Abstract
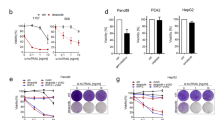
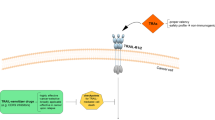
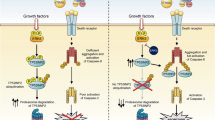
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a potent inducer of apoptosis in cancer cells. Examining primary cells of children with untreated acute leukemia, TRAIL induced apoptosis in 50% of cells, but to our surprise attenuated spontaneous apoptosis in the remaining samples or, most importantly, even mediated proliferation. We therefore examined tumor cell lines of leukemic and nonleukemic origin with apoptosis resistance towards TRAIL because of absent Caspase-8 or dysfunctional FADD. In all cell lines tested, TRAIL treatment increased cell numbers in average to 163% within 4 days and accelerated doubling time from 24 to 19 h. TRAIL-mediated proliferation was completely abrogated by blockade of NF-κB activation using proteasome inhibitors or in RIP-negative, IKKγ-negative cells or in cells overexpressing dominant-negative IκBα. Our data describe the biological significance of TRAIL-mediated activation of NF-κB in cancer cells resistant to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: TRAIL leads to an increase in tumor cell count by a prosurvival and possibly mitogenic function. Given the promising therapeutic potential of TRAIL as a novel anticancer drug, TRAIL-mediated survival or proliferation of target cells may restrict its use to apoptosis-sensitive tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baetu TM, Kwon H, Sharma S, Grandvaux N and Hiscott J. (2001). J. Immunol., 167, 3164–3173.
Budd RC . (2002). J. Clin. Invest., 109, 437–442.
Fulda S and Debatin KM . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 2295–2308.
Harhaj EW, Good L, Xiao G, Uhlik M, Cvijic ME, Rivera-Walsh I and Sun SC . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 1448–1456.
Herr I, Wilhelm D, Meyer E, Jeremias I, Angel P and Debatin KM . (1999). Cell Death Differ., 6, 130–135.
Hueber AO, Zornig M, Bernard AM, Chautan M and Evan G . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 10453–10462.
Jeremias I, Kupatt C, Baumann B, Herr I, Wirth T and Debatin KM . (1998a). Blood, 91, 4624–4631.
Jeremias I, Herr I, Boehler T and Debatin KM . (1998b). Eur. J. Immunol., 28, 143–152.
Juo P, Kuo CJ, Yuan J and Blenis J . (1998). Curr. Biol., 8, 1001–1008.
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 301–310.
Krammer PH . (2000). Nature, 407, 789–795.
Kupatt C, Habazettl H, Goedecke A, Wolf DA, Zahler S, Boekstegers P, Kelly RA and Becker BF . (1999). Circ. Res., 84, 392–400.
Lin Y, Devin A, Cook A, Keane MM, Kelliher M, Lipkowitz S and Liu ZG . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 6638–6645.
Mapara MY, Bargou R, Zugck C, Dohner H, Ustaoglu F, Jonker RR, Krammer PH and Dorken B . (1993). Eur. J. Immunol., 23, 702–708.
Muhlenbeck F, Haas E, Schwenzer R, Schubert G, Grell M, Smith C, Scheurich P and Wajant H . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 33091–33098.
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F and Riccardi C . (1991). J. Immunol. Methods, 139, 271–279.
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH and Peter ME . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 1541–1548.
Teitz T, Wei T, Valentine MB, Vanin EF, Grenet J, Valentine VA, Behm FG, Look AT, Lahti JM and Kidd VJ . (2000). Nat. Med., 6, 529–535.
Thilenius ARB, Braun K and Russell JH . (1997). Eur. J. Immunol., 27, 1108–1114.
Ting AT, Pimentel-Muinos FX and Seed B . (1996). EMBO J., 15, 6189–6196.
Acknowledgements
We thank Brian Seed for kindly providing RIP-negative JURKAT cells and Shao-Cong Sun for kindly providing IKKγ-negative JURKAT cells. We thank Elisabeth Ronft for performing gel shift assays. This work was supported by Wilhelm Sander Stiftung and FöFoLe #34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrhardt, H., Fulda, S., Schmid, I. et al. TRAIL induced survival and proliferation in cancer cells resistant towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis mediated by NF-κB. Oncogene 22, 3842–3852 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206520
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206520
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
TRAIL predisposes non-small cell lung cancer to ferroptosis by regulating ASK-1/JNK1 pathway
Discover Oncology (2024)
-
Harnessing TRAIL-induced cell death for cancer therapy: a long walk with thrilling discoveries
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
TRAIL receptors promote constitutive and inducible IL-8 secretion in non-small cell lung carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Stress-induced TRAILR2 expression overcomes TRAIL resistance in cancer cell spheroids
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
The regulation of combined treatment-induced cell death with recombinant TRAIL and bortezomib through TRAIL signaling in TRAIL-resistant cells
BMC Cancer (2018)