Abstract
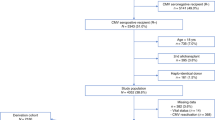
A retrospective evaluation of 200 consecutive recipients of autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT) was conducted to ascertain the incidence, risk factors, clinical features, complications, and outcome of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. A total of 26 patients (13%) developed CMV viremia (n = 5), DNAemia (n = 3), viruria (n = 18) and/or disease (n = 3) at a median of 45 days following stem cell infusion. None of the patients underwent surveillance testing for CMV. A diagnosis was established by culture and polymerase chain reaction of blood, urine or other tissue samples submitted when patients exhibited clinical features suggestive of CMV infection. Cytomegalovirus seropositivity prior to transplantation was the only statistically significant risk factor predicting subsequent identification of CMV (P < 0.001). the symptoms were severe enough in 23 patients to warrant treatment with intravenous ganciclovir. three patients developed cmv disease; two developed fatal cmv pneumonia and one developed cmv gastritis which responded to antiviral treatment. clinical signs and symptoms as well as viremia and viruria resolved with (20 patients) and without (three patients) treatment in the remaining individuals. all instances of cmv viremia, dnaemia, viruria and disease occurred within 3 months of stem cell infusion. these results demonstrate that cmv is a common pathogen after autologous pbsct and may result in fatality in rare instances. surveillance programs appear to be neither useful nor cost-effective. diagnostic evaluation should be performed only in patients exhibiting suspicious clinical features and antiviral chemotherapy should be administered for persistent and severe signs and symptoms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgrami, S., Aslanzadeh, J., Feingold, J. et al. Cytomegalovirus viremia, viruria and disease after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: no need for surveillance. Bone Marrow Transplant 24, 69–73 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701827
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1701827
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Incidence and risk factors of opportunistic infections after autologous stem cell transplantation: a nationwide, population-based cohort study in Korea
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Cytomegalovirus infection in patients with haematological diseases and after autologous stem cell transplantation as consolidation: a single-centre study
Annals of Hematology (2017)
-
Cytomegalovirus infection in autologous stem cell transplant recipients in the era of rituximab
Annals of Hematology (2016)
-
Management of CMV, HHV-6, HHV-7 and Kaposi-sarcoma herpesvirus (HHV-8) infections in patients with hematological malignancies and after SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Cellular and humoral immune reconstitution after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT)
Annals of Hematology (2003)