Abstract
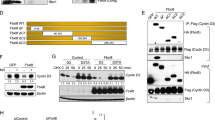
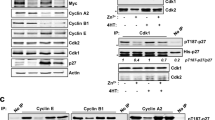
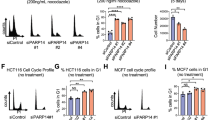
p130 is a member of the retinoblastoma family of pocket proteins, which includes pRB and p107. Unlike pRB and p107, p130 protein levels decrease dramatically following its hyperphosphorylation starting in the mid-G1 phase of the cell cycle. However, the mechanism leading to p130 downregulation is unknown. We have found that the proteasome inhibitor, lactacystin, inhibited p130 downregulation in T98G cells progressing through the G1/S transition and S phase and that p130 is multiubiquitylated in 293 cells. We have previously shown that ectopic expression of both cyclin D and E induces phosphorylation and downregulation of p130. Since the SKP1/Cul1/SKP2 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex mediates ubiquitylation of substrates previously phosphorylated by cyclin-dependent kinases, we investigated the potential role of this ubiquitin ligase in mediating p130 downregulation. We found that p130 interacts with SKP1, Cul-1 and SKP2 in human 293 cells. We also found that ectopic coexpression of SKP2 and p130 leads to dose-dependent downregulation of p130, reduces p130 protein half-life and induces p130 ubiquitylation in these cells. Moreover, adenoviral-mediated expression of SKP2 accelerates downregulation of endogenous hyperphosphorylated p130 in mitogen-stimulated T98G cells and primary WI38 fibroblasts. We conclude that p130 is a substrate of the SCFSKP2 ubiquitin ligase and this E3 ligase regulates p130 abundance during the cell cycle.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams PD, Sellers WR, Sharma SK, Wu AD, Nalin CM and Kaelin WG . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 6623–6633.
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kington RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA and Struhl KE . (1988). Current Protocols in Molecular Biology Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience: New York.
Calbó J, Parreño M, Sotillo E, Yong T, Mazo A, Garriga J and Graña X . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 50263–50274.
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A and Pagano M . (1999). Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 193–199.
Castano E, Kleyner Y and Dynlacht BD . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 5380–5391.
Cheng L, Rossi F, Fang W, Mori T and Cobrinik D . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 30317–30325.
Chiarle R, Fan Y, Piva R, Boggino H, Skolnik J, Novero D, Palestro G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Chilosi M, Pagano M and Inghirami G . (2002). Am. J. Pathol., 160, 1457–1466.
Clurman BE, Sheaff RJ, Thress K, Groudine M and Roberts JM . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 1979–1990.
Coats S, Whyte P, Fero ML, Lacy S, Chung G, Randel E, Firpo E and Roberts JM . (1999). Curr. Biol., 9, 163–173.
Deluca A, Maclachlan TK, Bagella L, Dean C, Howard CM, Claudio PP, Baldi A, Khalili K and Giordano A . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 20971–20974.
DeSalle LM and Pagano M . (2001). FEBS Lett., 490, 179–189.
Garriga J, Limon A, Mayol X, Rane SG, Albrecht JH, Reddy EP, Andrés V and Graña X . (1998). Biochem. J., 333, 645–654.
Garriga J, Mayol X and Graña X . (1996). Biochem. J., 319, 293–298.
Graña X, Garriga J and Mayol X . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 3365–3383.
Graña X and Reddy EP . (1995). Oncogene, 11, 211–219.
Gstaiger M, Jordan R, Lim M, Catzavelos C, Mestan J, Slingerland J and Krek W . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 5043–5048.
Hansen K, Farkas T, Lukas J, Holm K, Ronnstrand L and Bartek J . (2001). EMBO J., 20, 422–432.
Harper JW . (2001). Curr. Biol., 11, R431–R435.
Hershko D, Bornstein G, Ben-Izhak O, Carrano A, Pagano M, Krausz MM and Hershko A . (2001). Cancer, 91, 1745–1751.
Kiess M, Gill RM and Hamel PA . (1995). Cell Growth Differ., 6, 1287–1298.
Krek W . (1998). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 36–42.
