011: protect your kidneys, save your heart. Rev Investig Clin. 2011;63:8–11.
Ruiz-Hurtado G, Sarafidis P, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Waeber B, Ruilope LM. Global cardiovascular protection in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13:603–8.
Khosla N, Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL. Microalbuminuria. Clin Lab Med. 2006;26:635–53.
KDIGO. 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1–150.
WHO. Global report on diabetes; 2016. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204871 Accessed 4 May 2020.
Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. Lancet 2011;378:31–40.
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40–50.
Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Agodoa LYC, Bragg-Gresham J, Balkrishnan R, et al. US Renal Data System 2018 annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;73:A7–a8.
Kramer A, Pippias M, Noordzij M, Stel VS, Andrusev AM, Aparicio-Madre MI, et al. The European Renal Association - European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) Registry Annual Report 2016: a summary. Clin Kidney J. 2019;12:702–20.
Stel VS, Awadhpersad R, Pippias M, Ferrer-Alamar M, Finne P, Fraser SD, et al. International comparison of trends in patients commencing renal replacement therapy by primary renal disease. Nephrol (Carlton). 2019;24:1064–76.
Sarafidis PA, Khosla N, Bakris GL. Antihypertensive therapy in the presence of proteinuria. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49:12–26.
Sarafidis PA, Ruilope LM. Cardiorenal disease development under chronic renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system suppression. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012;13:217–9.
Sarafidis PA, Ruilope LM. Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin-angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation? Kidney Int. 2014;85:536–46.
Lasaridis AN, Sarafidis PA. Diabetic nephropathy and antihypertensive treatment: what are the lessons from clinical trials? Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:689–97.
Sarafidis PA, Blacklock R, Wood E, Rumjon A, Simmonds S, Fletcher-Rogers J, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with hyperkalemia in predialysis patients followed in a low-clearance clinic. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7:1234–41.
Sarafidis PA, Georgianos PI, Bakris GL. Advances in treatment of hyperkalemia in chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16:2205–15.
Loutradis C, Papadopoulou E, Angeloudi E, Karagiannis A, Sarafidis P. The beneficial actions of SGLT-2 inhibitors beyond management of hyperglycemia. Curr Med Chem. 2019. epub ahead of print.
Heerspink HJL, Kosiborod M, Inzucchi SE, Cherney DZI. Renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2018;94:26–39.
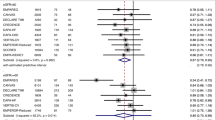
Piperidou A, Sarafidis P, Boutou A, Thomopoulos C, Loutradis C, Alexandrou ME, et al. The effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on albuminuria and proteinuria in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hypertens. 2019;37:1334–43.
Sarafidis P, Ferro CJ, Morales E, Ortiz A, Malyszko J, Hojs R, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists for nephroprotection and cardioprotection in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. A consensus statement by the EURECA-m and the DIABESITY working groups of the ERA-EDTA. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2019;34:208–30.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1456–62.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851–60.
The GISEN Group (Gruppo Italiano di Studi Epidemiologici in Nefrologia) Randomised placebo-controlled trial of effect of ramipril on decline in glomerular filtration rate and risk of terminal renal failure in proteinuric, non-diabetic nephropathy. Lancet . 1997;349:1857–63.
Wright JT Jr., Bakris G, Greene T, Agodoa LY, Appel LJ, Charleston J, et al. Effect of blood pressure lowering and antihypertensive drug class on progression of hypertensive kidney disease: results from the AASK trial. JAMA 2002;288:2421–31.
Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, et al. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2204–13.
Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1892–903.
KDIGO. Clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:337–414.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr., Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 2018;71:1269–324.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 Practice Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Cardiology: ESH/ESC Task Force for the management of Arterial Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36:2284–309.
Sarafidis PA, Memmos E, Alexandrou ME, Papagianni A. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists for nephroprotection: current evidence and future perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:5528–36.
Alexandrou ME, Papagianni A, Tsapas A, Loutradis C, Boutou A, Piperidou A, et al. Effects of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in proteinuric kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hypertens. 2019;37:2307–24.
