Abstract
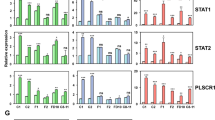
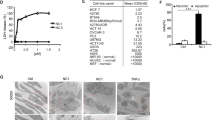
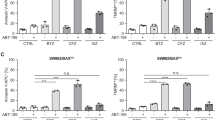
We have recently reported that the cytokine interferon-alpha (IFNα), commonly used in the treatment of cancer, induced a caspase-dependent apoptosis in tumor cell lines. The signaling mechanisms involved have not been defined. Here, we show that both proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bak and Bax were activated by IFNα, strictly in correlation with the induction of apoptosis. Using double stainings, we demonstrated that Bak was activated prior to cytochrome c (cyt c) release and caspase-3 activation, whereas activated Bax was only found in cells with released cyt c, mitochondrial depolarization, as well as activated caspase-3. Furthermore, IFNα-induced activation of Bak, and to a large extent also of Bax, was dependent on caspase activity. With the use of a panel of specific caspase inhibitors we found, however, that none of caspases-1 to -10 were responsible for this activation. Neither was the Ca2+-dependent protease calpain nor the stress-activated p38 SAPK pathway significantly involved. Overexpression of Bcl-2 blocked apoptosis induced by IFNα totally abolished Bak activation, as well as decreased the amount of activated Bax. We conclude that IFNα induces Bak and Bax activation via distinct mechanisms involving an unknown protease, and that their activation is regulated by Bcl-2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellosillo B, Villamor N, Lopez-Guillermo A, Marce S, Bosch F, Campo E, Montserrat E and Colomer D . (2002). Blood, 100, 1810–1816.
Bradbury DA, Zhu YM and Russell NH . (1997). Leukemia Lymphoma, 24, 221–228.
Cai J and Jones DP . (1999). J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 31, 327–334.
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernandez-Luna JL, Nunez G, Dalton WS and Jove R . (1999). Immunity, 10, 105–115.
Cheng EH, Wei MC, Weiler S, Flavell RA, Mak TW, Lindsten T and Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). Mol. Cell, 8, 705–711.
Consoli U, Santonocito A, Stagno F, Fiumara P, Privitera A, Parisi G, Giustolisi GM, Pavone B, Palumbo GA, Di Raimondo F, Milone G, Guglielmo P and Giustolisi R . (2002). Br. J. Haematol., 116, 774–780.
Dai C and Krantz SB . (1999). Blood, 93, 3309–3316.
Desagher S and Martinou JC . (2000). Trends Cell. Biol., 10, 369–377.
Grander D . (2000). Acta Oncol., 39, 801–805.
Griffiths GJ, Dubrez L, Morgan CP, Jones NA, Whitehouse J, Corfe BM, Dive C and Hickman JA . (1999). J. Cell. Biol., 144, 903–914.
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T and Alnemri ES . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 13430–13437.
Ichijo H . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6087–6093.
Korsmeyer SJ, Wei MC, Saito M, Weiler S, Oh KJ and Schlesinger PH . (2000). Cell Death Differ., 7, 1166–1173.
Krammer PH . (2000). Nature, 407, 789–795.
Lassus P, Opitz-Araya X and Lazebnik Y . (2002). Science, 297, 1352–1354.
Loeffler M and Kroemer G . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 256, 19–26.
Los M, Herr I, Friesen C, Fulda S, Schulze-Osthoff K and Debatin KM . (1997). Blood, 90, 3118–3129.
Ludwig H and Fritz E . (2000). Acta Oncol., 39, 815–821.
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X . (1998). Cell, 94, 481–490.
Lutz RJ . (2000). Biochem. Soc. Trans., 28, 51–56.
Mandic A, Viktorsson K, Strandberg L, Heiden T, Hansson J, Linder S and Shoshan MC . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 3003–3013.
Marsden VS, O'Connor L, O'Reilly LA, Silke J, Metcalf D, Ekert PG, Huang DC, Cecconi F, Kuida K, Tomaselli KJ, Roy S, Nicholson DW, Vaux DL, Bouillet P, Adams JM and Strasser A . (2002). Nature, 419, 634–637.
Marzo I, Brenner C, Zamzami N, Jurgensmeier JM, Susin SA, Vieira HL, Prevost MC, Xie Z, Matsuyama S, Reed JC and Kroemer G . (1998). Science, 281, 2027–2031.
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Hsu YT and Youle RJ . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 2330–2341.
Ogilvy S, Metcalf D, Print CG, Bath ML, Harris AW and Adams JM . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 14943–14948.
Panaretakis T, Pokrovskaja K, Shoshan MC and Grander D . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277(46), 44317–26.
Puthalakath H and Strasser A . (2002). Cell Death Differ., 9, 505–512.
Puthier D, Thabard W, Rapp M, Etrillard M, Harousseau J, Bataille R and Amiot M . (2001). Br. J. Haematol., 112, 358–363.
Raza A . (2000). Leukemia Res., 24, 63–72.
Sangfelt O, Erickson S, Castro J, Heiden T, Einhorn S and Grander D . (1997). Cell Growth Differ., 8, 343–352.
Sangfelt O, Osterborg A, Grander D, Anderbring E, Ost A, Mellstedt H and Einhorn S . (1995). Int. J. Cancer, 63, 190–192.
Smalley RV, Weller E, Hawkins MJ, Oken MM, O'Connell MJ, Haase-Statz S and Borden BC . (2001). Leukemia, 15, 1118–1122.
Strander H and Einhorn S . (1996). Biotherapy, 8, 213–218.
Thyrell L, Erickson S, Zhivotovsky B, Pokrovskaja K, Sangfelt O, Castro J, Einhorn S and Grander D . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 1251–1262.
Wang GQ, Gastman BR, Wieckowski E, Goldstein LA, Gambotto A, Kim TH, Fang B, Rabinovitz A, Yin XM and Rabinowich H . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 34307–34317.
Wei MC, Lindsten T, Mootha VK, Weiler S, Gross A, Ashiya M, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ . (2000). Genes Dev., 14, 2060–2071.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, Roth KA, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and Korsmeyer SJ . (2001). Science, 292, 727–730.
Acknowledgements
Dr Stanley Korsmeyer is thanked for kindly providing the human Bcl-2 vector. The excellent technical assistance of Mrs Ann-Charlotte Björklund is gratefully acknowledged. These studies were supported by the Swedish Cancer Society, the Cancer Society of Stockholm and the Sven and Lilly Lawsky foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panaretakis, T., Pokrovskaja, K., Shoshan, M. et al. Interferon-α-induced apoptosis in U266 cells is associated with activation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bak and Bax. Oncogene 22, 4543–4556 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206503
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206503
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dual EZH2 and G9a inhibition suppresses multiple myeloma cell proliferation by regulating the interferon signal and IRF4-MYC axis
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Essential role of HCMV deubiquitinase in promoting oncogenesis by targeting anti-viral innate immune signaling pathways
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Lycorine induces programmed necrosis in the multiple myeloma cell line ARH-77
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
Targeting of distinct signaling cascades and cancer-associated fibroblasts define the efficacy of Sorafenib against prostate cancer cells
Cell Death & Disease (2012)
-
Inhibition of cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein abolishes insensitivity to interferon-α and death receptor stimulation in resistant variants of the human U937 cell line
Apoptosis (2011)