Abstract
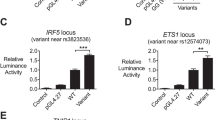
The BXSB mouse strain is an important model of glomerulonephritis observed in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Linkage studies have successfully identified disease-susceptibility intervals; however, extracting the identity of the susceptibility gene(s) in such regions is the crucial next step. Congenic mouse strains present a defined genetic resource that is highly amenable to microarray analysis. We have performed microarray analysis using a series of chromosome 1 BXSB congenic mice with partially overlapping disease-susceptibility intervals. Simultaneous comparison of the four congenic lines allowed the identification of expression differences associated with both the initiation and progression of disease. Thus, we have identified a number of novel SLE disease gene candidates and have confirmed the identity of Ifi202 as a disease candidate in the BXSB strain. Sequencing of the promoter regions of Gas5 has revealed polymorphisms in the BXSB strain, which may account for the differential expression profile. Furthermore, the combination of the microarray results with the different phenotypes of these mice has allowed the identification of a number of expression differences that do not necessarily map to the congenic interval, but may be implicated in disease pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Accessions
GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ
References
Murphy ED, Roths JB . New inbred strains. Mouse News Lett 1978; 58: 51–52.
Andrews BS, Eisenberg RA, Theofilopoulos AN, Izui S, Wilson CB, McConahey PJ et al. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med 1978; 148: 1198–1215.
Vyse TJ, Kotzin BL . Genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Immunol 1996; 8: 843–851.
Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN . Genetics of systemic autoimmunity in mouse models of lupus. Int Rev Immunol 2000; 19: 367–387.
Mohan C, Alas E, Morel L, Yang P, Wakeland EK . Genetic dissection of SLE pathogenesis. Sle1 on murine chromosome 1 leads to a selective loss of tolerance to H2A/H2B/DNA subnucleosomes. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1362–1372.
Vyse TJ, Morel L, Tanner FJ, Wakeland EK, Kotzin BL . Backcross analysis of genes linked to autoantibody production in New Zealand White mice. J Immunol 1996; 157: 2719–2727.
Hogarth MB, Slingsby JH, Allen PJ, Thompson EM, Chandler P, Davies KA et al. Multiple lupus susceptibility loci map to chromosome 1 in BXSB mice. J Immunol 1998; 161: 2753–2761.
Haywood ME, Rogers NJ, Rose SJ, Boyle J, McDermott A, Rankin JM et al. Dissection of BXSB lupus phenotype using mice congenic for chromosome 1 demonstrates that separate intervals direct different aspects of disease. J Immunol 2004; 173: 4277–4285.
Haywood ME, Hogarth MB, Slingsby JH, Rose SJ, Allen PJ, Thompson EM et al. Identification of intervals on chromosomes 1, 3, and 13 linked to the development of lupus in BXSB mice. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 349–355.
Vidal S, Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN . Loci predisposing to autoimmunity in MRL-Fas lpr and C57BL/6-Faslpr mice. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 696–702.
Vyse TJ, Rozzo SJ, Drake CG, Izui S, Kotzin BL . Control of multiple autoantibodies linked with a lupus nephritis susceptibility locus in New Zealand black mice. J Immunol 1997; 158: 5566–5574.
Murphy ED, Roths JB . A Y chromosome associated factor in strain BXSB producing accelerated autoimmunity and lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheum 1979; 22: 1188–1194.
Hudgins CC, Steinberg RT, Klinman DM, Reeves MJ, Steinberg AD . Studies of consomic mice bearing the Y chromosome of the BXSB mouse. J Immunol 1985; 134: 3849–3854.
Eaves IA, Wicker LS, Ghandour G, Lyons PA, Peterson LB, Todd JA et al. Combining mouse congenic strains and microarray gene expression analyses to study a complex trait: the NOD model of type 1 diabetes. Genome Res 2002; 12: 232–243.
Rozzo SJ, Allard JD, Choubey D, Vyse TJ, Izui S, Peltz G et al. Evidence for an interferon-inducible gene, Ifi202, in the susceptibility to systemic lupus. Immunity 2001; 15: 435–443.