Loutradis C, Tolika P, Skodra A, Avdelidou A, Sarafidis PA. Prevalence of hyperkalemia in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a nested Case-Control Study. Am J Nephrol. 2015;42:351–60.
Edwards NC, Steeds RP, Chue CD, Stewart PM, Ferro CJ, Townend JN. The safety and tolerability of spironolactone in patients with mild to moderate chronic kidney disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;73:447–54.
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, Cooper ME, Gansevoort RT, Haller H, et al. Effect of Finerenone on Albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized clinical trial. Jama 2015;314:884–94.
Ruilope LM, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Bakris GL, Filippatos G, Nowack C, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the Finerenone in reducing cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in diabetic kidney disease trial. Am J Nephrol. 2019;50:345–56.
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B, Ruilope LM, Nowack C, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the Finerenone in reducing kidney failure and disease progression in diabetic kidney disease trial. Am J Nephrol. 2019;50:333–44.
Wright EM. Glucose transport families SLC5 and SLC50. Mol Asp Med. 2013;34:183–96.
Wright EM, Loo DD, Hirayama BA, Turk E. Surprising versatility of Na+-glucose cotransporters: SLC5. Physiol (Bethesda). 2004;19:370–6.
Ferrannini E. Sodium-glucose co-transporters and their inhibition: clinical physiology. Cell Metab. 2017;26:27–38.
Lee YJ, Lee YJ, Han HJ. Regulatory mechanisms of Na(+)/glucose cotransporters in renal proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int Suppl. 2007:S27–S35.
DeFronzo RA, Davidson JA, Del Prato S. The role of the kidneys in glucose homeostasis: a new path towards normalizing glycaemia. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:5–14.
Wright EM, Hirayama BA, Loo DF. Active sugar transport in health and disease. J Intern Med. 2007;261:32–43.
American Diabetes Association Pharmacologic Approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:S73–S85.
Nauck MA. Update on developments with SGLT2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:1335–80.
Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, DeFronzo RA. Efficacy and safety of SGLT2 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12:230–8.
Dandona P, Mathieu C, Phillip M, Hansen L, Tschöpe D, Thorén F, et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes: the DEPICT-1 52-week study. Diabetes Care 2018;41:2552–9.
Forxiga®. Summary of product characteristics. 2012. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/forxiga-epar-product-information_en.pdf Accessed 4 May 2020.
Wright EM, Turk E. The sodium/glucose cotransport family SLC5. Pflug Arch. 2004;447:510–8.
Vlotides G, Mertens PR. Sodium-glucose cotransport inhibitors: mechanisms, metabolic effects and implications for the treatment of diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30:1272–6.
Chao EC, Henry RR. SGLT2 inhibition–a novel strategy for diabetes treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:551–9.
Filippatos TD, Tsimihodimos V, Elisaf MS. Mechanisms of blood pressure reduction with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17:1581–3.
Sarafidis PA, Georgianos PI, Lasaridis AN. Diuretics in clinical practice. Part I: mechanisms of action, pharmacological effects and clinical indications of diuretic compounds. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2010;9:243–57.
Tamura K, Wakui H, Azushima K, Uneda K, Umemura S. Circadian blood pressure rhythm as a possible key target of SGLT2 inhibitors used for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Hypertens Res. 2016;39:396–8.
Lambers Heerspink HJ, de Zeeuw D, Wie L, Leslie B, List J. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:853–62.
Cefalu WT, Stenlof K, Leiter LA, Wilding JP, Blonde L, Polidori D, et al. Effects of canagliflozin on body weight and relationship to HbA1c and blood pressure changes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015;58:1183–7.
Chino Y, Samukawa Y, Sakai S, Nakai Y, Yamaguchi J, Nakanishi T, et al. SGLT2 inhibitor lowers serum uric acid through alteration of uric acid transport activity in renal tubule by increased glycosuria. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2014;35:391–404.
Jordan J, Tank J, Heusser K, Heise T, Wanner C, Heer M, et al. The effect of empagliflozin on muscle sympathetic nerve activity in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017;11:604–12.
