Abstract
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the validity of a leg-to-leg bioimpedance analysis (BIA) system in predicting body composition as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) in postmenopausal women.
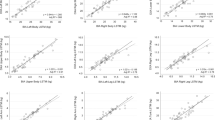
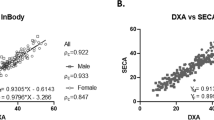
SUBJECTS AND METHODS: Body fat mass (FM), %Fat and fat free mass (FFM) were measured in 124 postmenopausal women (age: 51–63 y, body mass index (BMI): 17–38 kg/m2) first by the leg-to-leg BIA system, and then by DXA as reference method. Bland-Altman analysis was used to determine the bias and 95% limits of agreement between the two methods for the assessment of the individual. Precision error (CV%) of the BIA system was obtained by repeated measurements with intermediate repositioning.
RESULTS: The leg-to-leg BIA system had a high reproducibility with within-day CVs being 0.6% for FFM and 1.1% for FM, and between-day CVs about twice that. The impedance index (Ht2/Z) obtained by the leg-to-leg BIA was moderately correlated to FFM measured by DXA (r=0.66). A significant, systematic bias was observed between the two methods. The BIA system overestimated FM by a mean of 3.1 kg, and underestimated FFM by 2.7 kg. The analysis of 95% limits of agreement showed that for most individuals, %Fat estimated by the BIA might differ from that measured by DXA by 12% below to 45% above, indicating the lack of agreement between the two methods for the assessment of the individual.
CONCLUSIONS: The leg-to-leg BIA system can provide simple, rapid and highly reproducible measurements of body composition for groups, but it has limited accuracy for the assessment of the individual. Population-specific equations will be needed to improve its accuracy in estimating body composition in postmenopausal women.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, X., Kolthoff, N., Bärenholt, O. et al. Validation of a leg-to-leg bioimpedance analysis system in assessing body composition in postmenopausal women. Int J Obes 23, 1079–1084 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801034
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801034
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bio-structural monitoring of bone mineral alterations through electromechanical impedance measurements of a Piezo-device joined to a tooth
Biomedical Engineering Letters (2020)
-
Validity and reliability of a Wi-Fi smart scale to estimate body composition
Health and Technology (2019)
-
Perceptions of Body Habitus and Cultural Health Among Hispanic Adults
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health (2015)
-
Web-based interventions for weight loss and weight maintenance among rural midlife and older women: protocol for a randomized controlled trial
BMC Public Health (2011)
-
Bioimpedance: can its addition to simple clinical criteria enhance the diagnosis of osteoporosis?
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2009)