Abstract
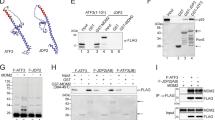
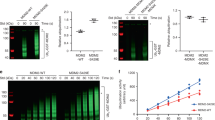
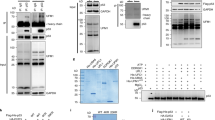
Wild-type p53 is stabilized and accumulates in the nucleus of DNA damaged cells. The effect of stabilizing p53 is to inhibit cell growth, either through a G1 cell cycle arrest or apoptotic cell death. MDM2 can inhibit p53 activity, in part, by promoting its rapid degradation through the ubiquitin proteolysis pathway. In the current study, MDM2-mediated degradation of p53 was partially inhibited in cells treated with leptomycin B (LMB), a specific inhibitor of nuclear export. In contrast, levels of ubiquitinated p53 increased in LMB-treated cells, indicating that nuclear export is not required for p53 ubiquitination. To investigate this further, p53 mutants were generated which localize to either the nucleus or cytoplasm, and their susceptibility to MDM2-mediated ubiquitination was assessed. p53 mutants that localized to either the nucleus or the cytoplasm were efficiently ubiquitinated, and their steady-state levels decreased, when coexpressed with MDM2. In addition, an MDM2-mutant that localized to the cytoplasm was able to ubiquitinate and degrade a p53 mutant which was similarly localized in the cytoplasm. Our results indicate that nuclear export is not required for p53 ubiquitination, and that p53 proteins that localize to either the nucleus or cytoplasm can be ubiquitinated and degraded by MDM2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Elela S and Nazar RN. . 1997 Cancer Lett. 117: 23–28.
Boyd D, Tsai KY and Jacks T. . 2000 Nature Cell Biol. 9: 563–568.
David-Pfeuty T, Chakrani F, Ory K and Nouvian-Dooghe Y. . 1996 Cell Growth Differ. 7: 1211–1225.
Dobblestein M, Wienzek S, Konig C and Roth J. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 2101–2106.
Fontoura BM, Atienza CA, Sorokina EA, Morimoto T and Carroll RB. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 3146–3154.
Freedman DA and Levine AJ. . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 288–7293.
Fuchs SY, Adler V, Buschmann T, Wu X and Ronai Z. . 1998 Oncogene 17: 2543–2547.
Funk W, Pak DT, Karas RH, Wright WE and Shay JW. . 1992 Mol. Cell. Biol. 12: 2866–2871.
Geyer RK, Yu Zk and Maki CG. . 2000 Nature Cell. Biol. 9: 569–573.
Guerra B and Issinger OG. . 1998 FEBS Lett. 434: 115–120.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M. . 1997 Nature 387: 296–299.
Hubbert NL, Sedman SA and Schiller JT. . 1992 J. Virol. 66: 6237–6241.
Kern SE, Pietenpol JA, Thiagalingam S, Seymour A, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1992 Science 256: 827–830.
Kubbutat MHG, Jones SN and Vousden KH. . 1997 Nature 387: 299–303.
Lane DP. . 1992 Nature 358: 15–16.
Levine AJ. . 1997 Cell 88: 323–331.
Liang S-H, Hong D and Clarke MF. . 1998 J. Biol. Chem. 273: 19817–19821.
Liang S-H and Clarke MF. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 2163–2166.
Maki CG. . 1999 J. Biol. Chem. 274: 16531–16535.
Maki CG and Howley PM. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 355–363.
Maki CG, Huibregtse JM and Howley PM. . 1996 Cancer Res. 56: 2649–2654.
Maltzman W and Czyzyk L. . 1984 Mol. Cell. Biol. 4: 1689–1694.
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson D, George D and Levine AJ. . 1992 Cell 69: 1237–1245.
Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Meltzer PS, George D and Vogelstein B. . 1992 Nature 358: 80–83.
Pietenpol JA, Tokino T, Thiagalingam S, El-Deiry WS, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 1988–2002.
Roth J, Dobbelstein M, Freedman DA, Shenk T and Levine AJ. . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 554–564.
Shaulsky G, Goldfinger N, Ben-Ze'ev A and Rotter V. . 1990 Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 6565–6577.
Stommel JM, Marchenko ND, Jimenez GS, Moll UM, Hope TJ and Wahl GM. . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 1660–1672.
Tao W and Levine AJ. . 1999 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 3077–3080.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z., Geyer, R. & Maki, C. MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of nuclear and cytoplasmic P53. Oncogene 19, 5892–5897 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203980
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203980
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori-induced NAT10 stabilizes MDM2 mRNA via RNA acetylation to facilitate gastric cancer progression
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Ribosomal L1 domain-containing protein 1 coordinates with HDM2 to negatively regulate p53 in human colorectal Cancer cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
Clinorotation-induced autophagy via HDM2-p53-mTOR pathway enhances cell migration in vascular endothelial cells
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
JS-K, a nitric oxide pro-drug, regulates growth and apoptosis through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in prostate cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
Mice defective in p53 nuclear localization signal 1 exhibit exencephaly
Transgenic Research (2011)