Tang Z, McGowan BS, Huber SA, McTiernan CF, Addya S, Surrey S et al. Gene expression profiling during the transition to failure in TNF-alpha over-expressing mice demonstrates the development of autoimmune myocarditis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2004; 36: 515–530.
Kagami Y, Furuichi T . Investigation of differentially expressed genes during the development of mouse cerebellum. Gene Expr Patterns 2001; 1: 39–59.
Kangas M, Brannstrom A, Elomaa O, Matsuda Y, Eddy R, Shows TB et al. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human and murine genes for the macrophage MARCO receptor. Genomics 1999; 58: 82–89.
Coccia EM, Cicala C, Charlesworth A, Ciccarelli C, Rossi GB, Philipson L et al. Regulation and expression of a growth arrest-specific gene (gas5) during growth, differentiation, and development. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 3514–3521.
Vyse TJ, Drake CG, Rozzo SJ, Roper E, Izui S, Kotzin BL . Genetic linkage of IgG autoantibody production in relation to lupus nephritis in New Zealand hybrid mice. J Clin Invest 1996; 98: 1762–1772.
Gebauer M, Zeiner M, Gehring U . Proteins interacting with the molecular chaperone hsp70/hsc70: physical associations and effects on refolding activity. FEBS Lett 1997; 417: 109–113.
Hallgren J, Spillmann D, Pejler G . Structural requirements and mechanism for heparin-induced activation of a recombinant mouse mast cell tryptase, mouse mast cell protease-6: formation of active tryptase monomers in the presence of low molecular weight heparin. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 42774–42781.
Bolland S, Yim YS, Tus K, Wakeland EK, Ravetch JV . Genetic modifiers of systemic lupus erythematosus in FcgammaRIIB(−/−) mice. J Exp Med 2002; 195: 1167–1174.
Xie S, Chang SH, Sedrak P, Kaliyaperumal A, Datta SK, Mohan C . Dominant NZB contributions to lupus in the (SWR × NZB)F1 model. Genes Immun 2002; 3 (Suppl 1): S13–S20.
Barbosa MD, Nguyen QA, Tchernev VT, Ashley JA, Detter JC, Blaydes SM et al. Identification of the homologous beige and Chediak–Higashi syndrome genes. Nature 1996; 382: 262–265.
Jackson IJ . Homologous pigmentation mutations in human, mouse and other model organisms. Hum Mol Genet 1997; 6: 1613–1624.
Rigby RJ, Rozzo SJ, Boyle JJ, Lewis M, Kotzin BL, Vyse TJ . New loci from New Zealand Black and New Zealand White mice on chromosomes 4 and 12 contribute to lupus-like disease in the context of BALB/c. J Immunol 2004; 172: 4609–4617.
Wang Y, Nose M, Kamoto T, Nishimura M, Hiai H . Host modifier genes affect mouse autoimmunity induced by the lpr gene. Am J Pathol 1997; 151: 1791–1798.
Haywood ME, Vyse TJ, McDermott A, Thompson EM, Ida A, Walport MJ et al. Autoantigen glycoprotein 70 expression is regulated by a single locus, which acts as a checkpoint for pathogenic anti-glycoprotein 70 autoantibody production and hence for the corresponding development of severe nephritis, in lupus-prone BXSB mice. J Immunol 2001; 167: 1728–1733.
Morel L, Rudofsky UH, Longmate JA, Schiffenbauer J, Wakeland EK . Polygenic control of susceptibility to murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 1994; 1: 219–229.
Kono DH, Burlingame RW, Owens DG, Kuramochi A, Balderas RS, Balomenos D et al. Lupus susceptibility loci in New Zealand mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 10168–10172.
Wakeland EK, Wandstrat AE, Liu K, Morel L . Genetic dissection of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Immunol 1999; 11: 701–707.
Podolin PL, Denny P, Armitage N, Lord CJ, Hill NJ, Levy ER et al. Localization of two insulin-dependent diabetes (Idd) genes to the Idd10 region on mouse chromosome 3. Mamm Genome 1998; 9: 283–286.
Denny P, Lord CJ, Hill NJ, Goy JV, Levy ER, Podolin PL et al. Mapping of the IDDM locus Idd3 to a 0.35-cM interval containing the interleukin-2 gene. Diabetes 1997; 46: 695–700.
