Abstract
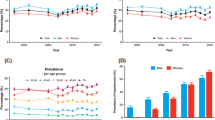
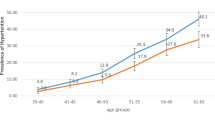
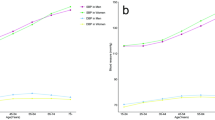
The objective of this paper is to describe hypertension status in Taiwan using data from the Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan (NAHSIT) 1993–1996, which adopted a clustered stratified multistage sampling scheme. A total of 4838 males and 4876 females aged 4 years and above were interviewed and examined corresponding to a response rate of 74%. Almost all of them (97.5%) had blood pressures measured. The results show that the mean blood pressure of adult males was higher than that of adult females below 45 years of age. After that, the pattern was reversed. When defined by JNC IV criteria (SBP/DBP ⩾160/95 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive drugs), the prevalence was 13% in adult males (⩾19 years) and 12% in adult females. When defined by JNC VI criteria (SBP/DBP ⩾140/90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive drugs), the prevalence was 26% in adult males and 19% in adult females. The prevalence in the mountainous area, was the highest among the seven survey strata. Under the JNC IV definition, 43% males and 53% females with hypertension knew their disease status, 31% of males and 45% of females took medicine for it, and 15% of males and 22% of females had their blood pressure under control. Percentages of awareness, treatment, and control were much lower with the JNC V definition, which was introduced toward the end of survey period. People in metropolitan areas had the highest rates of awareness, treatment, control, and compliance to medication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Department of Health Health and Vital Statistics: (2) Vital Statistics, Taiwan area, ROC, Taipei, Taiwan The Executive Yuan: Republic of China 1998
Laragh JH, Brenner BM Hypertension: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management Raven Press: New York 1990; pp 101–117
Pan W-Het al Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan (NAHSIT) 1993–1996: design, contents, and operation Nutr Sci J 1999 24 11–39
Ballew C et alThe utility of indirect measures of obesity in racial comparisons of blood pressure. CARDIA Study Group J Clin Epidemiol 1990 43 799–804
Hill MN, Russell RP Revision of guidelines for high blood pressure management: JNC IV. Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Pressure Maryland Med J 1988 37 698–701
Krishan I, Moser M 1980 Recommendations of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (editorial) Hypertension 1980 2 821–822
The Fifth Report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC V) Arch Intern Med 1993 153 154–183
National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute The Sixth Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. NIH Publication No 98–4080 1997
SAS Institute Inc SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Version 6, 4th edn, Vols 1 and 2 SAS Institute: Cary, NC 1989
Shah BV, Barnwell BG, Bieler GS SUDAAN, User’s Manual, Release 7.5 Research Triangle Institute: Research Triangle Park, NC 1997
Hung TP A study on the prevalence of elevated blood pressure among urban Chinese in Taiwan Jap Circ J 1961 25 2084–2100
Lin C-Y, Hung J-P, Chen J-M, Hsu J-C The first report of hypertension on metropolitan Chinese—the observed mean blood pressure [In Chinese] J Form Med Assoc 1956 55 150–161
Chen C-Het al Epidemiology of hypertension in Kin-Hu, Kinmen Am J Hypertension 1995 8 395–403
Chen C-Jet al Six-community hypertension intervention trial in Taiwan: epidemiological characteristics and treatment compliance [In Chinese; English abstract] J Natl Public Health Assoc (ROC) 1988 8 255–269
Ko YC, Hu HT Epidemiological survey of hypertension in Taiwan [In Chinese; English abstract] Chin Med J 1981 28 14–21
Tseng W-P Outcome of untreated hypertensives in an agricultural population, a 15-year follow-up study [In Chinese; English abstract] J Form Med Assoc 1980 79 556–563
Tseng W-P Blood pressure and hypertension in an agricultural and a fishing population in Taiwan Am J Epidemiol 1976 86 513–525
Kao MD et al Prevalence of obesity and distributions of anthropometric parameters of Taiwan residents. Report of The Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan (NAHSIT: 1993–1996) Department of Health, The Executive Yuan: Republic of China 1998
Burt VL et alTrends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population: data from the Health Examination Surveys, 1960–1991 Hypertension 1995 26 60–69
Acknowledgements
Appreciation should go to all the dedicated field workers and those who helped facilitate the field works in every survey site. This survey was sponsored by the Department of Health in Taiwan (DOH FN8202, DOH-84-FS-11, DOH-85-FS-11, DOH-86-FS-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, WH., Chang, HY., Yeh, WT. et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Taiwan: results of Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan (NAHSIT) 1993–1996. J Hum Hypertens 15, 793–798 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001268
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001268
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Risk Factors of Hypertension and Their Predictive Power in Identifying Patients Using a Decision Tree
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine (2024)
-
Prevalence of hypertension and associated risk factors in Dehui City of Jilin Province in China
Journal of Human Hypertension (2015)
-
Association of circadian genes with diurnal blood pressure changes and non-dipper essential hypertension: a genetic association with young-onset hypertension
Hypertension Research (2015)
-
The association of anthropometry indices with gout in Taiwanese men
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2013)
-
Difference of antihypertensive prescribing between office- and hospital-based clinics in Taiwan
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy (2012)