Abstract
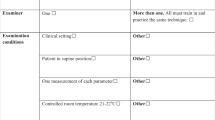
Accurate data regarding the size of the erect penis is of great importance to several disciplines working with male patients, but little data exists on the best technique to measure penile length. While some previous small studies have suggested good correlation between stretched penile length, others have shown significant variability. Penile girth has been less well studied, and little data exist on the possible errors induced by differing observers and different techniques. Much of the published data report penile length measured from the penopubic skin junction-to-glans tip (STT) rather than pubic bone-to-tip (BTT). We wished to assess the accuracy of different techniques of penile measurements with multiple observers. Men who achieved full erection using dynamic penile Doppler ultrasound for the diagnosis of sexual dysfunction or a desire for objective penile measurement were included in the study. Exclusion criteria were penile scarring, curvature, or congenital abnormality. In each case, the penis was measured by one of the seven andrology specialists in a private air-conditioned (21 °C) environment. Each patient had three parameters measured: circumference (girth) of the penile shaft, length from suprapubic skin-to-distal glans (STT), and pubis-to-distal glans (BTT). The three measurements were recorded in the stretched flaccid state, and the same three measurements were then repeated in the fully erect state, following induction of full erection with intracavernosal injection. We analyzed the accuracy of each flaccid measurement using the erect measurements as a reference, for the overall patient population and for each observer. In total, 201 adult men (mean age 49.4 years) were included in this study. Assessing the penis in the stretched and flaccid state gave a mean underestimate of the erect measurement of ~20% (STT length 23.39%, BTT length 19.86%, and circumference 21.38%). In this large, multicenter, multi-observer study of penis size, flaccid measurements were only moderately accurate in predicting erect size. They were also significantly observer dependent. Measuring penile length from pubic bone to tip of glans is more accurate and reliable, the discrepancy being most notable in overweight patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alter GJ, Salgado CJ, Chim H. Aesthetic surgery of the male genitalia. Semin Plast Surg. 2011;25:189–95.
Wessells H, Lue TF, McAninch JW. Penile length in the flaccid and erect states: guidelines for penile augmentation. J Urol. 1996;156:995–7.
Veale D, Miles S, Bramley S, Muir G, Hodsoll J. Am I normal? A systematic review and construction of nomograms for flaccid and erect penis length and circumference in up to 15,521 men. BJU Int. 2014; 15:978–986.
Sengezer M, Ozturk S, Deveci M. Accurate method for determining functional penile length in Turkish young men. Ann Plast Surg 2002;48:381–5.
Ponchietti R, Mondaini N, Bonafe M. Penile length and circumference: a study on 3,300 young Italian males. Eur Urol, 2001 2001;39:183–6.
Kinsey A, Pomeroy W, Martin C. Sexual Behaviour in the Human Male. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders co; 1948.
Söylemez H, Atar M, Sancaktutar AA, Penbegül N, Bozkurt Y, Onem K. Relationship between penile size and somatometric parameters in 2276 healthy young men. Int J Impot Res. 2012;24:126–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2011.53.
Mehraban D, Salehi M, Zayeri F. Penile size and somatometric parameters among Iranian normal adult men. Int J Impot Res. 2007;19:303–9.
Yılmaz A, Ali A, Ali Ö, Varol N, Altug T, Ateş K. Penile length and somatometric parameters: a study in healthy young Turkish men. Asian J Androl. 2011;13:339–41.
Kamel I, Gadalla A, Ghanem H, Oraby M. Comparing penile measurements in normal and erectile dysfunction subjects. J Sex Med. 2009;6:2305–10.
Bondil P, Costa P, Daures JP, Louis JF, Navratil H. Clinical study of the longitudinal deformation of the flaccid penis and of its variations with aging. Eur Urol. 1992;21:284–6.
Khan S, Somani B, Lam W, Donat R. Establishing a reference range for penile length in Caucasian British men: a prospective study of 609 men. BJU Int. 2012;109:740–4.
Ajmani ML, Jain SP, Saxena SK. Anthropometric study of male external genitalia of 320 healthy Nigerian adults. Anthropol Anz. 1985;43:179–86.
Promodu K, Shanmughadas KV, Bhat S, Nair KR. Penile length and circumference: an Indian study. Int J Impot Res. 2007;19:558–63. Epub 2007 Jun 14
Awwad Z, Abu-Hijleh M, Basri S, Shegam N, Murshidi M, Ajlouni K. Penile measurements in normal adult Jordanians and in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2005;17:191–5.
Smith AM, Jolley D, Hocking J, Benton K, Gerofi J. Does penis size influence condom slippage and breakage? Int J STD AIDS. 1998;9:444–7.
da Ros C, Teloken C, Sogari P, Barcelos M, Silva F, Souto C. Caucasian penis: what is the normal size? J Urol 1994;151:323A.
Choi IH, Kim KH, Yoon SJ, Kim SW, Kim TB. Second to fourth digit ratio: a predictor of adult penile length. Asian J Androl. 2011;13:710–4.
Son H, Lee H, Huh J, Kim S, Paick J. Studies on self-esteem of penile size in young Korean military men. Asian J Androl. 2003;5:185–9.
Schneider T, Sperlinga H, Lümmena G, Syllwasschyb J, Rübbena H. Does penile size in younger men cause problems in condom use? a prospective measurement of penile dimensions in 111 young and 32 older men. Urology 2001;57:314–8.
Shah J, Christopher N. Can shoe size predict penile length? BJU Int. 2002;90:586–7.
Mondaini N, Ponchietti R, Gontero P, Muir GH, Natali A, Caldarera E, Biscioni S, Rizzo M. Penile length is normal in most men seeking penile lengthening procedures. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:283–6.
Chen J, Gefen A, Greenstein A, Matzkin H, Elad D. Predicting penile size during erection. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:328–33.
Spyropoulos E, Borousas D, Mavrikos S, Dellis A, Bourounis M, Athanasiadis S. Size of external genital organs and somatometric parameters among physically normal men younger than 40 years old. Urology 2002;60:485–9. 2002.
Dillon BE, Chama NB, Honig SC. Penile size and penile enlargement surgery: a review. Int J Impot Res. 2008;20:519–29.
Lever J, Frederick DA, Peplau LA. Does size matter? Men’s and women’s views on penis size across the lifespan. Psychol Men Masc. 2006;7:129–43.
Spyropoulos E, Christoforidis C, Borousas D, Mavrikos S, Bourounis M, Athanasiadis S. Augmentation phalloplasty surgery for penile dysmorphophobia in young adults: considerations regarding patient selection, outcome evaluation and techniques applied. Eur Urol. 2005;48:121–7. discussion 27–8
Francoeur RT, Perper T, Scherzer NA. A Descriptive Dictionary and Atlas of Sexology. New York: Greenwood Press; 1991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habous, M., Muir, G., Soliman, T. et al. Outcomes of variation in technique and variation in accuracy of measurement in penile length measurement. Int J Impot Res 30, 21–26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-017-0013-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-017-0013-3
This article is cited by
-
Glans hypermobility scale (GHS): A simple grading scale and description of a modified glanspexy technique
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)
-
Plication surgery does not produce additional loss of length in Peyronie’s disease patients
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)
-
“Make it as long as you can, Doc.” Concomitant surgical treatments with penile implant to enhance penile size
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
A Review on Penile Length and Girth Issues in Penile Prosthetic Surgery
Current Urology Reports (2021)
-
Penile size in adult men—recommendations for clinical and research measurements
International Journal of Impotence Research (2020)