Pritchard NR, Cutler AJ, Uribe S, Chadban SJ, Morley BJ, Smith KG . Autoimmune-prone mice share a promoter haplotype associated with reduced expression and function of the Fc receptor FcgammaRII. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 227–230.
Stanfield GM, Horvitz HR . The ced-8 gene controls the timing of programmed cell deaths in C. elegans. Mol Cell 2000; 5: 423–433.
Botto M, Walport MJ . C1q, autoimmunity and apoptosis. Immunobiology 2002; 205: 395–406.
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Nagata S . Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature 1992; 356: 314–317.
Mohan C, Morel L, Yang P, Wakeland EK . Genetic dissection of systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis: Sle2 on murine chromosome 4 leads to B cell hyperactivity. J Immunol 1997; 159: 454–465.
Morel L, Blenman KR, Croker BP, Wakeland EK . The major murine systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility locus, Sle1, is a cluster of functionally related genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 1787–1792.
Xin H, Geng Y, Pramanik R, Choubey D . Induction of p202, a modulator of apoptosis, during oncogenic transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by activated H-Ras (Q61L) contributes to cell survival. J Cell Biochem 2003; 88: 191–204.
Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 2610–2615.
Baechler EC, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW . The emerging role of interferon in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Immunol 2004; 16: 801–807.
Virelizier JL, Lipinski M, Tursz T, Griscelli C . Defects of immune interferon secretion and natural killer activity in patients with immunological disorders. Lancet 1979; 2: 696–697.
Boackle SA, Holers VM, Chen X, Szakonyi G, Karp DR, Wakeland EK et al. Cr2, a candidate gene in the murine Sle1c lupus susceptibility locus, encodes a dysfunctional protein. Immunity 2001; 15: 775–785.
Chong WP, Ip WK, Wong WH, Lau CS, Chan TM, Lau YL . Association of interleukin-10 promoter polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 2004; 5: 484–492.
Russell AI, Cunninghame Graham DS, Shepherd C, Roberton CA, Whittaker J, Meeks J et al. Polymorphism at the C-reactive protein locus influences gene expression and predisposes to systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 137–147.
Prokunina L, Castillejo-Lopez C, Oberg F, Gunnarsson I, Berg L, Magnusson V et al. A regulatory polymorphism in PDCD1 is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in humans. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 666–669.
Troyanskaya OG, Garber ME, Brown PO, Botstein D, Altman RB . Nonparametric methods for identifying differentially expressed genes in microarray data. Bioinformatics 2002; 18: 1454–1461.
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G . Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 5116–5121.
Irizarry RA, Gautier L, Bolstad BM, Miller C with contributions from Astr M, Cope LM, Gentleman R, Workman C, Zhang J. Affy:Methods for Affymetrix Oligonucleotide Arrays, 2004 R package version 1.5.8.
R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2005. http://www.R-project.org.
Suzuki T, Higgins PJ, Crawford DR . Control selection for RNA quantitation. Biotechniques 2000; 29: 332–337.
Du Z, Hood L, Wilson R . Automated fluorescent DNA sequencing of polymerase chain reaction products. Methods Enzymol 1993; 218: 104–121.
Quandt K, Frech K, Karas H, Wingender E, Werner T . MatInd and MatInspector: new fast and versatile tools for detection of consensus matches in nucleotide sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 1995; 23: 4878–4884.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an Arthritis Research Campaign Program Grant. We thank all the staff at the CSC/IC Microarray Centre, Hammersmith Campus, Imperial College, for their technical help with the microarray experiments. We also thank Drs Tim Vyse and Nicola Rogers for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haywood, M., Rose, S., Horswell, S. et al. Overlapping BXSB congenic intervals, in combination with microarray gene expression, reveal novel lupus candidate genes. Genes Immun 7, 250–263 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364294
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364294
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic Dysregulation in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2022)
-
Dysregulation in growth arrest-specific 5 and metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 gene expression predicts diagnosis and renal fibrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2021)
-
Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs and mRNAs in children with systemic lupus erythematosus
Clinical Rheumatology (2019)
-
The role of long non-coding RNAs in rheumatic diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2017)
-
Long non-coding RNA expression profile in minor salivary gland of primary Sjögren’s syndrome
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2016)