Chilton R, Tikkanen I, Cannon CP, Crowe S, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, et al. Effects of empagliflozin on blood pressure and markers of arterial stiffness and vascular resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:1180–93.
Muskiet MH, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, Kramer MH, Heerspink HJ, van Raalte DH. Pleiotropic effects of type 2 diabetes management strategies on renal risk factors. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:367–81.
Heerspink HJ, Kropelin TF, Hoekman J, de Zeeuw D. Drug-induced reduction in albuminuria is associated with subsequent renoprotection: a meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:2055–64.
Ridderstrale M, Andersen KR, Zeller C, Kim G, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. Comparison of empagliflozin and glimepiride as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 104-week randomised, active-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:691–700.
Cherney D, Lund SS, Perkins BA, Groop PH, Cooper ME, Kaspers S, et al. The effect of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition with empagliflozin on microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016;59:1860–70.
Cherney DZI, Zinman B, Inzucchi SE, Koitka-Weber A, Mattheus M, von Eynatten M, et al. Effects of empagliflozin on the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease: an exploratory analysis from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:610–21.
Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Nieto J, David-Neto E, Yue D, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:1016–27.
Heerspink HJ, Desai M, Jardine M, Balis D, Meininger G, Perkovic V. Canagliflozin slows progression of renal function decline independently of glycemic effects. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:368–75.
Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D, Mahaffey KW, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: results from the CANVAS Program randomised clinical trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:691–704.
Nauck MA, Del Prato S, Meier JJ, Duran-Garcia S, Rohwedder K, Elze M, et al. Dapagliflozin versus glipizide as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycemic control with metformin: a randomized, 52-week, double-blind, active-controlled noninferiority trial. Diabetes Care 2011;34:2015–22.
Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W, List JF. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int. 2014;85:962–71.
Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Johnsson K, Parikh S, Ptaszynska A, Ying L. The effect of dapagliflozin on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Nephrol. 2016;29:391–400.
Heerspink HJ, Johnsson E, Gause-Nilsson I, Cain VA, Sjostrom CD. Dapagliflozin reduces albuminuria in patients with diabetes and hypertension receiving renin-angiotensin blockers. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18:590–7.
Mosenzon O, Wiviott SD, Cahn A, Rozenberg A, Yanuv I, Goodrich EL, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on development and progression of kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:606–17.
Kashiwagi A, Akiyama N, Shiga T, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, Yoshida S, et al. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to a sulfonylurea in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase III EMIT study. Diabetol Int. 2015;6:125–38.
Kashiwagi A, Shiga T, Akiyama N, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, Yoshida S, et al. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on to pioglitazone in Japanese patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (the SPOTLIGHT study). Diabetol Int. 2015;6:104–16.
Kashiwagi A, Takahashi H, Ishikawa H, Yoshida S, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on long-term efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: results of the long-term ASP1941 safety evaluation in patients with type 2 diabetes with renal impairment (LANTERN) study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:152–60.
Haneda M, Seino Y, Inagaki N, Kaku K, Sasaki T, Fukatsu A, et al. Influence of renal function on the 52-week efficacy and safety of the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor luseogliflozin in japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther. 2016;38:66–88.e20.
Cherney DZI, Heerspink HJL, Frederich R, Maldonado M, Liu J, Pong A, et al. Effects of ertugliflozin on renal function over 104 weeks of treatment: a post hoc analysis of two randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia 2020;63:1128–40.
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323–34.
Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D, Mahaffey KW, Fulcher G, Stein P, et al. Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study (CANVAS)–a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am Heart J. 2013;166:217–223.e211.
Neal B, Perkovic V, Matthews DR, Mahaffey KW, Fulcher G, Meininger G, et al. Rationale, design and baseline characteristics of the CANagliflozin cardioVascular Assessment Study-Renal (CANVAS-R): a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:387–93.
Neuen BL, Ohkuma T, Neal B, Matthews DR, de Zeeuw D, Mahaffey KW, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with canagliflozin according to baseline kidney function. Circulation 2018;138:1537–50.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295–306.
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347–57.
A study to evaluate the effect of dapagliflozin on renal outcomes and cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (Dapa-CKD). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03036150. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03036150 Accessed 5/5/2020.
