Abstract
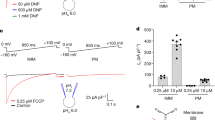
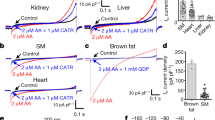
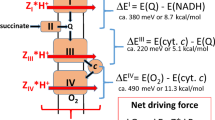
There is a futile cycle of pump and leak of protons across the mitochondrial inner membrane. The contribution of the proton cycle to standard metabolic rate is significant, particularly in skeletal muscle, and it accounts for 20% or more of the resting respiration of a rat. The mechanism of the proton leak is uncertain: basal proton conductance is not a simple biophysical leak across the unmodified phospholipid bilayer. Equally, the evidence that it is catalysed by homologues of the brown adipose uncoupling protein, UCP1, is weak. The yeast genome contains no clear UCP homologue but yeast mitochondria have normal basal proton conductance. UCP1 catalyses a regulated inducible proton conductance in brown adipose tissue and the possibility remains open that UCP2 and UCP3 have a similar role in other tissues, although this has yet to be demonstrated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brand, M., Brindle, K., Buckingham, J. et al. The significance and mechanism of mitochondrial proton conductance. Int J Obes 23 (Suppl 6), S4–S11 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800936
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800936
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MFSD7C switches mitochondrial ATP synthesis to thermogenesis in response to heme
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Light-driven activation of mitochondrial proton-motive force improves motor behaviors in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease
Communications Biology (2019)
-
Response of skeletal muscle UCP2-expression during metabolic adaptation to caloric restriction
International Journal of Obesity (2018)
-
Mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate facilitates bumblebee pre-flight thermogenesis
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Bed rest and resistive vibration exercise unveil novel links between skeletal muscle mitochondrial function and insulin resistance
Diabetologia (2017)