Lacy S and Whyte P . (1997). Oncogene, 14, 2395–2406.
Latres E, Chiarle R, Schulman BA, Pavletich NP, Pellicer A, Inghirami G and Pagano M . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 2515–2520.
Lim MS, Adamson A, Lin Z, Perez-Ordonez B, Jordan RC, Tripp S, Perkins SL and Elenitoba-Johnson KS . (2002). Blood, 100, 2950–2956.
Lu L, Schulz H and Wolf DA . (2002). BMC Cell Biol., 3, 22.
Masuda TA, Inoue H, Sonoda H, Mine S, Yoshikawa Y, Nakayama K and Mori M . (2002). Cancer Res., 62, 3819–3825.
Mayol X, Garriga J and Graña X . (1995). Oncogene, 11, 801–808.
Mayol X, Garriga J and Graña X . (1996). Oncogene, 13, 237–246.
Mayol X and Graña X . (1998). Front. Biosci., 3, 11–24.
Mulligan G and Jacks T . (1998). Trends Genet., 14, 223–229.
Parreño M, Garriga J, Limon A, Albrecht J and Graña X . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 4793–4806.
Parreño M, Garriga J, Limon A, Mayol X, Beck Jr GR, Moran E and Graña X . (2000). J. Virol., 74, 3166–3176.
Penin RM, Fernandez-Figueras MT, Puig L, Rex J, Ferrandiz C and Ariza A . (2002). Mod. Pathol., 15, 1227–1235.
Prince AM, May JS, Burton GR, Lyle RE and McGehee Jr RE . (2002). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 290(3), 1066–1071.
Richon VM, Lyle RE and McGehee Jr RE . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 10117–10124.
Signoretti S, Di Marcotullio L, Richardson A, Ramaswamy S, Isaac B, Rue M, Monti F, Loda M and Pagano M . (2002). J. Clin. Invest., 110, 633–641.
Smith EJ, Leone G and Nevins JR . (1998). Cell Growth Differ., 9, 297–303.
Sutterluty H, Chatelain E, Marti A, Wirbelauer C, Senften M, Muller U and Krek W . (1999). Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 207–214.
Tedesco D, Lukas J and Reed SI . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 2946–2957.
Woo MS, Sanchez I and Dynlacht BD . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 3566–3579.
Yang G, Ayala G, Marzo AD, Tian W, Frolov A, Wheeler TM, Thompson TC and Harper JW . (2002). Clin. Cancer Res., 8, 3419–3426.
Yew PR . (2001). J. Cell Physiol., 187, 1–10.
Zalvide J, Stubdal H and DeCaprio JA . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 1408–1415.
Acknowledgements
We thank Willhem Krek and Jeffry Albrecht for providing recombinant adenoviruses and plasmids, Ed Harlow for antibodies and D Bohmann for the HA-ubiquitin construct. We thank Ana Limón for initial observations and useful discussions. We thank Renée Marshall, Elena Sotillo and Dominic Salerno for critically reading the manuscript, Rosemary Dillon for manuscript editing and May Truongcao for technical assistance. JC was partially supported by fellowships from Dirección General de Investigación Científica y Técnica (Ministerio de Educación y Cultura, Spain). This work was supported in part by grants to XG including a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIH-R29, GM54894), a grant (NIH R01, AI45450) and a Career Development Award (K02 AI01823) from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and a WW Smith grant (A9802/9901). Facilities used for this work were supported in part by a Shared Resources for Cancer Research Grant R24 (CA88261-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, S., Garriga, J., Calbó, J. et al. SKP2 associates with p130 and accelerates p130 ubiquitylation and degradation in human cells. Oncogene 22, 2443–2451 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206339
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206339
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RBL2 represses the transcriptional activity of Multicilin to inhibit multiciliogenesis
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
Inhibitors Targeting the F-BOX Proteins
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (2023)
-
Ubiquitin signaling in cell cycle control and tumorigenesis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2021)
-
Mint3 depletion restricts tumor malignancy of pancreatic cancer cells by decreasing SKP2 expression via HIF-1
Oncogene (2020)
-
Regulation of cell cycle drivers by Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)