Farxiga Phase III DAPA-CKD trial will be stopped early after overwhelming efficacy in patients with chronic kidney disease. 2020. https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2020/farxiga-phase-iii-dapa-ckd-trial-will-be-stopped-early-after-overwhelming-efficacy-in-patients-with-chronic-kidney-disease.html Accessed 5 May 2020.
EMPA-KIDNEY (The Study of Heart and Kidney Protection With Empagliflozin). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03594110. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03594110 Accessed 5 May 2020.
Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL. The antinatriuretic effect of insulin: an unappreciated mechanism for hypertension associated with insulin resistance? Am J Nephrol. 2007;27:44–54.
Artunc F, Schleicher E, Weigert C, Fritsche A, Stefan N, Haring HU. The impact of insulin resistance on the kidney and vasculature. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12:721–37.
Heerspink HJ, Perkins BA, Fitchett DH, Husain M, Cherney DZ. Sodium glucose Cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes mellitus: cardiovascular and kidney effects, potential mechanisms, and clinical applications. Circulation 2016;134:752–72.
Terami N, Ogawa D, Tachibana H, Hatanaka T, Wada J, Nakatsuka A, et al. Long-term treatment with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, ameliorates glucose homeostasis and diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. PLoS ONE 2014;9:e100777.
O’Neill J, Fasching A, Pihl L, Patinha D, Franzen S, Palm F. Acute SGLT inhibition normalizes O2 tension in the renal cortex but causes hypoxia in the renal medulla in anaesthetized control and diabetic rats. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2015;309:F227–234.
Chang YK, Choi H, Jeong JY, Na KR, Lee KW, Lim BJ, et al. Dapagliflozin, SGLT2 inhibitor, attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2016;11:e0158810.
Górriz JL, Navarro-González JF, Ortiz A, Vergara A, Nuñez J, Jacobs-Cachá C, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition: towards an indication to treat diabetic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020;35:i13–i23.
Brenner BM, Lawler EV, Mackenzie HS. The hyperfiltration theory: a paradigm shift in nephrology. Kidney Int. 1996;49:1774–7.
Norton L, Shannon CE, Fourcaudot M, Hu C, Wang N, Ren W, et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT) and glucose transporter (GLUT) expression in the kidney of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1322–6.
Solini A, Rossi C, Mazzanti CM, Proietti A, Koepsell H, Ferrannini E. Sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT)2 and SGLT1 renal expression in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19:1289–94.
Cherney DZ, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Maione M, Lai V, Lee A, et al. Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2014;129:587–97.
van Bommel EJM, Muskiet MHA, van Baar MJB, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, Emanuel AL, et al. The renal hemodynamic effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin are caused by post-glomerular vasodilatation rather than pre-glomerular vasoconstriction in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes in the randomized, double-blind RED trial. Kidney Int. 2020;97:202–12.
Soler MJ, Porrini E, Fernandez-Fernandez B, Ortiz A. SGLT2i and postglomerular vasodilation. Kidney Int. 2020;97:805–6.
Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2018;41:2669–701.
Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, Rossing P, Mingrone G, Mathieu C, et al. 2019 update to: management of Hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020;43:487–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
AP have not any financial or other relationships, which might lead to a conflict of interest regarding this paper. CL received scholarship from the Hellenic Society for Medical Education. PS is an advisor/speaker to Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Elpen Pharmaceuticals, Genesis Pharma, Menarini, Innovis Pharma, Winmedica and has received research support for an Investigator-Initiated Study from Astra Zeneca.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piperidou, A., Loutradis, C. & Sarafidis, P. SGLT-2 inhibitors and nephroprotection: current evidence and future perspectives. J Hum Hypertens 35, 12–25 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-00393-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-020-00393-4
This article is cited by
-
Budget impact analyses for treatment of heart failure. A systematic review
Heart Failure Reviews (2024)
-
Effects of renal denervation on kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Human Hypertension (2023)
-
Role of hypertension in progression of pediatric CKD
Pediatric Nephrology (2023)
-
The current role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus management
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2022)
-
Herzinsuffizienz
Die Kardiologie (2022)